Blogmarks
Filters: Sorted by date
Extracting Prompts by Inverting LLM Outputs (via) New paper from Meta research:
We consider the problem of language model inversion: given outputs of a language model, we seek to extract the prompt that generated these outputs. We develop a new black-box method, output2prompt, that learns to extract prompts without access to the model's logits and without adversarial or jailbreaking queries. In contrast to previous work, output2prompt only needs outputs of normal user queries.
This is a way of extracting the hidden prompt from an application build on an LLM without using prompt injection techniques.
The trick is to train a dedicated model for guessing hidden prompts based on public question/answer pairs.
They conclude:
Our results demonstrate that many user and system prompts are intrinsically vulnerable to extraction.
This reinforces my opinion that it's not worth trying to protect your system prompts. Think of them the same as your client-side HTML and JavaScript: you might be able to obfuscate them but you should expect that people can view them if they try hard enough.
Towards Standardizing Place. Overture Maps announced General Availability of its global maps datasets last week, covering places, buildings, divisions, and base layers.
Drew Breunig demonstrates how this can be accessed using both the Overture Explorer tool and DuckDB, and talks about Overture's GERS IDs - reminiscent of Who's On First IDs - which provide stable IDs for all kinds of geographic places.
Footnotes that work in RSS readers. Chris Coyier explained the mechanism used by Feedbin to render custom footnotes back in 2019.
I stumbled upon this after I spotted an inline footnote rendered in NetNewsWire the other day (from this post by Drew Breunig):
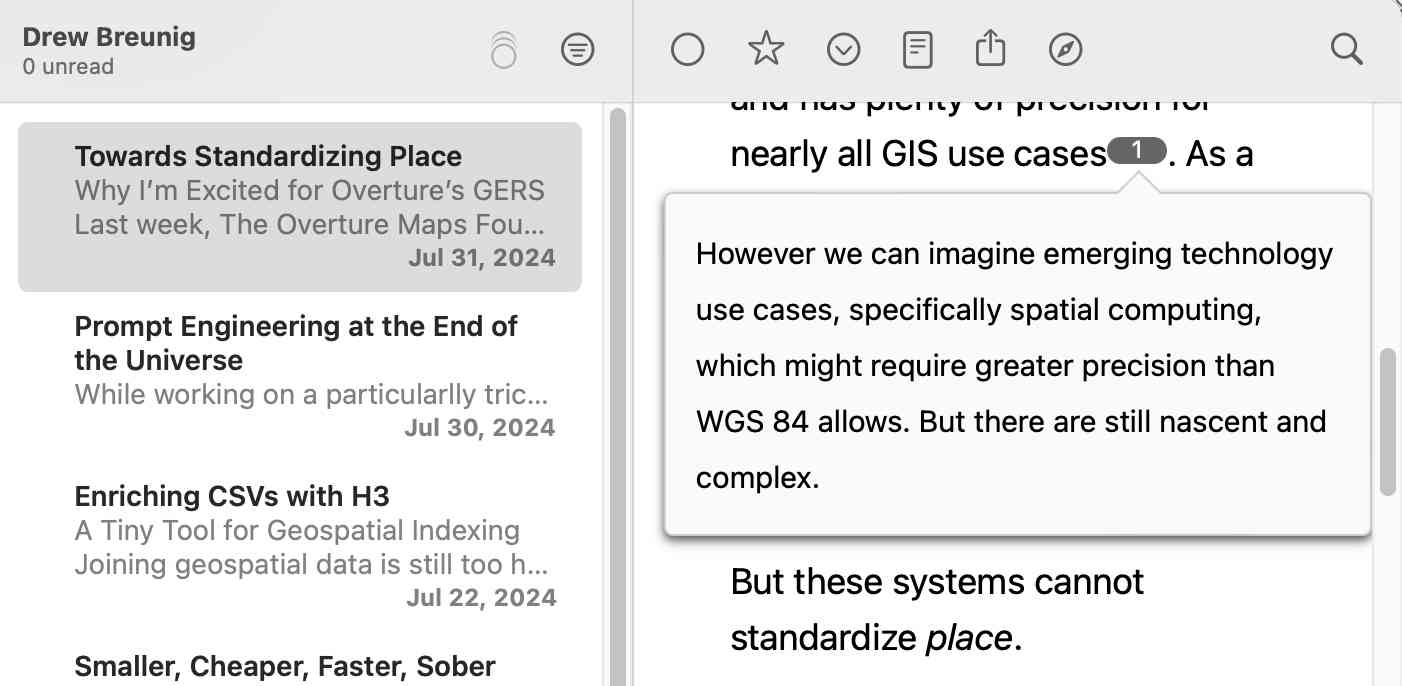
Since feed readers generally strip JavaScript and CSS and only allow a subset of HTML tags I was intrigued to figure out how that worked.
I found this code in the NetNewsWire source (it's MIT licensed) which runs against elements matching this CSS selector:
sup > a[href*='#fn'], sup > div > a[href*='#fn']
So any link with an href attribute containing #fn that is a child of a <sup> (superscript) element.
In Drew's post the HTML looks like this:
<!-- Footnote link: -->
<sup id="fnref:precision" role="doc-noteref">
<a href="#fn:precision" class="footnote" rel="footnote">1</a>
</sup>
<!-- Then at the bottom: -->
<div class="footnotes" role="doc-endnotes">
<ol>
<li id="fn:precision" role="doc-endnote">
<p>This is the footnote.
<a href="#fnref:precision" class="reversefootnote" role="doc-backlink">↩</a>
</p>
</li>
</ol>
</div>
Where did this convention come from? It doesn't seem to be part of any specific standard. Chris linked to www.bigfootjs.com (no longer resolving) which was the site for the bigfoot.js jQuery plugin, so my best guess is the convention came from that.
1991-WWW-NeXT-Implementation on GitHub. I fell down a bit of a rabbit hole today trying to answer that question about when World Wide Web Day was first celebrated. I found my way to www.w3.org/History/1991-WWW-NeXT/Implementation/ - an Apache directory listing of the source code for Tim Berners-Lee's original WorldWideWeb application for NeXT!
The code wasn't particularly easy to browse: clicking a .m file would trigger a download rather than showing the code in the browser, and there were no niceties like syntax highlighting.
