228 posts tagged “css”
2025
If you've found web development frustrating over the past 5-10 years, here's something that has worked worked great for me: give yourself permission to avoid any form of frontend build system (so no npm / React / TypeScript / JSX / Babel / Vite / Tailwind etc) and code in HTML and JavaScript like it's 2009.
The joy came flooding back to me! It turns out browser APIs are really good now.
You don't even need jQuery to paper over the gaps any more - use document.querySelectorAll() and fetch() directly and see how much value you can build with a few dozen lines of code.
CSS Minecraft (via) Incredible project by Benjamin Aster:
There is no JavaScript on this page. All the logic is made 100% with pure HTML & CSS. For the best performance, please close other tabs and running programs.
The page implements a full Minecraft-style world editor: you can place and remove blocks of 7 different types in a 9x9x9 world, and rotate that world in 3D to view it from different angles.
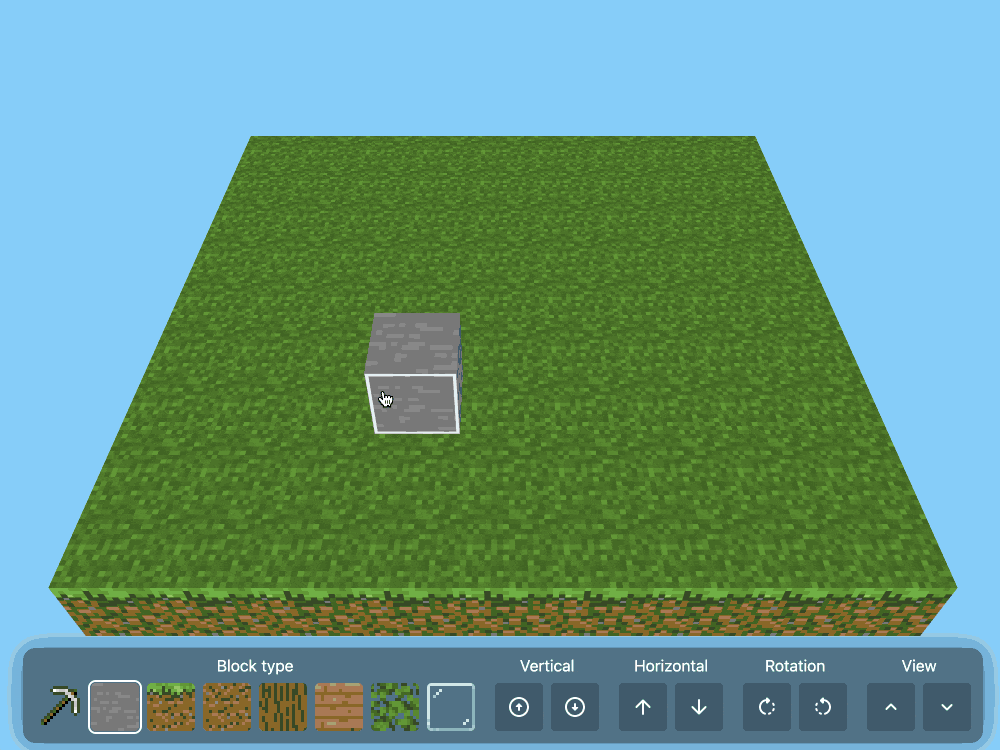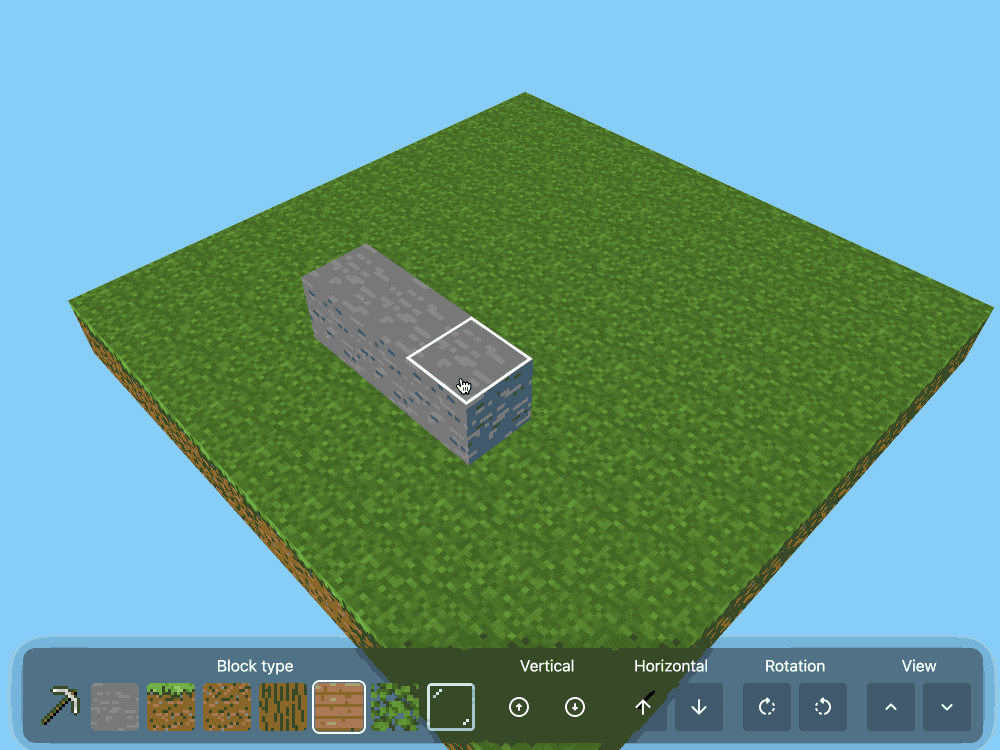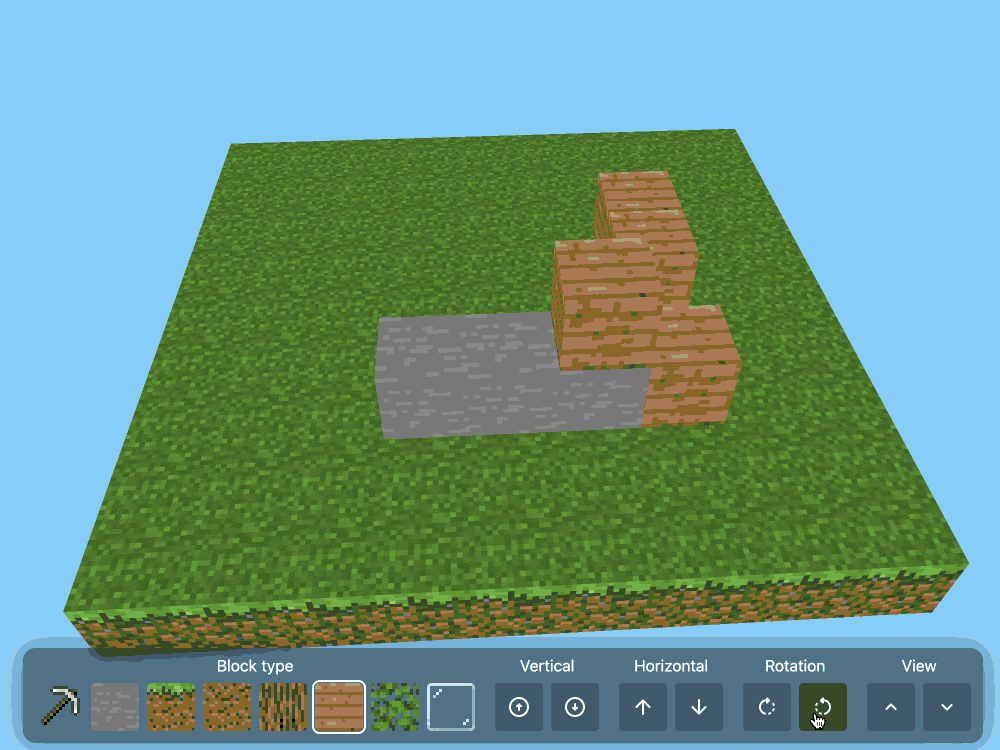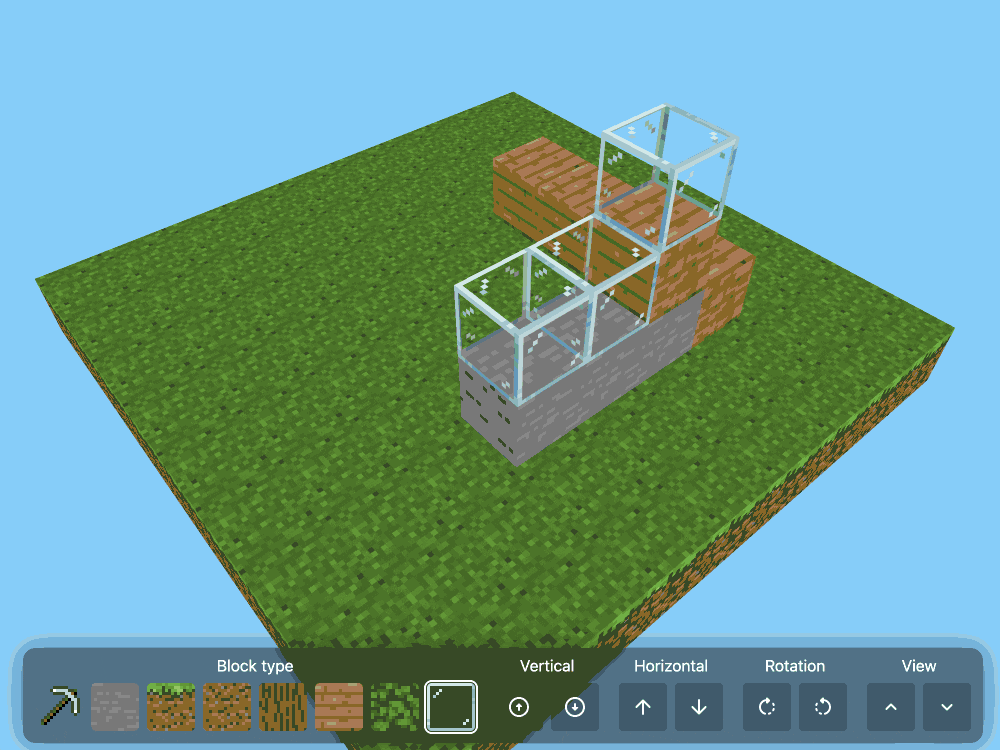
It's implemented in just 480 lines of CSS... and 46,022 lines (3.07MB) of HTML!
The key trick that gets this to work is labels combined with the has() selector. The page has 35,001 <label> elements and 5,840 <input type="radio"> elements - those radio elements are the state storage engine. Clicking on any of the six visible faces of a cube is clicking on a label, and the for="" of that label is the radio box for the neighboring cube in that dimension.
When you switch materials you're actually switching the available visible labels:
.controls:has( > .block-chooser > .stone > input[type=radio]:checked ) ~ main .cubes-container > .cube:not(.stone) { display: none; }
Claude Opus 4 explanation: "When the "stone" radio button is checked, all cube elements except those with the .stone class are hidden (display: none)".
Here's a shortened version of the Pug template (full code here) which illustrates how the HTML structure works:
//- pug index.pug -w - const blocks = ["air", "stone", "grass", "dirt", "log", "wood", "leaves", "glass"]; - const layers = 9; - const rows = 9; - const columns = 9; <html lang="en" style="--layers: #{layers}; --rows: #{rows}; --columns: #{columns}"> <!-- ... --> <div class="blocks"> for _, layer in Array(layers) for _, row in Array(rows) for _, column in Array(columns) <div class="cubes-container" style="--layer: #{layer}; --row: #{row}; --column: #{column}"> - const selectedBlock = layer === layers - 1 ? "grass" : "air"; - const name = `cube-layer-${layer}-row-${row}-column-${column}`; <div class="cube #{blocks[0]}"> - const id = `${name}-${blocks[0]}`; <input type="radio" name="#{name}" id="#{id}" !{selectedBlock === blocks[0] ? "checked" : ""} /> <label for="#{id}" class="front"></label> <label for="#{id}" class="back"></label> <label for="#{id}" class="left"></label> <label for="#{id}" class="right"></label> <label for="#{id}" class="top"></label> <label for="#{id}" class="bottom"></label> </div> each block, index in blocks.slice(1) - const id = `${name}-${block}`; - const checked = index === 0; <div class="cube #{block}"> <input type="radio" name="#{name}" id="#{id}" !{selectedBlock === block ? "checked" : ""} /> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer}-row-#{row + 1}-column-#{column}-#{block}" class="front"></label> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer}-row-#{row - 1}-column-#{column}-#{block}" class="back"></label> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer}-row-#{row}-column-#{column + 1}-#{block}" class="left"></label> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer}-row-#{row}-column-#{column - 1}-#{block}" class="right"></label> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer - 1}-row-#{row}-column-#{column}-#{block}" class="top"></label> <label for="cube-layer-#{layer + 1}-row-#{row}-column-#{column}-#{block}" class="bottom"></label> </div> //- /each </div> //- /for //- /for //- /for </div> <!-- ... -->
So for every one of the 9x9x9 = 729 cubes there is a set of eight radio boxes sharing the same name such as cube-layer-0-row-0-column-3 - which means it can have one of eight values ("air" is clear space, the others are material types). There are six labels, one for each side of the cube - and those label for="" attributes target the next block over of the current selected, visible material type.
