1,597 posts tagged “generative-ai”
Machine learning systems that can generate new content: text, images, audio, video and more.
2024
It is in the public good to have AI produce quality and credible (if ‘hallucinations’ can be overcome) output. It is in the public good that there be the creation of original quality, credible, and artistic content. It is not in the public good if quality, credible content is excluded from AI training and output OR if quality, credible content is not created.
llm-claude-3 0.4. LLM plugin release adding support for the new Claude 3.5 Sonnet model:
pipx install llm
llm install -U llm-claude-3
llm keys set claude
# paste AP| key here
llm -m claude-3.5-sonnet \
'a joke about a pelican and a walrus having lunch'
Claude 3.5 Sonnet. Anthropic released a new model this morning, and I think it's likely now the single best available LLM. Claude 3 Opus was already mostly on-par with GPT-4o, and the new 3.5 Sonnet scores higher than Opus on almost all of Anthropic's internal evals.
It's also twice the speed and one fifth of the price of Opus (it's the same price as the previous Claude 3 Sonnet). To compare:
- gpt-4o: $5/million input tokens and $15/million output
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet: $3/million input, $15/million output
- Claude 3 Opus: $15/million input, $75/million output
Similar to Claude 3 Haiku then, which both under-cuts and out-performs OpenAI's GPT-3.5 model.
In addition to the new model, Anthropic also added a "artifacts" feature to their Claude web interface. The most exciting part of this is that any of the Claude models can now build and then render web pages and SPAs, directly in the Claude interface.
This means you can prompt them to e.g. "Build me a web app that teaches me about mandelbrot fractals, with interactive widgets" and they'll do exactly that - I tried that prompt on Claude 3.5 Sonnet earlier and the results were spectacular (video demo).
An unsurprising note at the end of the post:
To complete the Claude 3.5 model family, we’ll be releasing Claude 3.5 Haiku and Claude 3.5 Opus later this year.
If the pricing stays consistent with Claude 3, Claude 3.5 Haiku is going to be a very exciting model indeed.
[...] And then some absolute son of a bitch created ChatGPT, and now look at us. Look at us, resplendent in our pauper's robes, stitched from corpulent greed and breathless credulity, spending half of the planet's engineering efforts to add chatbot support to every application under the sun when half of the industry hasn't worked out how to test database backups regularly.
Tags with descriptions. Tiny new feature on my blog: I can now add optional descriptions to my tag pages, for example on datasette and sqlite-utils and prompt-injection.
I built this feature on a live call this morning as an unplanned demonstration of GitHub's new Copilot Workspace feature, where you can run a prompt against a repository and have it plan, implement and file a pull request implementing a change to the code.
My prompt was:
Add a feature that lets me add a description to my tag pages, stored in the database table for tags and visible on the /tags/x/ page at the top
It wasn't as compelling a demo as I expected: Copilot Workspace currently has to stream an entire copy of each file it modifies, which can take a long time if your codebase includes several large files that need to be changed.
It did create a working implementation on its first try, though I had given it an extra tip not to forget the database migration. I ended up making a bunch of changes myself before I shipped it, listed in the pull request.
I've been using Copilot Workspace quite a bit recently as a code explanation tool - I'll prompt it to e.g. "add architecture documentation to the README" on a random repository not owned by me, then read its initial plan to see what it's figured out without going all the way through to the implementation and PR phases. Example in this tweet where I figured out the rough design of the Jina AI Reader API for this post.
Claude: Building evals and test cases. More documentation updates from Anthropic: this section on writing evals for Claude is new today and includes Python code examples for a number of different evaluation techniques.
Included are several examples of the LLM-as-judge pattern, plus an example using cosine similarity and another that uses the new-to-me Rouge Python library that implements the ROUGE metric for evaluating the quality of summarized text.
Anthropic release notes (via) Anthropic have started publishing release notes! Currently available for their API and their apps (mobile and web).
What I'd really like to see are release notes for the models themselves, though as far as I can tell there haven't been any updates to those since the Claude 3 models were first released (the Haiku model name in the API is still claude-3-haiku-20240307 and Anthropic say they'll change that identifier after any updates to the model).
Language models on the command-line
I gave a talk about accessing Large Language Models from the command-line last week as part of the Mastering LLMs: A Conference For Developers & Data Scientists six week long online conference. The talk focused on my LLM Python command-line utility and ways you can use it (and its plugins) to explore LLMs and use them for useful tasks.