So I decided to mirror that code to a new repository on GitHub. I grabbed the code using wget -r and was delighted to find that the last modified dates (from the early 1990s) were preserved ... which made me want to preserve them in the GitHub repo too.
I used Claude to write a Python script to back-date those commits, and wrote up what I learned in this new TIL: Back-dating Git commits based on file modification dates.
End result: I now have a repo with Tim's original code, plus commit dates that reflect when that code was last modified.
Today’s research challenge: why is August 1st “World Wide Web Day”? Here's a fun mystery. A bunch of publications will tell you that today, August 1st, is "World Wide Web Day"... but where did that idea come from?
It's not an official day marked by any national or international organization. It's not celebrated by CERN or the W3C.
The date August 1st doesn't appear to hold any specific significance in the history of the web. The first website was launched on August 6th 1991.
I posed the following three questions this morning on Mastodon:
- Who first decided that August 1st should be "World Wide Web Day"?
- Why did they pick that date?
- When was the first World Wide Web Day celebrated?
Finding answers to these questions has proven stubbornly difficult. Searches on Google have proven futile, and illustrate the growing impact of LLM-generated slop on the web: they turn up dozens of articles celebrating the day, many from news publications playing the "write about what people might search for" game and many others that have distinctive ChatGPT vibes to them.
One early hint we've found is in the "Bylines 2010 Writer's Desk Calendar" by Snowflake Press, published in January 2009. Jessamyn West spotted that on the book's page in the Internet Archive, but it merely lists "World Wide Web Day" at the bottom of the July calendar page (clearly a printing mistake, the heading is meant to align with August 1st on the next page) without any hint as to the origin:

I found two earlier mentions from August 1st 2008 on Twitter, from @GabeMcCauley and from @iJess.
Our earliest news media reference, spotted by Hugo van Kemenade, is also from August 1st 2008: this opinion piece in the Attleboro Massachusetts Sun Chronicle, which has no byline so presumably was written by the paper's editorial board:
Today is World Wide Web Day, but who cares? We'd rather nap than surf. How about you? Better relax while you can: August presages the start of school, a new season of public meetings, worries about fuel costs, the rundown to the presidential election and local races.
So the mystery remains! Who decided that August 1st should be "World Wide Web Day", why that date and how did it spread so widely without leaving a clear origin story?
If your research skills are up to the challenge, join the challenge!
Build your own SQS or Kafka with Postgres (via) Anthony Accomazzo works on Sequin, an open source "message stream" (similar to Kafka) written in Elixir and Go on top of PostgreSQL.
This detailed article describes how you can implement message queue patterns on PostgreSQL from scratch, including this neat example using a CTE, returning and for update skip locked to retrieve $1 messages from the messages table and simultaneously mark them with not_visible_until set to $2 in order to "lock" them for processing by a client:
with available_messages as (
select seq
from messages
where not_visible_until is null
or (not_visible_until <= now())
order by inserted_at
limit $1
for update skip locked
)
update messages m
set
not_visible_until = $2,
deliver_count = deliver_count + 1,
last_delivered_at = now(),
updated_at = now()
from available_messages am
where m.seq = am.seq
returning m.seq, m.data;
This month in Servo: parallel tables and more (via) New in Servo:
Parallel table layout is now enabled (@mrobinson, #32477), spreading the work for laying out rows and their columns over all available CPU cores. This change is a great example of the strengths of Rayon and the opportunistic parallelism in Servo's layout engine.
The commit landing the change is quite short, and much of the work is done by refactoring the code to use .par_iter().enumerate().map(...) - par_iter() is the Rayon method that allows parallel iteration over a collection using multiple threads, hence multiple CPU cores.
Aider. Aider is an impressive open source local coding chat assistant terminal application, developed by Paul Gauthier (founding CTO of Inktomi back in 1996-2000).
I tried it out today, using an Anthropic API key to run it using Claude 3.5 Sonnet:
pipx install aider-chat
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=api-key-here
aider --dark-mode
I found the --dark-mode flag necessary to make it legible using the macOS terminal "Pro" theme.
Aider starts by generating a concise map of files in your current Git repository. This is passed to the LLM along with the prompts that you type, and Aider can then request additional files be added to that context - or you can add the manually with the /add filename command.
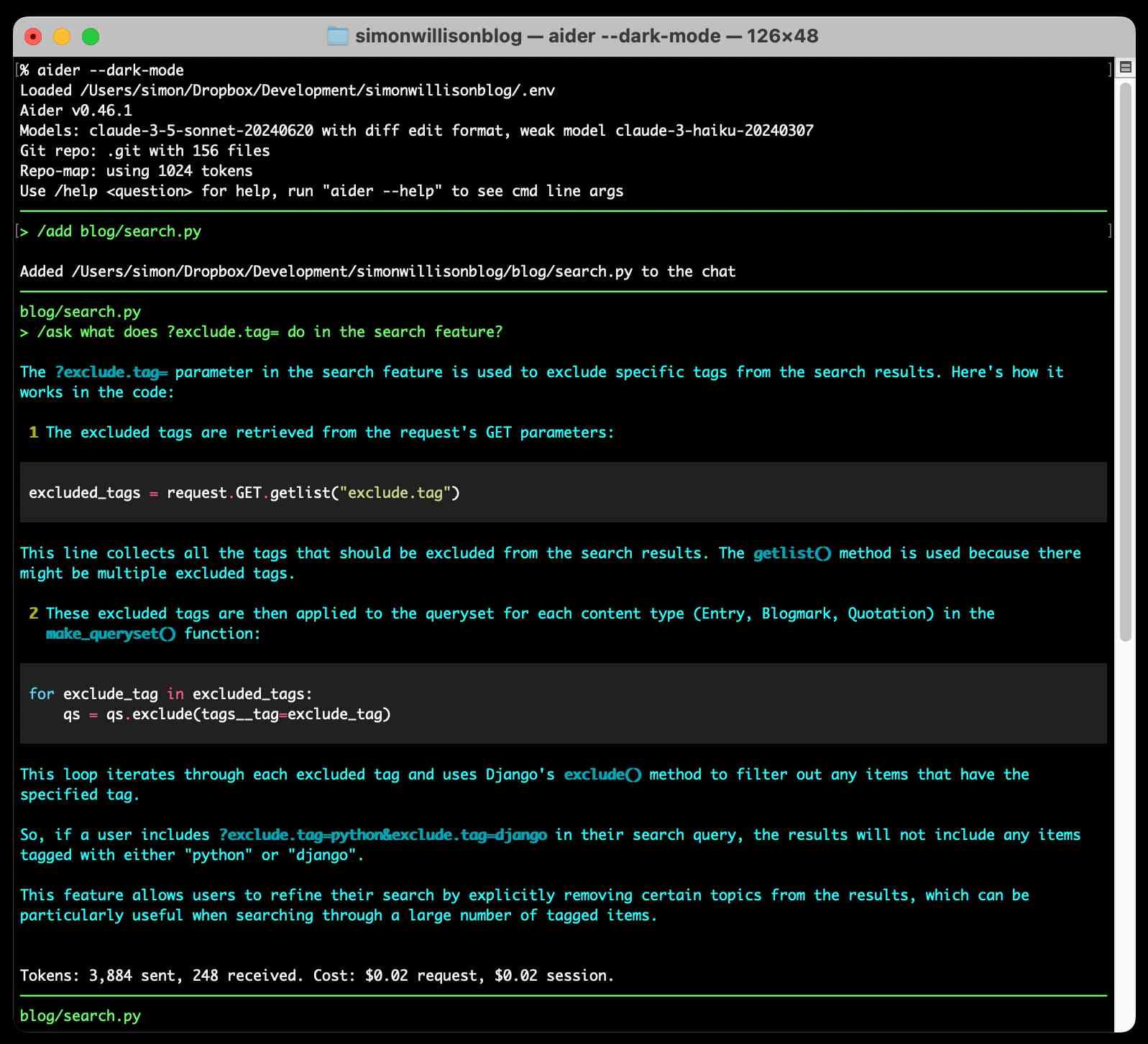
It defaults to making modifications to files and then committing them directly to Git with a generated commit message. I found myself preferring the /ask command which lets you ask a question without making any file modifications:
The Aider documentation includes extensive examples and the tool can work with a wide range of different LLMs, though it recommends GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet (or 3 Opus) and DeepSeek Coder V2 for the best results. Aider maintains its own leaderboard, emphasizing that "Aider works best with LLMs which are good at editing code, not just good at writing code".
The prompts it uses are pretty fascinating - they're tucked away in various *_prompts.py files in aider/coders.
Ralph Sheldon’s Portrait of Henry VIII Reidentified (via) Here's a delightful two part story on art historian Adam Busiakiewicz's blog. Adam was browsing Twitter when he spotted this tweet by Tim Cox, Lord Lieutenant of Warwickshire, celebrating a reception.
He noticed a curve-framed painting mounted on a wall in the top left of the photo:
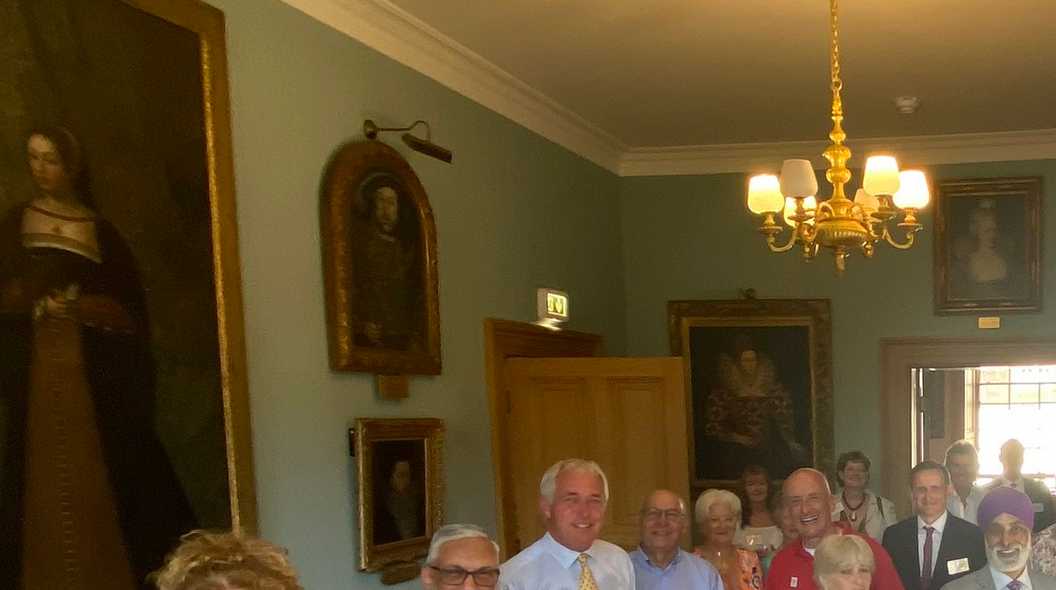

Adam had previously researched a similar painting while working at Sotheby's:
Seeing this round topped portrait immediately reminded me of a famous set of likenesses commissioned by the local politician and tapestry maker Ralph Sheldon (c. 1537--1613) for his home Weston House, Warwickshire, during the 1590s. Consisting of twenty-two portraits, mostly images of Kings, Queens and significant contemporary international figures, only a handful are known today.
Adam contacted Warwickshire County Council and was invited to Shire Hall. In his follow-up post he describes his first-hand observations from the visit.
It turns out the painting really was one of those 22 portraits made for tapestry maker Ralph Sheldon in the 1590s, long thought lost. The discovery has now made international news:
Making Machines Move. Another deep technical dive into Fly.io infrastructure from Thomas Ptacek, this time describing how they can quickly boot up an instance with a persistent volume on a new host (for things like zero-downtime deploys) using a block-level cloning operation, so the new instance gets a volume that becomes accessible instantly, serving proxied blocks of data until the new volume has been completely migrated from the old host.
GPT-4o Long Output (via) "OpenAI is offering an experimental version of GPT-4o with a maximum of 64K output tokens per request."
It's a new model (for alpha testers only) called gpt-4o-64k-output-alpha that costs $6/million input tokens and $18/million output tokens.