The other brilliant technique is the way it implements 3D viewing with controls for rotation and moving the viewport. The trick here relies on CSS animation:
.controls:has(.up:active) ~ main .down { animation-play-state: running; } .controls:has(.down:active) ~ main .up { animation-play-state: running; } .controls:has(.clockwise:active) ~ main .clockwise { animation-play-state: running; } .controls:has(.counterclockwise:active) ~ main .counterclockwise { animation-play-state: running; }
Then later on there are animations defined for each of those different controls:
.content .clockwise { animation: var(--animation-duration) linear 1ms paused rotate-clockwise; } @keyframes rotate-clockwise { from { rotate: y 0turn; } to { rotate: y calc(-1 * var(--max-rotation)); } } .content .counterclockwise { animation: var(--animation-duration) linear 1ms paused rotate-counterclockwise; } @keyframes rotate-counterclockwise { from { rotate: y 0turn; } to { rotate: y calc(var(--max-rotation)); } }
Any time you hold the mouse down on one of the controls you switch the animation state out of paused to running, until you release that button again. As the animation runs it changes the various 3D transform properties applied to the selected element.
It's fiendishly clever, and actually quite elegant and readable once you figure out the core tricks it's using.
Annotated Presentation Creator. I've released a new version of my tool for creating annotated presentations. I use this to turn slides from my talks into posts like this one - here are a bunch more examples.
I wrote the first version in August 2023 making extensive use of ChatGPT and GPT-4. That older version can still be seen here.
This new edition is a design refresh using Claude 3.7 Sonnet (thinking). I ran this command:
llm \
-f https://til.simonwillison.net/tools/annotated-presentations \
-s 'Improve this tool by making it respnonsive for mobile, improving the styling' \
-m claude-3.7-sonnet -o thinking 1
That uses -f to fetch the original HTML (which has embedded CSS and JavaScript in a single page, convenient for working with LLMs) as a prompt fragment, then applies the system prompt instructions "Improve this tool by making it respnonsive for mobile, improving the styling" (typo included).
Here's the full transcript (generated using llm logs -cue) and a diff illustrating the changes. Total cost 10.7781 cents.
There was one visual glitch: the slides were distorted like this:
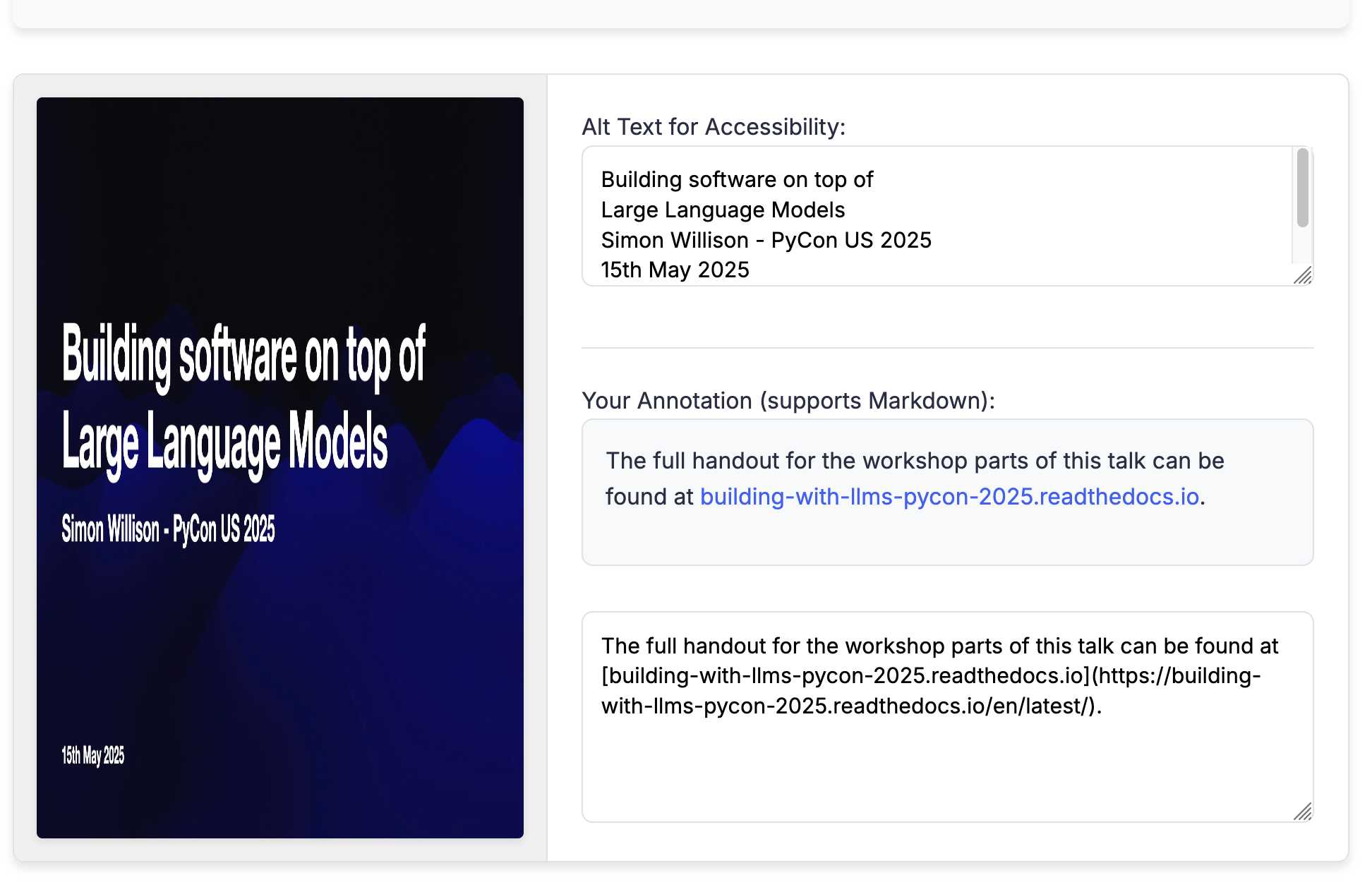
I decided to try o4-mini to see if it could spot the problem (after fixing this LLM bug):
llm o4-mini \
-a bug.png \
-f https://tools.simonwillison.net/annotated-presentations \
-s 'Suggest a minimal fix for this distorted image'
It suggested adding align-items: flex-start; to my .bundle class (it quoted the @media (min-width: 768px) bit but the solution was to add it to .bundle at the top level), which fixed the bug.