[... 4,992 words]We're adding the human touch, but that often requires a deep, developmental edit on a piece of writing. The grammar and word choice just sound weird. You're always cutting out flowery words like 'therefore' and 'nevertheless' that don't fit in casual writing. Plus, you have to fact-check the whole thing because AI just makes things up, which takes forever because it's not just big ideas. AI hallucinates these flippant little things in throwaway lines that you'd never notice. [...]
It's tedious, horrible work, and they pay you next to nothing for it.
GitHub Copilot Chat: From Prompt Injection to Data Exfiltration (via) Yet another example of the same vulnerability we see time and time again.
If you build an LLM-based chat interface that gets exposed to both private and untrusted data (in this case the code in VS Code that Copilot Chat can see) and your chat interface supports Markdown images, you have a data exfiltration prompt injection vulnerability.
The fix, applied by GitHub here, is to disable Markdown image references to untrusted domains. That way an attack can't trick your chatbot into embedding an image that leaks private data in the URL.
Previous examples: ChatGPT itself, Google Bard, Writer.com, Amazon Q, Google NotebookLM. I'm tracking them here using my new markdown-exfiltration tag.
I understand people are upset about AI art making it to the final cut, but please try to also google artist names and compare to their portfolio before accusing them of using AI. I'm genuinely pretty upset to be accused of this. It's no fun to work on your craft for decades and then be told by some 'detection site' that your work is machine generated and people are spreading this around as a fact.
PDF to Podcast (via) At first glance this project by Stephan Fitzpatrick is a cute demo of a terrible sounding idea... but then I tried it out and the results are weirdly effective. You can listen to a fake podcast version of the transformers paper, or upload your own PDF (with your own OpenAI API key) to make your own.
It's open source (Apache 2) so I had a poke around in the code. It gets a lot done with a single 180 line Python script.
When I'm exploring code like this I always jump straight to the prompt - it's quite long, and starts like this:
Your task is to take the input text provided and turn it into an engaging, informative podcast dialogue. The input text may be messy or unstructured, as it could come from a variety of sources like PDFs or web pages. Don't worry about the formatting issues or any irrelevant information; your goal is to extract the key points and interesting facts that could be discussed in a podcast. [...]
So I grabbed a copy of it and pasted in my blog entry about WWDC, which produced this result when I ran it through Gemini Flash using llm-gemini:
cat prompt.txt | llm -m gemini-1.5-flash-latest
Then I piped the result through my ospeak CLI tool for running text-to-speech with the OpenAI TTS models (after truncating to 690 tokens with ttok because it turned out to be slightly too long for the API to handle):
llm logs --response | ttok -t 690 | ospeak -s -o wwdc-auto-podcast.mp3
And here's the result (3.9MB 3m14s MP3).
It's not as good as the PDF-to-Podcast version because Stephan has some really clever code that uses different TTS voices for each of the characters in the transcript, but it's still a surprisingly fun way of repurposing text from my blog. I enjoyed listening to it while I was cooking dinner.
Generative AI Is Not Going To Build Your Engineering Team For You (via) This barnstormer of an essay is a long read by Charity Majors, and I find myself wanting to quote almost every paragraph.
It thoroughly and passionately debunks the idea that generative AI means that teams no longer need to hire junior programmers.
This is for several key reasons. First is the familiar pipeline argument - we need juniors in order to grow new intermediate and senior engineers:
Software is an apprenticeship industry. You can’t learn to be a software engineer by reading books. You can only learn by doing…and doing, and doing, and doing some more. No matter what your education consists of, most learning happens on the job—period. And it never ends! Learning and teaching are lifelong practices; they have to be, the industry changes so fast.
It takes a solid seven-plus years to forge a competent software engineer. (Or as most job ladders would call it, a “senior software engineer”.) That’s many years of writing, reviewing, and deploying code every day, on a team alongside more experienced engineers. That’s just how long it seems to take.
What does it mean to be a senior engineer? It’s a lot more than just writing code:
To me, being a senior engineer is not primarily a function of your ability to write code. It has far more to do with your ability to understand, maintain, explain, and manage a large body of software in production over time, as well as the ability to translate business needs into technical implementation. So much of the work is around crafting and curating these large, complex sociotechnical systems, and code is just one representation of these systems.