That's a little bit more than GPT-4o ($5/$15) and a LOT more than GPT-4o mini ($0.15/$0.60).
Long output is primarily useful for data transformation use-cases - things like translating documents from one language into another, or extracting structured data from documents where almost every input token is needed in the output JSON.
Prior to this the longest output model I knew of was GPT-4o mini, at 16,000 tokens. Most of OpenAI's competitors still cap out at around 4,000 or 8,000.
What we got wrong about HTTP imports (via) HTTP imports are one of the most interesting design features of Deno:
import { assertEquals } from "https://deno.land/std@0.224.0/assert/mod.ts";
Six years after their introduction, Ryan Dahl reviews their disadvantages:
- Lengthy (non-memorable) URLs littering the codebase
- A slightly cumbersome
import { concat } from "../../deps.ts";pattern for managing dependencies in one place - Large projects can end up using multiple slightly different versions of the same dependencies
- If a website becomes unavailable, new builds will fail (existing builds will continue to use their cached version)
Deno 2 - due in September - will continue to support them, but will lean much more on the combination of import maps (design borrowed from modern browsers) and the Deno project's JSR npm competitor. An import map like this:
{
"imports": {
"@std/assert": "jsr:@std/assert@1"
}
}
Will then enable import statements that look like this:
import { assertEquals } from "@std/assert";
AWS CodeCommit quietly deprecated (via) CodeCommit is AWS's Git hosting service. In a reply from an AWS employee to this forum thread:
Beginning on 06 June 2024, AWS CodeCommit ceased onboarding new customers. Going forward, only customers who have an existing repository in AWS CodeCommit will be able to create additional repositories.
[...] If you would like to use AWS CodeCommit in a new AWS account that is part of your AWS Organization, please let us know so that we can evaluate the request for allowlisting the new account. If you would like to use an alternative to AWS CodeCommit given this news, we recommend using GitLab, GitHub, or another third party source provider of your choice.
What's weird about this is that, as far as I can tell, this is the first official public acknowledgement from AWS that CodeCommit is no longer accepting customers. The CodeCommit landing page continues to promote the product, though it does link to the How to migrate your AWS CodeCommit repository to another Git provider blog post from July 25th, which gives no direct indication that CodeCommit is being quietly sunset.
I wonder how long they'll continue to support their existing customers?
Amazon QLDB too
It looks like AWS may be having a bit of a clear-out. Amazon QLDB - Quantum Ledger Database (a blockchain-adjacent immutable ledger, launched in 2019) - quietly put out a deprecation announcement in their release history on July 18th (again, no official announcement elsewhere):
End of support notice: Existing customers will be able to use Amazon QLDB until end of support on 07/31/2025. For more details, see Migrate an Amazon QLDB Ledger to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL.
This one is more surprising, because migrating to a different Git host is massively less work than entirely re-writing a system to use a fundamentally different database.
It turns out there's an infrequently updated community GitHub repo called SummitRoute/aws_breaking_changes which tracks these kinds of changes. Other services listed there include CodeStar, Cloud9, CloudSearch, OpsWorks, Workdocs and Snowmobile, and they cleverly (ab)use the GitHub releases mechanism to provide an Atom feed.
Here Are All of the Apple Intelligence Features in the iOS 18.1 Developer Beta (via) Useful rundown from Juli Clover at MacRumors of the Apple Intelligence features that are available in the brand new iOS 18.1 beta, available to developer account holders with an iPhone 15 or iPhone 15 Pro Max or Apple Silicon iPad.
I've been trying this out today. It's still clearly very early, and the on-device model that powers Siri is significantly weaker than more powerful models that I've become used to over the past two years. Similar to old Siri I find myself trying to figure out the sparse, undocumented incantations that reliably work for the things I might want my voice assistant to do for me.
My early Siri AI experience has just underlined the fact that, while there is a lot of practical, useful things that can be done with small models, they really lack the horsepower to do anything super interesting.
SAM 2: The next generation of Meta Segment Anything Model for videos and images (via) Segment Anything is Meta AI's model for image segmentation: for any image or frame of video it can identify which shapes on the image represent different "objects" - things like vehicles, people, animals, tools and more.
SAM 2 "outperforms SAM on its 23 dataset zero-shot benchmark suite, while being six times faster". Notably, SAM 2 works with video where the original SAM only worked with still images. It's released under the Apache 2 license.