Default styles for h1 elements are changing
(via)
Wow, this is a rare occurrence! Firefox are rolling out a change to the default user-agent stylesheet for nested <h1> elements, currently ramping from 5% to 50% of users and with full roll-out planned for Firefox 140 in June 2025. Chrome is showing deprecation warnings and Safari are expected to follow suit in the future.
What's changing? The default sizes of <h1> elements that are nested inside <article>, <aside>, <nav> and <section>.
These are the default styles being removed:
/* where x is :is(article, aside, nav, section) */ x h1 { margin-block: 0.83em; font-size: 1.50em; } x x h1 { margin-block: 1.00em; font-size: 1.17em; } x x x h1 { margin-block: 1.33em; font-size: 1.00em; } x x x x h1 { margin-block: 1.67em; font-size: 0.83em; } x x x x x h1 { margin-block: 2.33em; font-size: 0.67em; }
The short version is that, many years ago, the HTML spec introduced the idea that an <h1> within a nested section should have the same meaning (and hence visual styling) as an <h2>. This never really took off and wasn't reflected by the accessibility tree, and was removed from the HTML spec in 2022. The browsers are now trying to cleanup the legacy default styles.
This advice from that post sounds sensible to me:
- Do not rely on default browser styles for conveying a heading hierarchy. Explicitly define your document hierarchy using
<h2>for second-level headings,<h3>for third-level, etc.- Always define your own
font-sizeandmarginfor<h1>elements.
First look at the modern attr().
Chrome 133 (released February 25th 2025) was the first browser to ship support for the advanced CSS attr() function (MDN), which lets attr() be used to compose values using types other than strings.
Ahmad Shadeed explores potential applications of this in detail, trying it out for CSS grid columns, progress bars, background images, animation delays and more.
I like this example that uses the rows="5" attribute on a <textarea> to calculate its max-height - here wrapped in a feature detection block:
@supports (x: attr(x type(*))) { textarea { min-height: calc( attr(rows type(<number>)) * 50px ); } }
That type(<number>) is the new syntax.
Many of Ahmad's examples can be achieved today across all browsers using a slightly more verbose CSS custom property syntax.
Here are the tracking issues for CSS values support in attr() for Firefox (opened 17 years ago) and WebKit (16 years ago).
Minimal CSS-only blurry image placeholders (via) Absolutely brilliant piece of CSS ingenuity by Lean Rada, who describes a way to implement blurry placeholder images using just CSS, with syntax like this:
<img src="…" style="--lqip:192900">
That 192900 number encodes everything needed to construct the placeholder - it manages to embed a single base color and six brightness components (in a 3x2 grid) in 20 bits, then encodes those as an integer in the roughly 2 million available values between -999,999 and 999,999 - beyond which range Lean found some browsers would start to lose precision.
The implementation for decoding that value becomes a bunch of clever bit-fiddling CSS expressions to expand it into further CSS variables:
[style*="--lqip:"] { --lqip-ca: mod(round(down, calc((var(--lqip) + pow(2, 19)) / pow(2, 18))), 4); --lqip-cb: mod(round(down, calc((var(--lqip) + pow(2, 19)) / pow(2, 16))), 4); /* more like that */ }
Which are expanded to even more variables with code like this:
--lqip-ca-clr: hsl(0 0% calc(var(--lqip-ca) / 3 * 100%)); --lqip-cb-clr: hsl(0 0% calc(var(--lqip-cb) / 3 * 100%));
And finally rendered using a CSS gradient definition that starts like this:
[style*="--lqip:"] { background-image: radial-gradient(50% 75% at 16.67% 25%, var(--lqip-ca-clr), transparent), radial-gradient(50% 75% at 50% 25%, var(--lqip-cb-clr), transparent), /* ... */ linear-gradient(0deg, var(--lqip-base-clr), var(--lqip-base-clr)); }
The article includes several interactive explainers (most of which are also powered by pure CSS) illustrating how it all works.
Their Node.js script for converting images to these magic integers uses Sharp to resize the image to 3x2 and then use the Oklab perceptually uniform color space (new to me, that was created by Björn Ottosson in 2020) to derive the six resulting values.
Backstory on the default styles for the HTML dialog modal. My TIL about Styling an HTML dialog modal to take the full height of the viewport (here's the interactive demo) showed up on Hacker News this morning, and attracted this fascinating comment from Chromium engineer Ian Kilpatrick.
There's quite a bit of history here, but the abbreviated version is that the dialog element was originally added as a replacement for window.alert(), and there were a libraries polyfilling dialog and being surprisingly widely used.
The mechanism which dialog was originally positioned was relatively complex, and slightly hacky (magic values for the insets).
Changing the behaviour basically meant that we had to add "overflow:auto", and some form of "max-height"/"max-width" to ensure that the content within the dialog was actually reachable.
The better solution to this was to add "max-height:stretch", "max-width:stretch". You can see the discussion for this here.
The problem is that no browser had (and still has) shipped the "stretch" keyword. (Blink likely will "soon")
However this was pushed back against as this had to go in a specification - and nobody implemented it ("-webit-fill-available" would have been an acceptable substitute in Blink but other browsers didn't have this working the same yet).
Hence the calc() variant. (Primarily because of "box-sizing:content-box" being the default, and pre-existing border/padding styles on dialog that we didn't want to touch). [...]
I particularly enjoyed this insight into the challenges of evolving the standards that underlie the web, even for something this small:
One thing to keep in mind is that any changes that changes web behaviour is under some time pressure. If you leave something too long, sites will start relying on the previous behaviour - so it would have been arguably worse not to have done anything.
Also from the comments I learned that Firefox DevTools can show you user-agent styles, but that option is turned off by default - notes on that here. Once I turned this option on I saw references to an html.css stylesheet, so I dug around and found that in the Firefox source code. Here's the commit history for that file on the official GitHub mirror, which provides a detailed history of how Firefox default HTML styles have evolved with the standards over time.