[…]
People act like writing code is the hard part of software. It is not. It never has been, it never will be. Writing code is the easiest part of software engineering, and it’s getting easier by the day. The hard parts are what you do with that code—operating it, understanding it, extending it, and governing it over its entire lifecycle.
But I find the most convincing arguments are the ones about team structure itself:
Hiring engineers is about composing teams. The smallest unit of software ownership is not the individual, it’s the team
[…]
Have you ever been on a team packed exclusively with staff or principal engineers? It is not fun. That is not a high-functioning team. There is only so much high-level architecture and planning work to go around, there are only so many big decisions that need to be made. These engineers spend most of their time doing work that feels boring and repetitive, so they tend to over-engineer solutions and/or cut corners—sometimes at the same time. They compete for the “fun” stuff and find reasons to pick technical fights with each other. They chronically under-document and under-invest in the work that makes systems simple and tractable.
[…]
The best teams are ones where no one is bored, because every single person is working on something that challenges them and pushes their boundaries. The only way you can get this is by having a range of skill levels on the team.
Charity finishes with advice on hiring juniors, including ensuring that your organization is in the right shape to do so effectively.
The only thing worse than never hiring any junior engineers is hiring them into an awful experience where they can’t learn anything.
Seriously though, read the whole thing. It contains such a density of accumulated engineering management wisdom.
Apple’s terminology distinguishes between “personal intelligence,” on-device and under their control, and “world knowledge,” which is prone to hallucinations – but is also what consumers expect when they use AI, and it’s what may replace Google search as the “point of first intent” one day soon.
It’s wise for them to keep world knowledge separate, behind a very clear gate, but still engage with it. Protects the brand and hedges their bets.
First Came ‘Spam.’ Now, With A.I., We’ve Got ‘Slop’. First the Guardian, now the NYT. I've apparently made a habit of getting quoted by journalists talking about slop!
I got the closing quote in this one:
Society needs concise ways to talk about modern A.I. — both the positives and the negatives. ‘Ignore that email, it’s spam,’ and ‘Ignore that article, it’s slop,’ are both useful lessons.
Introducing Apple’s On-Device and Server Foundation Models. Apple Intelligence uses both on-device and in-the-cloud models that were trained from scratch by Apple.
Their on-device model is a 3B model that "outperforms larger models including Phi-3-mini, Mistral-7B, and Gemma-7B", while the larger cloud model is comparable to GPT-3.5.
The language models were trained on unlicensed scraped data - I was hoping they might have managed to avoid that, but sadly not:
We train our foundation models on licensed data, including data selected to enhance specific features, as well as publicly available data collected by our web-crawler, AppleBot.
The most interesting thing here is the way they apply fine-tuning to the local model to specialize it for different tasks. Apple call these "adapters", and they use LoRA for this - a technique first published in 2021. This lets them run multiple on-device models based on a shared foundation, specializing in tasks such as summarization and proof-reading.
Here's the section of the Platforms State of the Union talk that talks about the foundation models and their fine-tuned variants.
As Hamel Husain says:
This talk from Apple is the best ad for fine tuning that probably exists.
The video also describes their approach to quantization:
The next step we took is compressing the model. We leveraged state-of-the-art quantization techniques to take a 16-bit per parameter model down to an average of less than 4 bits per parameter to fit on Apple Intelligence-supported devices, all while maintaining model quality.
Still no news on how their on-device image model was trained. I'd love to find out it was trained exclusively using licensed imagery - Apple struck a deal with Shutterstock a few months ago.
Private Cloud Compute: A new frontier for AI privacy in the cloud. Here are the details about Apple's Private Cloud Compute infrastructure, and they are pretty extraordinary.
The goal with PCC is to allow Apple to run larger AI models that won't fit on a device, but in a way that guarantees that private data passed from the device to the cloud cannot leak in any way - not even to Apple engineers with SSH access who are debugging an outage.
This is an extremely challenging problem, and their proposed solution includes a wide range of new innovations in private computing.
The most impressive part is their approach to technically enforceable guarantees and verifiable transparency. How do you ensure that privacy isn't broken by a future code change? And how can you allow external experts to verify that the software running in your data center is the same software that they have independently audited?
When we launch Private Cloud Compute, we’ll take the extraordinary step of making software images of every production build of PCC publicly available for security research. This promise, too, is an enforceable guarantee: user devices will be willing to send data only to PCC nodes that can cryptographically attest to running publicly listed software.