The best way to understand SAM 2 is to try it out. Meta have a web demo which worked for me in Chrome but not in Firefox. I uploaded a recent video of my brand new cactus tweezers (for removing detritus from my cacti without getting spiked) and selected the succulent and the tweezers as two different objects:
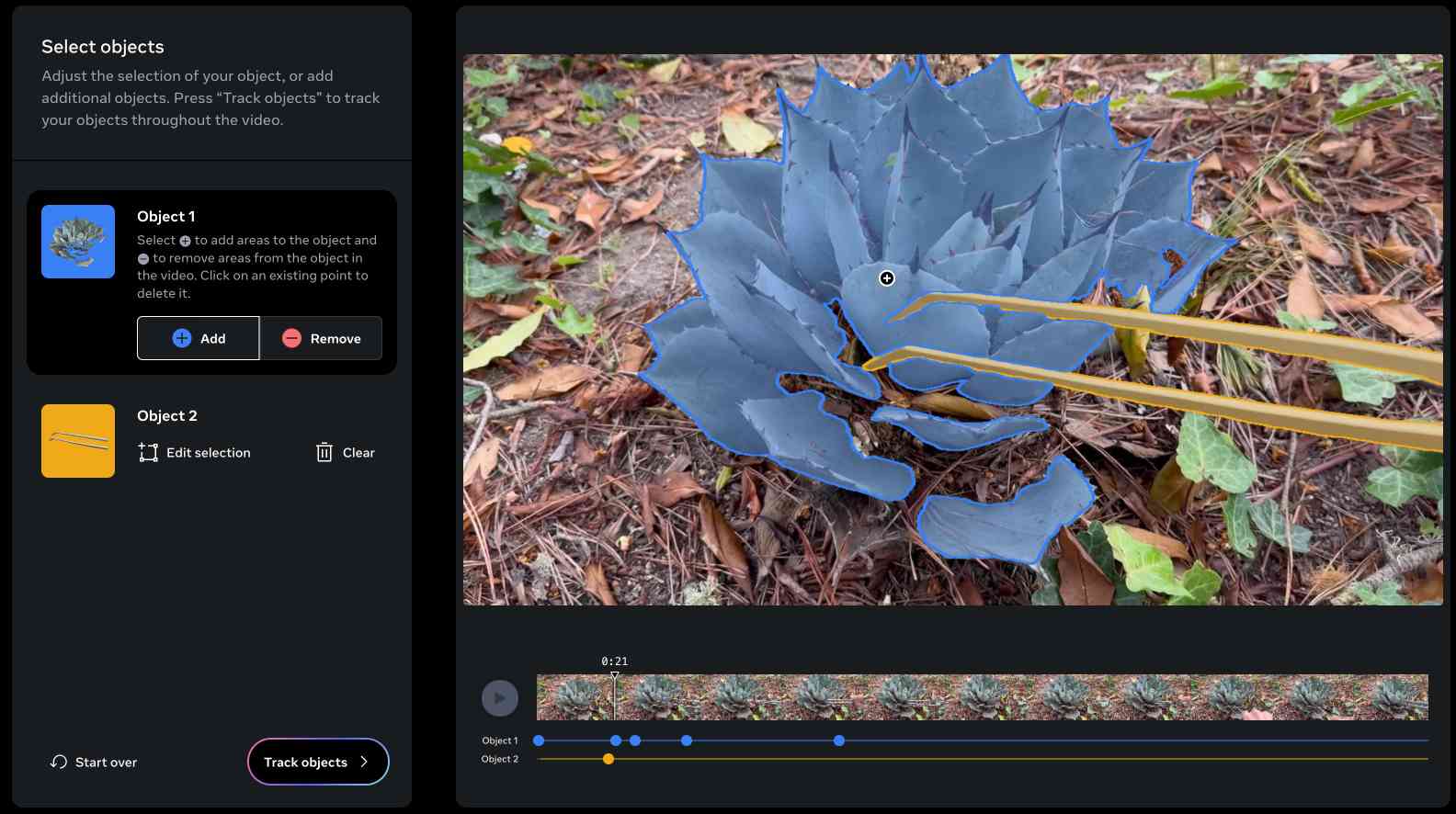
Then I applied a "desaturate" filter to the background and exported this resulting video, with the background converted to black and white while the succulent and tweezers remained in full colour:
Also released today: the full SAM 2 paper, the SA-V dataset of "51K diverse videos and 643K spatio-temporal segmentation masks" and a Dataset explorer tool (again, not supported by Firefox) for poking around in that collection.
Dealing with your AI-obsessed co-worker (TikTok). The latest in Alberta 🤖 Tech's excellent series of skits:
You asked the CEO what he thinks of our project? Oh, you asked ChatGPT to pretend to be our CEO and then asked what he thought of our project. I don't think that counts.
Everlasting jobstoppers: How an AI bot-war destroyed the online job market (via) This story by Joe Tauke highlights several unpleasant trends from the online job directory space at the moment.
The first is "ghost jobs" - job listings that company put out which don't actually correspond to an open role. A survey found that this is done for a few reasons: to keep harvesting resumes for future reference, to imply that the company is successful, and then:
Perhaps the most infuriating replies came in at 39% and 33%, respectively: “The job was filled” (but the post was left online anyway to keep gathering résumés), and “No reason in particular.”
That’s right, all you go-getters out there: When you scream your 87th cover letter into the ghost-job void, there’s a one in three chance that your time was wasted for “no reason in particular.”
Another trend is "job post scraping". Plenty of job listings sites are supported by advertising, so the more content they can gather the better. This has lead to an explosion of web scraping, resulting in vast tracts of listings that were copied from other sites and likely to be out-of-date or no longer correspond to open positions.
Most worrying of all: scams.
With so much automation available, it’s become easier than ever for identity thieves to flood the employment market with their own versions of ghost jobs — not to make a real company seem like it’s growing or to make real employees feel like they’re under constant threat of being replaced, but to get practically all the personal information a victim could ever provide.
I'm not 100% convinced by the "AI bot-war" component of this headline though. The article later notes that the "ghost jobs" report it quotes was written before ChatGPT's launch in November 2022. The story ends with a flurry of examples of new AI-driven tools for both applicants and recruiters, and I've certainly heard anecdotes of LinkedIn spam that clearly has a flavour of ChatGPT to it, but I'm not convinced that the AI component is (yet) as frustration-inducing as the other patterns described above.
The rich history of ham radio culture (via) This long excerpt from Kristen Haring's 2008 book Ham Radio's Technical Culture filled in so many gaps for me. I'm ham licensed in the USA (see my recent notes on passing the general exam) but prior to reading this I hadn't appreciated quite how much the 100+ year history of the hobby explains the way it works today. Some ham abbreviations derive from the Phillips Code created in 1879!
The Hacker News thread attracted some delightful personal stories from older ham operators: "my exposure to ham radio really started in the 1970s...". I also liked this description of the core of the hobby:
A ham radio license is permission from your country's government to get on the air for the sake of playing with radio waves and communicating with other hams locally or around the globe without any further agenda.
I'm increasingly using the Listen to Page feature in my iPhone's Mobile Safari to read long-form articles like this one, which means I can do household chores at the same time.
The many lives of Null Island (via) Stamen's custom basemaps have long harbored an Easter egg: zoom all the way in on 0, 0 to see the outline of the mystical "null island", the place where GIS glitches and data bugs accumulate, in the Gulf of Guinea south of Ghana.
Stamen's Alan McConchie provides a detailed history of the Easter egg - first introduced by Mike Migurski in 2010 - along with a definitive guide to the GIS jokes and traditions that surround it.
Here's Null Island on Stamen's Toner map. The shape (also available as GeoJSON) is an homage to the island from 1993's Myst, hence the outline of a large docked ship at the bottom.
Alan recently gave a talk about Stamen's updated custom maps at State of the Map US 2024 (video, slides) - their Toner and Terrain maps are now available as vector tiles served by Stadia Maps (here's the announcement), but their iconic watercolor style is yet to be updated to vectors, due to the weird array of raster tricks it used to achieve the effect.
