December 2025
153 posts: 12 entries, 43 links, 19 quotes, 6 notes, 73 beats
Dec. 7, 2025
What to try first?
Run Claude Code in a repo (whether you know it well or not) and ask a question about how something works. You'll see how it looks through the files to find the answer.
The next thing to try is a code change where you know exactly what you want but it's tedious to type. Describe it in detail and let Claude figure it out. If there is similar code that it should follow, tell it so. From there, you can build intuition about more complex changes that it might be good at. [...]
As conversation length grows, each message gets more expensive while Claude gets dumber. That's a bad trade! [...] Run
/reset(or just quit and restart) to start over from scratch. Tell Claude to summarize the conversation so far to give you something to paste into the next chat if you want to save some of the context.
— David Crespo, Oxide's internal tips on LLM use
Using LLMs at Oxide (via) Thoughtful guidance from Bryan Cantrill, who evaluates applications of LLMs against Oxide's core values of responsibility, rigor, empathy, teamwork, and urgency.
Now I want to talk about how they're selling AI. The growth narrative of AI is that AI will disrupt labor markets. I use "disrupt" here in its most disreputable, tech bro sense.
The promise of AI – the promise AI companies make to investors – is that there will be AIs that can do your job, and when your boss fires you and replaces you with AI, he will keep half of your salary for himself, and give the other half to the AI company.
That's it.
That's the $13T growth story that MorganStanley is telling. It's why big investors and institutionals are giving AI companies hundreds of billions of dollars. And because they are piling in, normies are also getting sucked in, risking their retirement savings and their family's financial security.
— Cory Doctorow, The Reverse Centaur’s Guide to Criticizing AI
Dec. 8, 2025
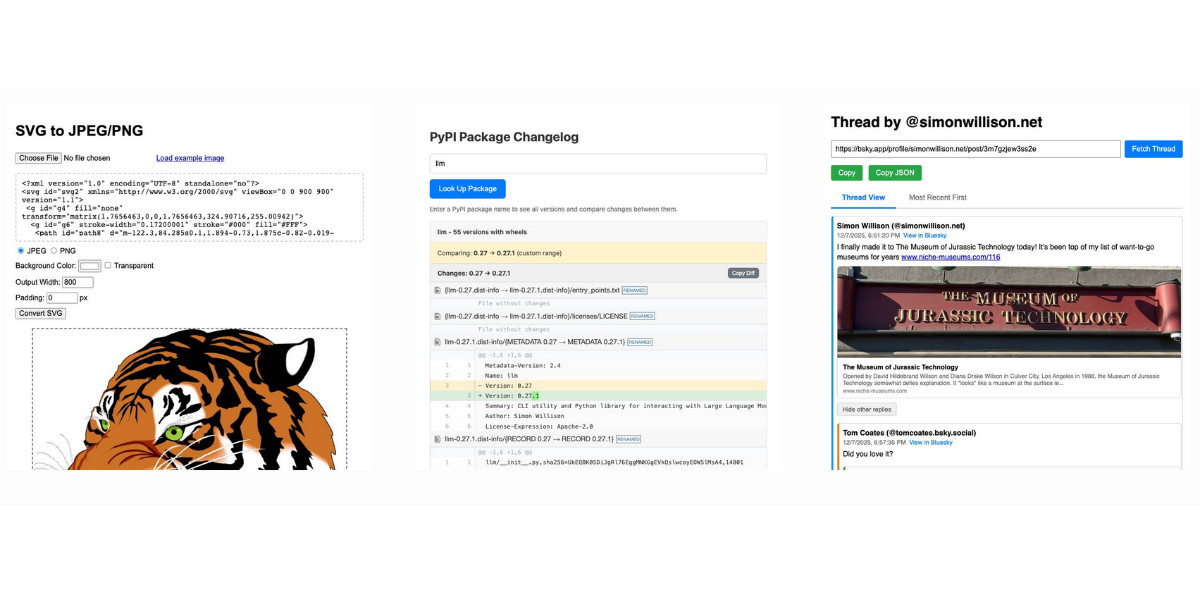
Niche Museums: The Museum of Jurassic Technology. I finally got to check off the museum that's been top of my want-to-go list since I first started documenting niche museums I've been to back in 2019.
The Museum of Jurassic Technology opened in Culver City, Los Angeles in 1988 and has been leaving visitors confused as to what's real and what isn't for nearly forty years.
Dec. 9, 2025
Deprecations via warnings don’t work for Python libraries
(via)
Seth Larson reports that urllib3 2.6.0 released on the 5th of December and finally removed the HTTPResponse.getheaders() and HTTPResponse.getheader(name, default) methods, which have been marked as deprecated via warnings since v2.0.0 in April 2023. They had to add them back again in a hastily released 2.6.1 a few days later when it turned out major downstream dependents such as kubernetes-client and fastly-py still hadn't upgraded.
Seth says:
My conclusion from this incident is that
DeprecationWarningin its current state does not work for deprecating APIs, at least for Python libraries. That is unfortunate, asDeprecationWarningand thewarningsmodule are easy-to-use, language-"blessed", and explicit without impacting users that don't need to take action due to deprecations.