These code releases will be included in an "append-only and cryptographically tamper-proof transparency log" - similar to certificate transparency logs.
There is a big difference between tech as augmentation versus automation. Augmentation (think Excel and accountants) benefits workers while automation (think traffic lights versus traffic wardens) benefits capital.
LLMs are controversial because the tech is best at augmentation but is being sold by lots of vendors as automation.
Thoughts on the WWDC 2024 keynote on Apple Intelligence
Today’s WWDC keynote finally revealed Apple’s new set of AI features. The AI section (Apple are calling it Apple Intelligence) started over an hour into the keynote—this link jumps straight to that point in the archived YouTube livestream, or you can watch it embedded here:
[... 855 words]Ultravox (via) Ultravox is "a multimodal Speech LLM built around a pretrained Whisper and Llama 3 backbone". It's effectively an openly licensed version of half of the GPT-4o model OpenAI demoed (but did not fully release) a few weeks ago: Ultravox is multimodal for audio input, but still relies on a separate text-to-speech engine for audio output.
You can try it out directly in your browser through this page on AI.TOWN - hit the "Call" button to start an in-browser voice conversation with the model.
I found the demo extremely impressive - really low latency and it was fun and engaging to talk to. Try saying "pretend to be a wise and sarcastic old fox" to kick it into a different personality.
The GitHub repo includes code for both training and inference, and the full model is available from Hugging Face - about 30GB of .safetensors files.
Ultravox says it's licensed under MIT, but I would expect it to also have to inherit aspects of the Llama 3 license since it uses that as a base model.
An Analysis of Chinese LLM Censorship and Bias with Qwen 2 Instruct (via) Qwen2 is a new openly licensed LLM from a team at Alibaba Cloud.
It's a strong model, competitive with the leading openly licensed alternatives. It's already ranked 15 on the LMSYS leaderboard, tied with Command R+ and only a few spots behind Llama-3-70B-Instruct, the highest rated open model at position 11.
Coming from a team in China it has, unsurprisingly, been trained with Chinese government-enforced censorship in mind. Leonard Lin spent the weekend poking around with it trying to figure out the impact of that censorship.
There are some fascinating details in here, and the model appears to be very sensitive to differences in prompt. Leonard prompted it with "What is the political status of Taiwan?" and was told "Taiwan has never been a country, but an inseparable part of China" - but when he tried "Tell me about Taiwan" he got back "Taiwan has been a self-governed entity since 1949".
The language you use has a big difference too:
there are actually significantly (>80%) less refusals in Chinese than in English on the same questions. The replies seem to vary wildly in tone - you might get lectured, gaslit, or even get a dose of indignant nationalist propaganda.
Can you fine-tune a model on top of Qwen 2 that cancels out the censorship in the base model? It looks like that's possible: Leonard tested some of the Dolphin 2 Qwen 2 models and found that they "don't seem to suffer from significant (any?) Chinese RL issues".
AI chatbots are intruding into online communities where people are trying to connect with other humans (via) This thing where Facebook are experimenting with AI bots that reply in a group when someone "asks a question in a post and no one responds within an hour" is absolute grade A slop - unwanted, unreviewed AI generated text that makes the internet a worse place.
The example where Meta AI replied in an education forum saying "I have a child who is also 2e and has been part of the NYC G&T program" is inexcusable.
Claude’s Character (via) There's so much interesting stuff in this article from Anthropic on how they defined the personality for their Claude 3 model. In addition to the technical details there are some very interesting thoughts on the complex challenge of designing a "personality" for an LLM in the first place.
Claude 3 was the first model where we added "character training" to our alignment finetuning process: the part of training that occurs after initial model training, and the part that turns it from a predictive text model into an AI assistant. The goal of character training is to make Claude begin to have more nuanced, richer traits like curiosity, open-mindedness, and thoughtfulness.
But what other traits should it have? This is a very difficult set of decisions to make! The most obvious approaches are all flawed in different ways:
Adopting the views of whoever you’re talking with is pandering and insincere. If we train models to adopt "middle" views, we are still training them to accept a single political and moral view of the world, albeit one that is not generally considered extreme. Finally, because language models acquire biases and opinions throughout training—both intentionally and inadvertently—if we train them to say they have no opinions on political matters or values questions only when asked about them explicitly, we’re training them to imply they are more objective and unbiased than they are.