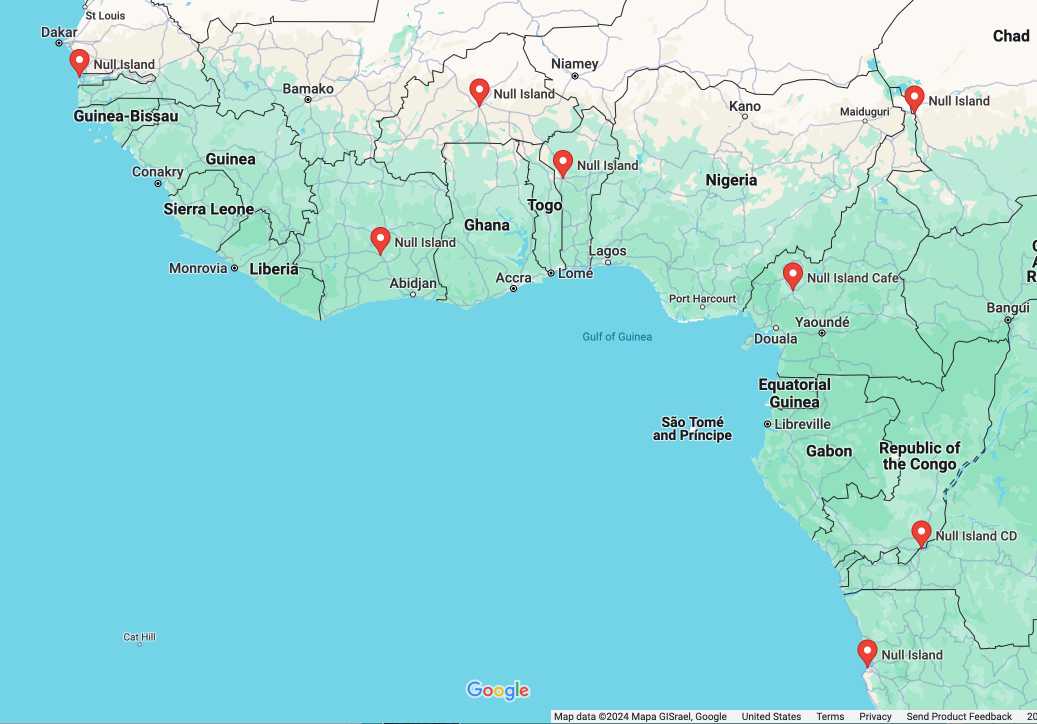
In researching this post I searched for null island on Google Maps and was delighted to learn that a bunch of entrepreneurs in Western Africa have tapped into the meme for their own businesses:
CalcGPT (via) Fun satirical GPT-powered calculator demo by Calvin Liang, originally built in July 2023. From the ChatGPT-generated artist statement:
The piece invites us to reflect on the necessity and relevance of AI in every aspect of our lives as opposed to its prevailing use as a mere marketing gimmick. With its delightful slowness and propensity for computational errors, CalcGPT elicits mirth while urging us to question our zealous indulgence in all things AI.
The source code shows that it's using babbage-002 (a GPT3-era OpenAI model which I hadn't realized was still available through their API) that takes a completion-style prompt, which Calvin primes with some examples before including the user's entered expression from the calculator:
1+1=2
5-2=3
2*4=8
9/3=3
10/3=3.33333333333
${math}=
It sets \n as the stop sequence.
Image resize and quality comparison. Another tiny tool I built with Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Artifacts. This one lets you select an image (or drag-drop one onto an area) and then displays that same image as a JPEG at 1, 0.9, 0.7, 0.5, 0.3 quality settings, then again but with at half the width. Each image shows its size in KB and can be downloaded directly from the page.

I'm trying to use more images on my blog (example 1, example 2) and I like to reduce their file size and quality while keeping them legible.
The prompt sequence I used for this was:
Build an artifact (no React) that I can drop an image onto and it presents that image resized to different JPEG quality levels, each with a download link
Claude produced this initial artifact. I followed up with:
change it so that for any image it provides it in the following:
- original width, full quality
- original width, 0.9 quality
- original width, 0.7 quality
- original width, 0.5 quality
- original width, 0.3 quality
- half width - same array of qualities
For each image clicking it should toggle its display to full width and then back to max-width of 80%
Images should show their size in KB
Claude produced this v2.
I tweaked it a tiny bit (modifying how full-width images are displayed) - the final source code is available here. I'm hosting it on my own site which means the Download links work correctly - when hosted on claude.site Claude's CSP headers prevent those from functioning.