And via uallo here are the same default HTML styles for other browsers:
TIL: Styling an HTML dialog modal to take the full height of the viewport.
I spent some time today trying to figure out how to have a modal <dialog> element present as a full height side panel that animates in from the side. The full height bit was hard, until Natalie helped me figure out that browsers apply a default max-height: calc(100% - 6px - 2em); rule which needs to be over-ridden.
Also included: some spelunking through the HTML spec to figure out where that calc() expression was first introduced. The answer was November 2020.
Building Websites With Lots of Little HTML Pages (via) Jim Nielsen coins a confusing new acronym - LLMS for (L)ots of (L)ittle ht(M)l page(S). He's using this to describe his latest site refresh which makes extensive use of cross-document view transitions - a fabulous new progressive enhancement CSS technique that's supported in Chrome and Safari (and hopefully soon in Firefox).
With cross-document view transitions getting broader and broader support, I’m realizing that building in-page, progressively-enhanced interactions is more work than simply building two HTML pages and linking them.
Jim now has small static pages powering his home page filtering interface and even his navigation menu, with CSS view transitions configured to smoothly animate between the pages. I think it feels really good - here's what it looked like for me in Chrome (it looked the same both with and without JavaScript disabled):
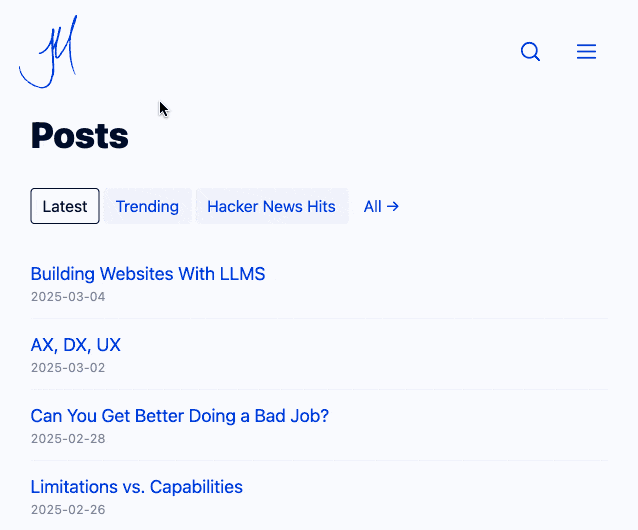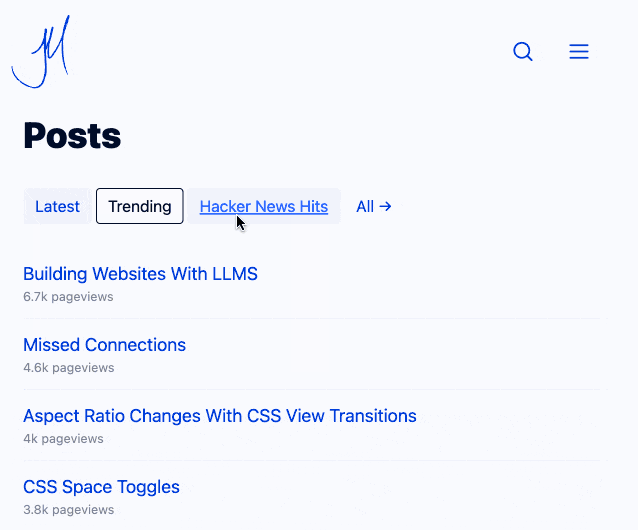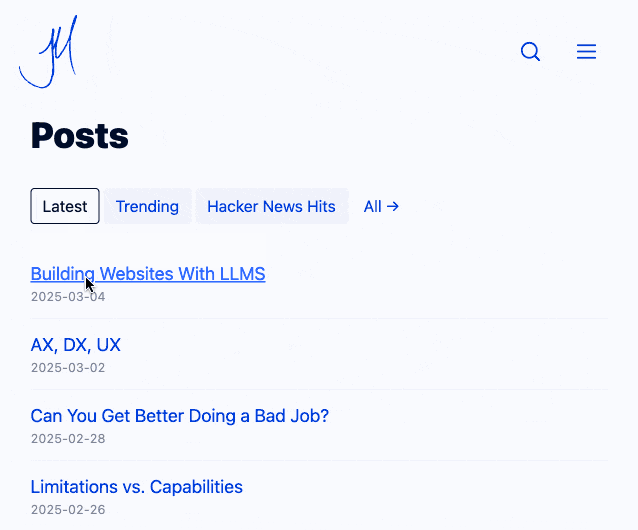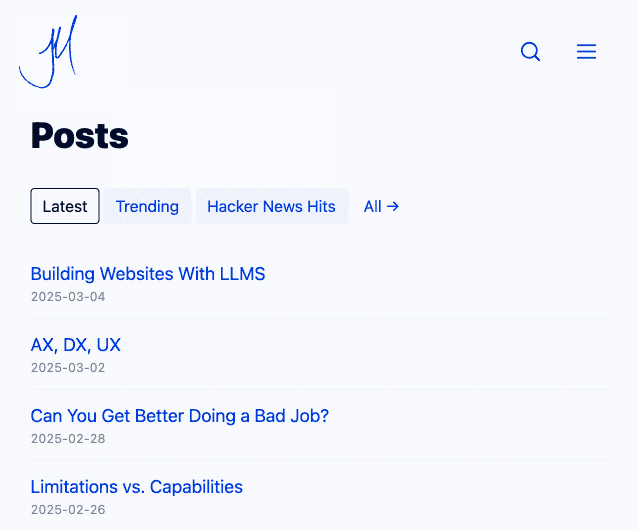
Watching the network panel in my browser, most of these pages are 17-20KB gzipped (~45KB after they've decompressed). No wonder it feels so snappy.
I poked around in Jim's CSS and found this relevant code:
@view-transition {
navigation: auto;
}
.posts-nav a[aria-current="page"]:not(:last-child):after {
border-color: var(--c-text);
view-transition-name: posts-nav;
}
/* Old stuff going out */
::view-transition-old(posts-nav) {
animation: fade 0.2s linear forwards;
/* https://jakearchibald.com/2024/view-transitions-handling-aspect-ratio-changes/ */
height: 100%;
}
/* New stuff coming in */
::view-transition-new(posts-nav) {
animation: fade 0.3s linear reverse;
height: 100%;
}
@keyframes fade {
from {
opacity: 1;
}
to {
opacity: 0;
}
}Jim observes:
This really feels like a game-changer for simple sites. If you can keep your site simple, it’s easier to build traditional, JavaScript-powered on-page interactions as small, linked HTML pages.