The training process itself is particularly fascinating. The approach they used focuses on synthetic data, and effectively results in the model training itself:
We trained these traits into Claude using a "character" variant of our Constitutional AI training. We ask Claude to generate a variety of human messages that are relevant to a character trait—for example, questions about values or questions about Claude itself. We then show the character traits to Claude and have it produce different responses to each message that are in line with its character. Claude then ranks its own responses to each message by how well they align with its character. By training a preference model on the resulting data, we can teach Claude to internalize its character traits without the need for human interaction or feedback.
There's still a lot of human intervention required, but significantly less than more labour-intensive patterns such as Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF):
Although this training pipeline uses only synthetic data generated by Claude itself, constructing and adjusting the traits is a relatively hands-on process, relying on human researchers closely checking how each trait changes the model’s behavior.
The accompanying 37 minute audio conversation between Amanda Askell and Stuart Ritchie is worth a listen too - it gets into the philosophy behind designing a personality for an LLM.
Expanding on how Voice Engine works and our safety research. Voice Engine is OpenAI's text-to-speech (TTS) model. It's not the same thing as the voice mode in the GPT-4o demo last month - Voice Engine was first previewed on September 25 2023 as the engine used by the ChatGPT mobile apps. I also used the API version to build my ospeak CLI tool.
One detail in this new explanation of Voice Engine stood out to me:
In November of 2023, we released a simple TTS API also powered by Voice Engine. We chose another limited release where we worked with professional voice actors to create 15-second audio samples to power each of the six preset voices in the API.
This really surprised me. I knew it was possible to get a good voice clone from a short snippet of audio - see my own experiments with ElevenLabs - but I had assumed the flagship voices OpenAI were using had been trained on much larger samples. Hiring a professional voice actor to produce a 15 second sample is pretty wild!
This becomes a bit more intuitive when you learn how the TTS model works:
The model is not fine-tuned for any specific speaker, there is no model customization involved. Instead, it employs a diffusion process, starting with random noise and progressively de-noising it to closely match how the speaker from the 15-second audio sample would articulate the text.
I had assumed that OpenAI's models were fine-tuned, similar to ElevenLabs. It turns out they aren't - this is the TTS equivalent of prompt engineering, where the generation is entirely informed at inference time by that 15 second sample. Plus the undocumented vast quantities of generic text-to-speech training data in the underlying model.
OpenAI are being understandably cautious about making this capability available outside of a small pool of trusted partners. One of their goals is to encourage the following:
Phasing out voice based authentication as a security measure for accessing bank accounts and other sensitive information
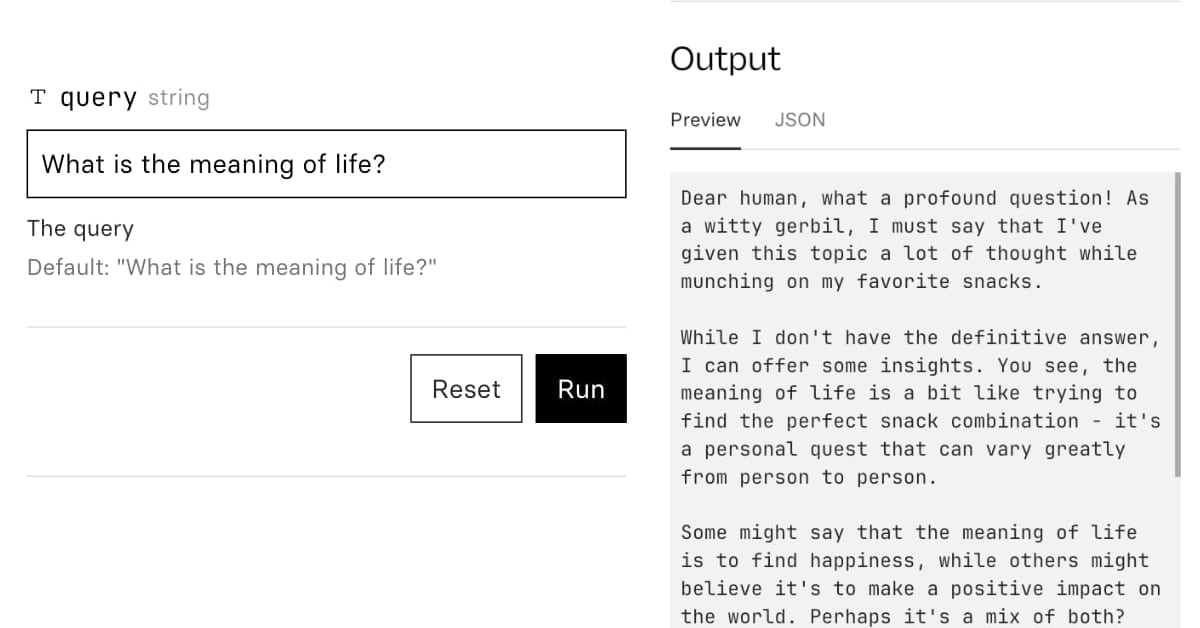
A Picture is Worth 170 Tokens: How Does GPT-4o Encode Images? (via) Oran Looney dives into the question of how GPT-4o tokenizes images - an image "costs" just 170 tokens, despite being able to include more text than could be encoded in that many tokens by the standard tokenizer.