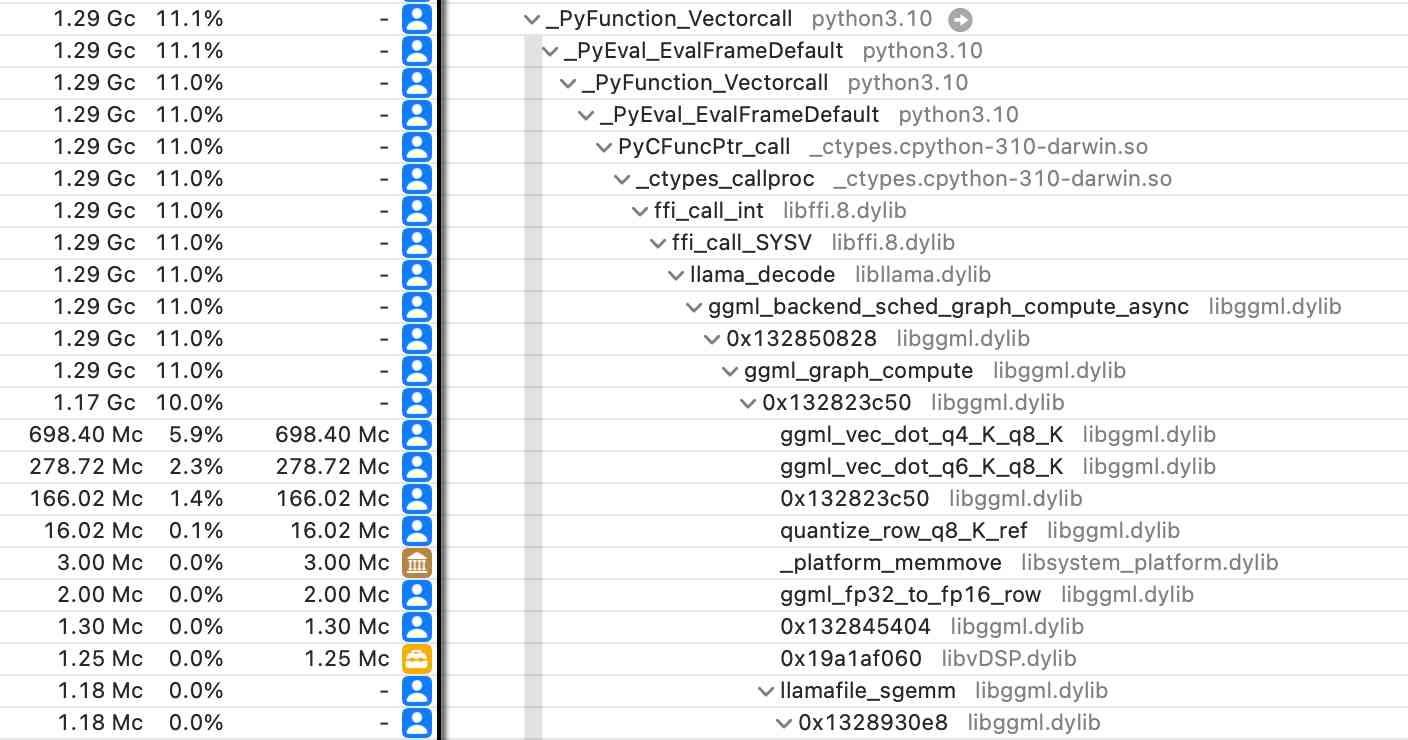
Did you know about Instruments? (via) Thorsten Ball shows how the macOS Instruments app (installed as part of Xcode) can be used to run a CPU profiler against any application - not just code written in Swift/Objective C.
I tried this against a Python process running LLM executing a Llama 3.1 prompt with my new llm-gguf plugin and captured this:
Introducing sqlite-lembed: A SQLite extension for generating text embeddings locally (via) Alex Garcia's latest SQLite extension is a C wrapper around the llama.cpp that exposes just its embedding support, allowing you to register a GGUF file containing an embedding model:
INSERT INTO temp.lembed_models(name, model)
select 'all-MiniLM-L6-v2',
lembed_model_from_file('all-MiniLM-L6-v2.e4ce9877.q8_0.gguf');
And then use it to calculate embeddings as part of a SQL query:
select lembed(
'all-MiniLM-L6-v2',
'The United States Postal Service is an independent agency...'
); -- X'A402...09C3' (1536 bytes)
all-MiniLM-L6-v2.e4ce9877.q8_0.gguf here is a 24MB file, so this should run quite happily even on machines without much available RAM.
What if you don't want to run the models locally at all? Alex has another new extension for that, described in Introducing sqlite-rembed: A SQLite extension for generating text embeddings from remote APIs. The rembed is for remote embeddings, and this extension uses Rust to call multiple remotely-hosted embeddings APIs, registered like this:
INSERT INTO temp.rembed_clients(name, options)
VALUES ('text-embedding-3-small', 'openai');
select rembed(
'text-embedding-3-small',
'The United States Postal Service is an independent agency...'
); -- X'A452...01FC', Blob<6144 bytes>
Here's the Rust code that implements Rust wrapper functions for HTTP JSON APIs from OpenAI, Nomic, Cohere, Jina, Mixedbread and localhost servers provided by Ollama and Llamafile.
Both of these extensions are designed to complement Alex's sqlite-vec extension, which is nearing a first stable release.
AI crawlers need to be more respectful (via) Eric Holscher:
At Read the Docs, we host documentation for many projects and are generally bot friendly, but the behavior of AI crawlers is currently causing us problems. We have noticed AI crawlers aggressively pulling content, seemingly without basic checks against abuse.
One crawler downloaded 73 TB of zipped HTML files just in Month, racking up $5,000 in bandwidth charges!
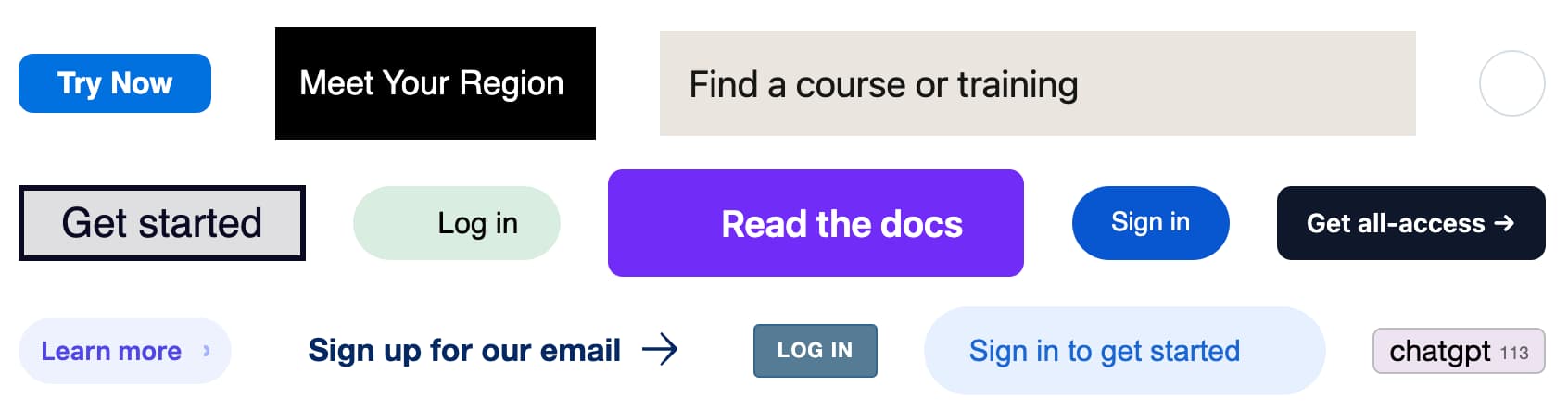
Button Stealer (via) Really fun Chrome extension by Anatoly Zenkov: it scans every web page you visit for things that look like buttons and stashes a copy of them, then provides a page where you can see all of the buttons you have collected. Here's Anatoly's collection, and here are a few that I've picked up trying it out myself:
The extension source code is on GitHub. It identifies potential buttons by looping through every <a> and <button> element and applying some heuristics like checking the width/height ratio, then clones a subset of the CSS from window.getComputedStyle() and stores that in the style= attribute.
wat
(via)
This is a really neat Python debugging utility. Install with pip install wat-inspector and then inspect any Python object like this:
from wat import wat
wat / myvariable
The wat / x syntax is a shortcut for wat(x) that's quicker to type.