I've experimented with view transitions for Datasette in the past and the results were very promising. Maybe I'll pick that up again.
Bonus: Jim has a clever JavaScript trick to avoid clicks to the navigation menu being added to the browser's history in the default case.
2024
Clay UI library (via) Fascinating project by Nic Barker, who describes Clay like this:
Clay is a flex-box style UI auto layout library in C, with declarative syntax and microsecond performance.
His intro video to the library is outstanding: I learned a ton about how UI layout works from this, and the animated visual explanations are clear, tasteful and really helped land the different concepts:
Clay is a C library delivered in a single ~2000 line clay.h dependency-free header file. It only handles layout calculations: if you want to render the result you need to add an additional rendering layer.
In a fascinating demo of the library, the Clay site itself is rendered using Clay C compiled to WebAssembly! You can even switch between the default HTML renderer and an alternative based on Canvas.
This isn't necessarily a great idea: because the layout is entirely handled using <div> elements positioned using transform: translate(0px, 70px) style CSS attempting to select text across multiple boxes behaves strangely, and it's not clear to me what the accessibility implications are.
Update: Matt Campbell:
The accessibility implications are as serious as you might guess. The links aren't properly labeled, there's no semantic markup such as headings, and since there's a div for every line, continuous reading with a screen reader is choppy, that is, it pauses at the end of every physical line.
It does make for a very compelling demo of what Clay is capable of though, especially when you resize your browser window and the page layout is recalculated in real-time via the Clay WebAssembly bridge.
You can hit "D" on the website and open up a custom Clay debugger showing the hierarchy of layout elements on the page:
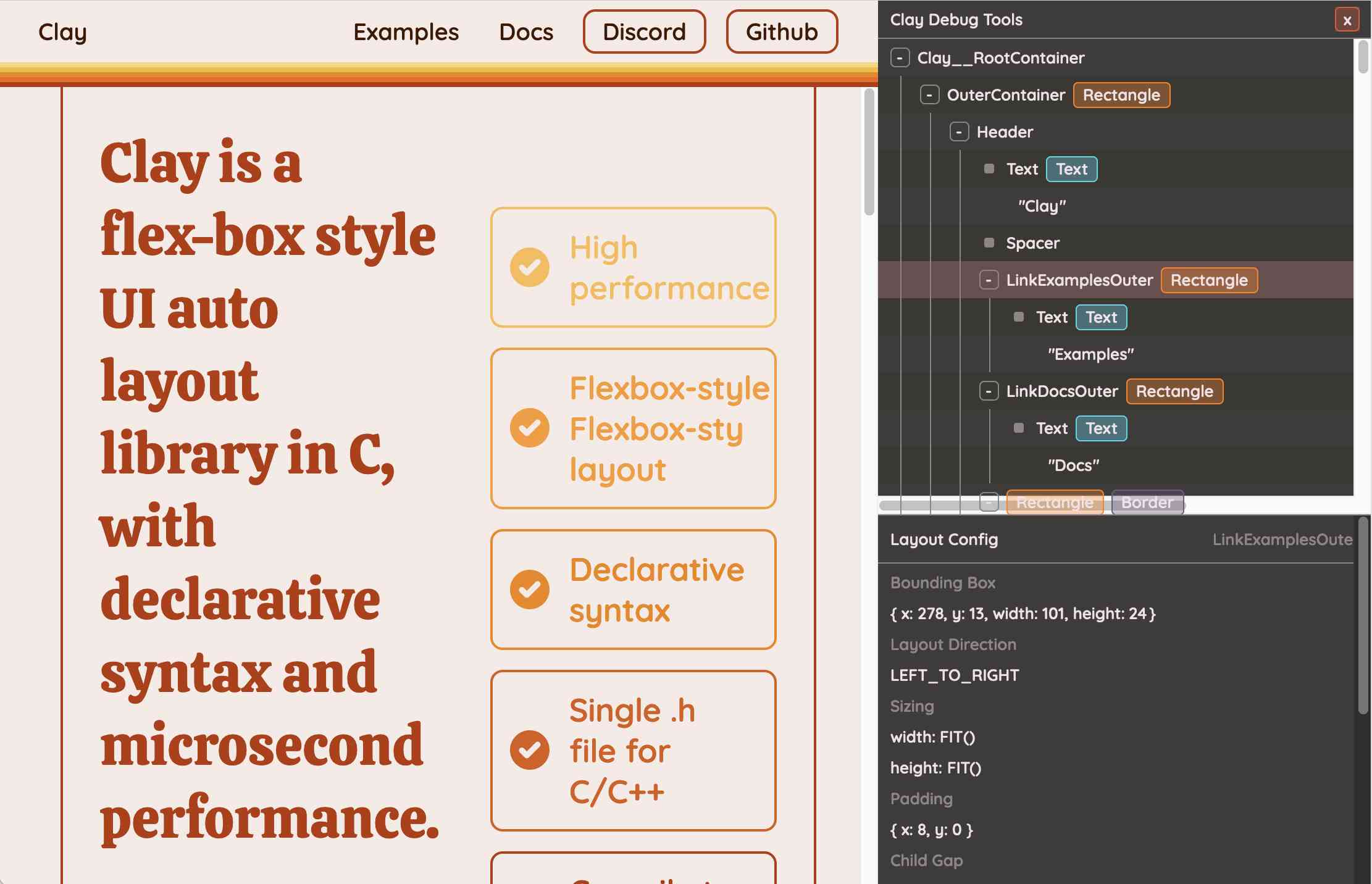
This also means that the entire page is defined using C code! Given that, I find the code itself surprisingly readable
void DeclarativeSyntaxPageDesktop() {
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxPageDesktop"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_GROW(), CLAY_SIZING_FIT({ .min = windowHeight - 50 }) }, .childAlignment = {0, CLAY_ALIGN_Y_CENTER}, .padding = {.x = 50} })) {
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxPage"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_GROW(), CLAY_SIZING_GROW() }, .childAlignment = { 0, CLAY_ALIGN_Y_CENTER }, .padding = { 32, 32 }, .childGap = 32 }), CLAY_BORDER({ .left = { 2, COLOR_RED }, .right = { 2, COLOR_RED } })) {
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxPageLeftText"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_PERCENT(0.5) }, .layoutDirection = CLAY_TOP_TO_BOTTOM, .childGap = 8 })) {
CLAY_TEXT(CLAY_STRING("Declarative Syntax"), CLAY_TEXT_CONFIG({ .fontSize = 52, .fontId = FONT_ID_TITLE_56, .textColor = COLOR_RED }));
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxSpacer"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_GROW({ .max = 16 }) } })) {}
CLAY_TEXT(CLAY_STRING("Flexible and readable declarative syntax with nested UI element hierarchies."), CLAY_TEXT_CONFIG({ .fontSize = 28, .fontId = FONT_ID_BODY_36, .textColor = COLOR_RED }));
CLAY_TEXT(CLAY_STRING("Mix elements with standard C code like loops, conditionals and functions."), CLAY_TEXT_CONFIG({ .fontSize = 28, .fontId = FONT_ID_BODY_36, .textColor = COLOR_RED }));
CLAY_TEXT(CLAY_STRING("Create your own library of re-usable components from UI primitives like text, images and rectangles."), CLAY_TEXT_CONFIG({ .fontSize = 28, .fontId = FONT_ID_BODY_36, .textColor = COLOR_RED }));
}
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxPageRightImage"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_PERCENT(0.50) }, .childAlignment = {.x = CLAY_ALIGN_X_CENTER} })) {
CLAY(CLAY_ID("SyntaxPageRightImageInner"), CLAY_LAYOUT({ .sizing = { CLAY_SIZING_GROW({ .max = 568 }) } }), CLAY_IMAGE({ .sourceDimensions = {1136, 1194}, .sourceURL = CLAY_STRING("/clay/images/declarative.png") })) {}
}
}
}
}I'm not ready to ditch HTML and CSS for writing my web pages in C compiled to WebAssembly just yet, but as an exercise in understanding layout engines (and a potential tool for building non-web interfaces in the future) this is a really interesting project to dig into.