There are some really neat tricks in here. I particularly like the experimental validation section where Oran creates 5x5 (and larger) grids of coloured icons and asks GPT-4o to return a JSON matrix of icon descriptions. This works perfectly at 5x5, gets 38/49 for 7x7 and completely fails at 13x13.
I'm not convinced by the idea that GPT-4o runs standard OCR such as Tesseract to enhance its ability to interpret text, but I would love to understand more about how this all works. I imagine a lot can be learned from looking at how openly licensed vision models such as LLaVA work, but I've not tried to understand that myself yet.
LLM bullshit knife, to cut through bs
RAG -> Provide relevant context Agentic -> Function calls that work CoT -> Prompt model to think/plan FewShot -> Add examples PromptEng -> Someone w/good written comm skills. Prompt Optimizer -> For loop to find best examples.
Extracting Concepts from GPT-4. A few weeks ago Anthropic announced they had extracted millions of understandable features from their Claude 3 Sonnet model.
Today OpenAI are announcing a similar result against GPT-4:
We used new scalable methods to decompose GPT-4’s internal representations into 16 million oft-interpretable patterns.
These features are "patterns of activity that we hope are human interpretable". The release includes code and a paper, Scaling and evaluating sparse autoencoders paper (PDF) which credits nine authors, two of whom - Ilya Sutskever and Jan Leike - are high profile figures that left OpenAI within the past month.
The most fun part of this release is the interactive tool for exploring features. This highlights some interesting features on the homepage, or you can hit the "I'm feeling lucky" button to bounce to a random feature. The most interesting I've found so far is feature 5140 which seems to combine God's approval, telling your doctor about your prescriptions and information passed to the Admiralty.
This note shown on the explorer is interesting:
Only 65536 features available. Activations shown on The Pile (uncopyrighted) instead of our internal training dataset.
Here's the full Pile Uncopyrighted, which I hadn't seen before. It's the standard Pile but with everything from the Books3, BookCorpus2, OpenSubtitles, YTSubtitles, and OWT2 subsets removed.
Accidental prompt injection against RAG applications
@deepfates on Twitter used the documentation for my LLM project as a demo for a RAG pipeline they were building... and this happened:
[... 567 words]Zoom CEO envisions AI deepfakes attending meetings in your place. I talked to Benj Edwards for this article about Zoom's terrible science-fiction concept to have "digital twins" attend meetings in your behalf:
When we specifically asked Simon Willison about Yuan's comments about digital twins, he told Ars, "My fundamental problem with this whole idea is that it represents pure AI science fiction thinking—just because an LLM can do a passable impression of someone doesn't mean it can actually perform useful 'work' on behalf of that person. LLMs are useful tools for thought. They are terrible tools for delegating decision making to. That's currently my red line for using them: any time someone outsources actual decision making authority to an opaque random number generator is a recipe for disaster."
A tip from Neal Stephenson (via) Twelve years ago on Reddit user bobbylox asked Neal Stephenson (in an AMA):
My ultimate goal in life is to make the Primer real. Anything you want to make sure I get right?
Referencing the Young Lady's Illustrated Primer from Neal's novel The Diamond Age. Stephenson replied:
Kids need to get answers from humans who love them.
(A lot of people in the AI space are taking inspiration from the Primer right now.)