The tool dumps out all sorts of useful introspection about the variable, value, class or package that you pass to it.
There are several variants: wat.all / x gives you all of them, or you can chain several together like wat.dunder.code / x.
The documentation also provides a slightly intimidating copy-paste version of the tool which uses exec(), zlib and base64 to help you paste the full implementation directly into any Python interactive session without needing to install it first.
Google is the only search engine that works on Reddit now thanks to AI deal (via) This is depressing. As of around June 25th reddit.com/robots.txt contains this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Along with a link to Reddit's Public Content Policy.
Is this a direct result of Google's deal to license Reddit content for AI training, rumored at $60 million? That's not been confirmed but it looks likely, especially since accessing that robots.txt using the Google Rich Results testing tool (hence proxied via their IP) appears to return a different file, via this comment, my copy here.
Mistral Large 2 (via) The second release of a GPT-4 class open weights model in two days, after yesterday's Llama 3.1 405B.
The weights for this one are under Mistral's Research License, which "allows usage and modification for research and non-commercial usages" - so not as open as Llama 3.1. You can use it commercially via the Mistral paid API.
Mistral Large 2 is 123 billion parameters, "designed for single-node inference" (on a very expensive single-node!) and has a 128,000 token context window, the same size as Llama 3.1.
Notably, according to Mistral's own benchmarks it out-performs the much larger Llama 3.1 405B on their code and math benchmarks. They trained on a lot of code:
Following our experience with Codestral 22B and Codestral Mamba, we trained Mistral Large 2 on a very large proportion of code. Mistral Large 2 vastly outperforms the previous Mistral Large, and performs on par with leading models such as GPT-4o, Claude 3 Opus, and Llama 3 405B.
They also invested effort in tool usage, multilingual support (across English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Dutch, Russian, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, and Hindi) and reducing hallucinations:
One of the key focus areas during training was to minimize the model’s tendency to “hallucinate” or generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect or irrelevant information. This was achieved by fine-tuning the model to be more cautious and discerning in its responses, ensuring that it provides reliable and accurate outputs.
Additionally, the new Mistral Large 2 is trained to acknowledge when it cannot find solutions or does not have sufficient information to provide a confident answer.
I went to update my llm-mistral plugin for LLM to support the new model and found that I didn't need to - that plugin already uses llm -m mistral-large to access the mistral-large-latest endpoint, and Mistral have updated that to point to the latest version of their Large model.
Ollama now have mistral-large quantized to 4 bit as a 69GB download.
llm-gguf. I just released a new alpha plugin for LLM which adds support for running models from Meta's new Llama 3.1 family that have been packaged as GGUF files - it should work for other GGUF chat models too.
If you've already installed LLM the following set of commands should get you setup with Llama 3.1 8B:
llm install llm-gguf
llm gguf download-model \
https://huggingface.co/lmstudio-community/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF/resolve/main/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf \
--alias llama-3.1-8b-instruct --alias l31i
This will download a 4.92GB GGUF from lmstudio-community/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF on Hugging Face and save it (at least on macOS) to your ~/Library/Application Support/io.datasette.llm/gguf/models folder.
Once installed like that, you can run prompts through the model like so:
llm -m l31i "five great names for a pet lemur"
Or use the llm chat command to keep the model resident in memory and run an interactive chat session with it:
llm chat -m l31i
I decided to ship a new alpha plugin rather than update my existing llm-llama-cpp plugin because that older plugin has some design decisions baked in from the Llama 2 release which no longer make sense, and having a fresh plugin gave me a fresh slate to adopt the latest features from the excellent underlying llama-cpp-python library by Andrei Betlen.
Introducing Llama 3.1: Our most capable models to date. We've been waiting for the largest release of the Llama 3 model for a few months, and now we're getting a whole new model family instead.
Meta are calling Llama 3.1 405B "the first frontier-level open source AI model" and it really is benchmarking in that GPT-4+ class, competitive with both GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
I'm equally excited by the new 8B and 70B 3.1 models - both of which now support a 128,000 token context and benchmark significantly higher than their Llama 3 equivalents. Same-sized models getting more powerful and capable a very reassuring trend. I expect the 8B model (or variants of it) to run comfortably on an array of consumer hardware, and I've run a 70B model on a 64GB M2 in the past.
The 405B model can at least be run on a single server-class node:
To support large-scale production inference for a model at the scale of the 405B, we quantized our models from 16-bit (BF16) to 8-bit (FP8) numerics, effectively lowering the compute requirements needed and allowing the model to run within a single server node.
Meta also made a significant change to the license:
We’ve also updated our license to allow developers to use the outputs from Llama models — including 405B — to improve other models for the first time.
We’re excited about how this will enable new advancements in the field through synthetic data generation and model distillation workflows, capabilities that have never been achieved at this scale in open source.
I'm really pleased to see this. Using models to help improve other models has been a crucial technique in LLM research for over a year now, especially for fine-tuned community models release on Hugging Face. Researchers have mostly been ignoring this restriction, so it's reassuring to see the uncertainty around that finally cleared up.
Lots more details about the new models in the paper The Llama 3 Herd of Models including this somewhat opaque note about the 15 trillion token training data:
Our final data mix contains roughly 50% of tokens corresponding to general knowledge, 25% of mathematical and reasoning tokens, 17% code tokens, and 8% multilingual tokens.
Update: I got the Llama 3.1 8B Instruct model working with my LLM tool via a new plugin, llm-gguf.