To clarify here: I don't think the web layout / WebAssembly thing is the key idea behind Clay at all - I think it's a neat demo of the library, but it's not what Clay is for. It's certainly an interesting way to provide a demo of a layout library!
Nic confirms:
You totally nailed it, the fact that you can compile to wasm and run in HTML stemmed entirely from a “wouldn’t it be cool if…” It was designed for my C projects first and foremost!
You can use text-wrap: balance; on icons. Neat CSS experiment from Terence Eden: the new text-wrap: balance CSS property is intended to help make text like headlines display without ugly wrapped single orphan words, but Terence points out it can be used for icons too:
![]()
This inspired me to investigate if the same technique could work for text based navigation elements. I used Claude to build this interactive prototype of a navigation bar that uses text-wrap: balance against a list of display: inline menu list items. It seems to work well!
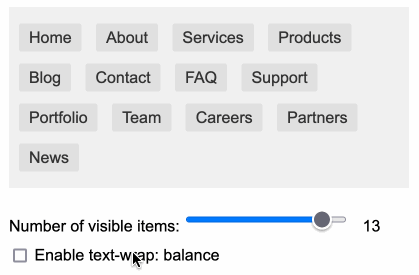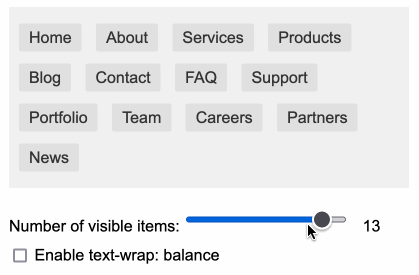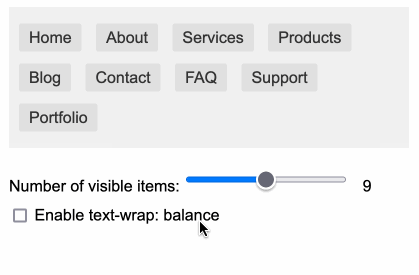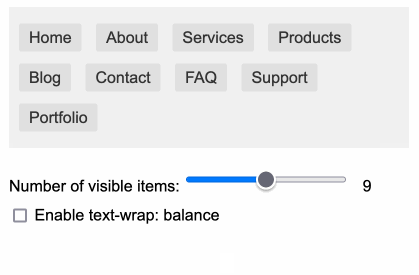
My first attempt used display: inline-block which worked in Safari but failed in Firefox.
Notable limitation from that MDN article:
Because counting characters and balancing them across multiple lines is computationally expensive, this value is only supported for blocks of text spanning a limited number of lines (six or less for Chromium and ten or less for Firefox)
So it's fine for these navigation concepts but isn't something you can use for body text.
HTML for People (via) Blake Watson's brand new HTML tutorial, presented as a free online book (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0, on GitHub). This seems very modern and well thought-out to me. It focuses exclusively on HTML, skipping JavaScript entirely and teaching with Simple.css to avoid needing to dig into CSS while still producing sites that are pleasing to look at. It even touches on Web Components (described as Custom HTML tags) towards the end.
Calling LLMs from client-side JavaScript, converting PDFs to HTML + weeknotes
I’ve been having a bunch of fun taking advantage of CORS-enabled LLM APIs to build client-side JavaScript applications that access LLMs directly. I also span up a new Datasette plugin for advanced permission management.
[... 2,050 words]Button Stealer (via) Really fun Chrome extension by Anatoly Zenkov: it scans every web page you visit for things that look like buttons and stashes a copy of them, then provides a page where you can see all of the buttons you have collected. Here's Anatoly's collection, and here are a few that I've picked up trying it out myself:
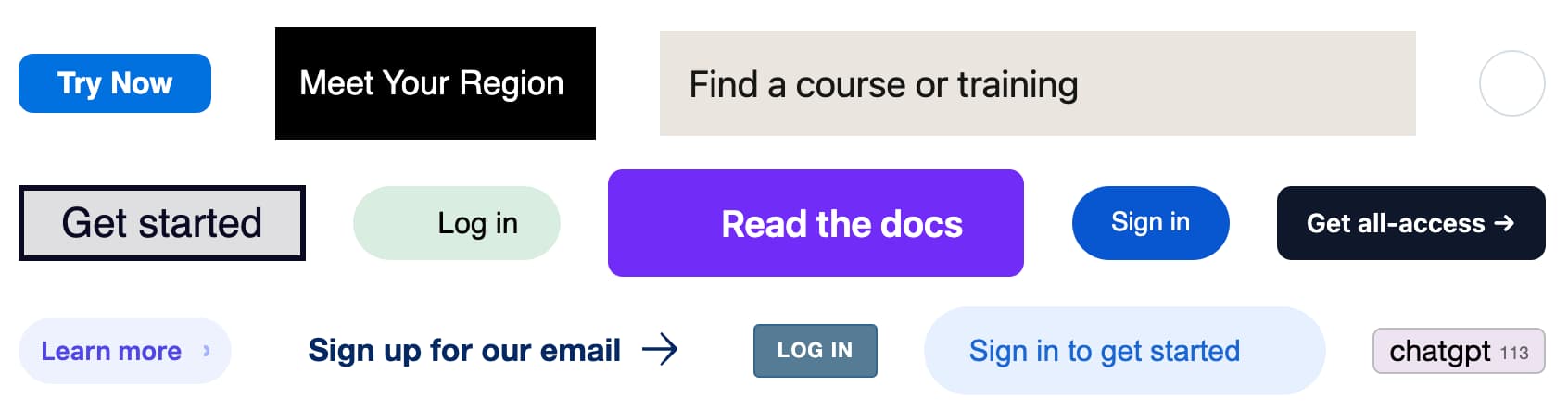
The extension source code is on GitHub. It identifies potential buttons by looping through every <a> and <button> element and applying some heuristics like checking the width/height ratio, then clones a subset of the CSS from window.getComputedStyle() and stores that in the style= attribute.
So you think you know box shadows? (via) David Gerrells dives deep into CSS box shadows. How deep? Implementing a full ray tracer with them deep.
Box shadow CSS generator (via) Another example of a tiny personal tool I built using Claude 3.5 Sonnet and artifacts. In this case my prompt was:
CSS for a slight box shadow, build me a tool that helps me twiddle settings and preview them and copy and paste out the CSS
I changed my mind half way through typing the prompt and asked it for a custom tool, and it built me this!
Here's the full transcript - in a follow-up prompt I asked for help deploying it and it rewrote the tool to use <script type="text/babel"> and the babel-standalone library to add React JSX support directly in the browser - a bit of a hefty dependency (387KB compressed / 2.79MB total) but I think acceptable for this kind of one-off tool.
Being able to knock out tiny custom tools like this on a whim is a really interesting new capability. It's also a lot of fun!
What You Need to Know about Modern CSS (Spring 2024 Edition) (via) Useful guide to the many new CSS features that have become widely enough supported to start using as-of May 2024. Time to learn container queries!
View transitions are still mostly limited to Chrome—I can’t wait for those to land in Firefox and Safari.
Printing music with CSS Grid (via) Stephen Bond demonstrates some ingenious tricks for creating surprisingly usable sheet music notation using clever application of CSS grids.
It uses rules like .stave > [data-duration="0.75"] { grid-column-end: span 18; } to turn data- attributes for musical properties into positions on the rendered stave.
Kobold letters (via) Konstantin Weddige explains a sophisticated HTML email phishing vector he calls Kobold emails.
When you forward a message, most HTML email clients will indent the forward by nesting it inside another element.
This means CSS rules within the email can be used to cause an element that was invisible in the original email to become visible when it is forwarded—allowing tricks like a forwarded innocuous email from your boss adding instructions for wiring money from the company bank account.
Gmail strips style blocks before forwarding—which it turns out isn’t protection against this, because you can put a style block in the original email to hide the attack text which will then be stripped for you when the email is forwarded.
The Dropflow Playground (via) Dropflow is a “CSS layout engine” written in TypeScript and taking advantage of the HarfBuzz text shaping engine (used by Chrome, Android, Firefox and more) compiled to WebAssembly to implement glyph layout.
This linked demo is fascinating: on the left hand side you can edit HTML with inline styles, and the right hand side then updates live to show that content rendered by Dropflow in a canvas element.
Why would you want this? It lets you generate images and PDFs with excellent performance using your existing knowledge HTML and CSS. It’s also just really cool!
Upside down table trick with CSS (via) I was complaining how hard it is to build a horizontally scrollable table with a scrollbar at the top rather than the bottom and RGBCube on Lobste.rs suggested rotating the container 180 degrees and then the table contents and headers 180 back again... and it totally works! Demo in this CodePen.
How To Center a Div (via) Josh Comeau: “I think that my best blog posts are accessible to beginners while still having some gold nuggets for more experienced devs, and I think I’ve nailed that here. Even if you have years of CSS experience, I bet you’ll learn something new.”
Lots of interactive demos in this.
2023
An Interactive Guide to CSS Grid (via) Josh Comeau’s extremely clear guide to CSS grid, with interactive examples for all of the core properties.
The anatomy of visually-hidden (via) James Edwards provides a detailed breakdown of the current recommended CSS for hiding content while keeping it available for assistive technologies in the browser accessibility and render trees. Lots of accumulated tricks and screen reader special cases in this.
The Page With No Code
(via)
A fun demo by Dan Q, who created a web page with no HTML at all - but in Firefox it still renders content, thanks to a data URI base64 encoded stylesheet served in a link: header that uses html::before, html::after, body::before and body::after with content: properties to serve the content. It even has a background image, encoded as a base64 SVG nested inside another data URI.
2022
An Interactive Guide to Flexbox. Joshua Comeau built this fantastic guide to CSS flexbox layouts, with interactive examples of all of the properties. This is a really useful tour of the layout model.
Inside the mind of a frontend developer: Hero section. Ahmad Shadeed provides a fascinating, hyper-detailed breakdown of his approach to implementing a “hero section” component using HTML and CSS, including notes on CSS grids and gradient backgrounds.
Can :has Connect 4? (via) Spectacular CSS demo by Jhey Tompkins, implementing a working 3D Connect 4 game using just CSS (brilliant trickery with the new :has() selector) and not a single line of JavaScript.
Supporting logical properties. A frustrating reminder from Jeremy Keith that Safari is not an evergreen browser: older iOS devices (1st gen iPad Air for example) get stuck on the last iOS version that supports them, which also sticks them with an old version of Safari, which means they will never get support for newer CSS properties such as inline-start and block-end. Jeremy shows how to use the @supports rule to hide this new syntax from those older browsers.
Shoelace (via) Saw this for the first time today: it’s a relatively new library of framework-agnostic Web Components, built on lit-html and covering a huge array of common functionality: buttons and sliders and dialogs and drawer interfaces and dropdown menus and so on. The design is very clean, the documentation is superb—and it looks like you can cherry pick just the components you are using for a pretty lean addition to your page weight. So refreshing to see libraries like this that really take advantage of modern web standards.