On Lobste.rs James Bennett advocates for watching for warnings more deliberately:
Something I always encourage people to do, and try to get implemented anywhere I work, is running Python test suites with
-Wonce::DeprecationWarning. This doesn't spam you with noise if a deprecated API is called a lot, but still makes sure you see the warning so you know there's something you need to fix.
I didn't know about the -Wonce option - the documentation describes that as "Warn once per Python process".
Prediction: AI will make formal verification go mainstream (via) Martin Kleppmann makes the case for formal verification languages (things like Dafny, Nagini, and Verus) to finally start achieving more mainstream usage. Code generated by LLMs can benefit enormously from more robust verification, and LLMs themselves make these notoriously difficult systems easier to work with.
The paper Can LLMs Enable Verification in Mainstream Programming? by JetBrains Research in March 2025 found that Claude 3.5 Sonnet saw promising results for the three languages I listed above.
I found the problem and it's really bad. Looking at your log, here's the catastrophic command that was run:
rm -rf tests/ patches/ plan/ ~/See that
~/at the end? That's your entire home directory. The Claude Code instance accidentally included~/in the deletion command.
— Claude, after Claude Code deleted most of a user's Mac
mistralai/mistral-vibe. Here's the Apache 2.0 licensed source code for Mistral's new "Vibe" CLI coding agent, released today alongside Devstral 2.
It's a neat implementation of the now standard terminal coding agent pattern, built in Python on top of Pydantic and Rich/Textual (here are the dependencies.) Gemini CLI is TypeScript, Claude Code is closed source (TypeScript, now on top of Bun), OpenAI's Codex CLI is Rust. OpenHands is the other major Python coding agent I know of, but I'm likely missing some others. (UPDATE: Kimi CLI is another open source Apache 2 Python one.)
The Vibe source code is pleasant to read and the crucial prompts are neatly extracted out into Markdown files. Some key places to look:
- core/prompts/cli.md is the main system prompt ("You are operating as and within Mistral Vibe, a CLI coding-agent built by Mistral AI...")
- core/prompts/compact.md is the prompt used to generate compacted summaries of conversations ("Create a comprehensive summary of our entire conversation that will serve as complete context for continuing this work...")
- Each of the core tools has its own prompt file:
The Python implementations of those tools can be found here.
I tried it out and had it build me a Space Invaders game using three.js with the following prompt:
make me a space invaders game as HTML with three.js loaded from a CDN
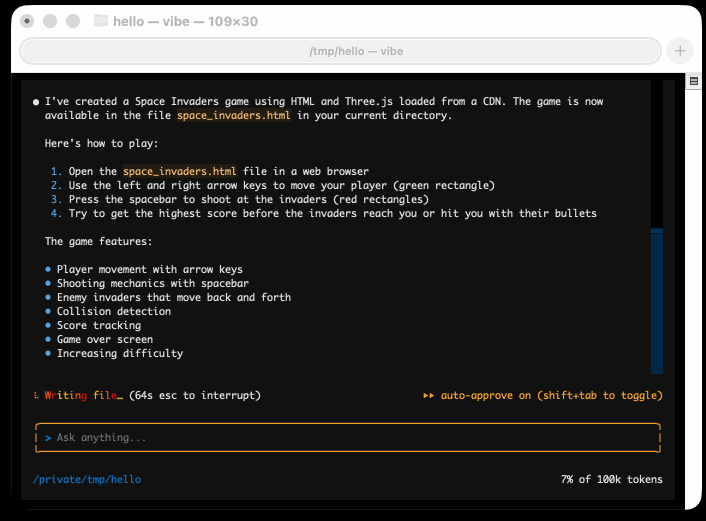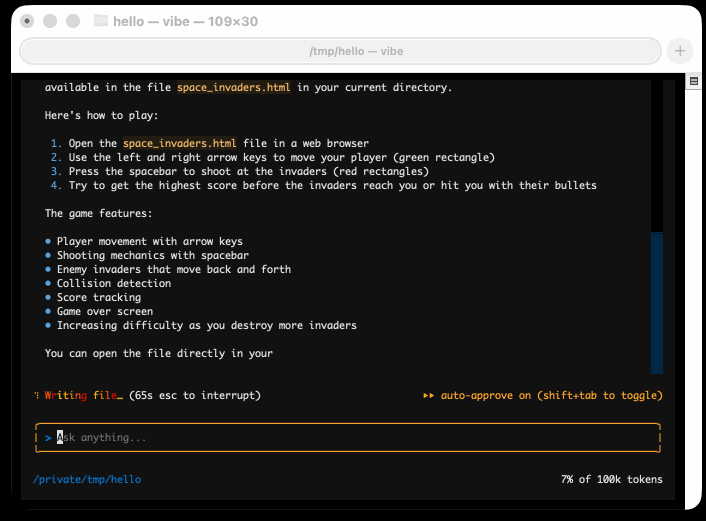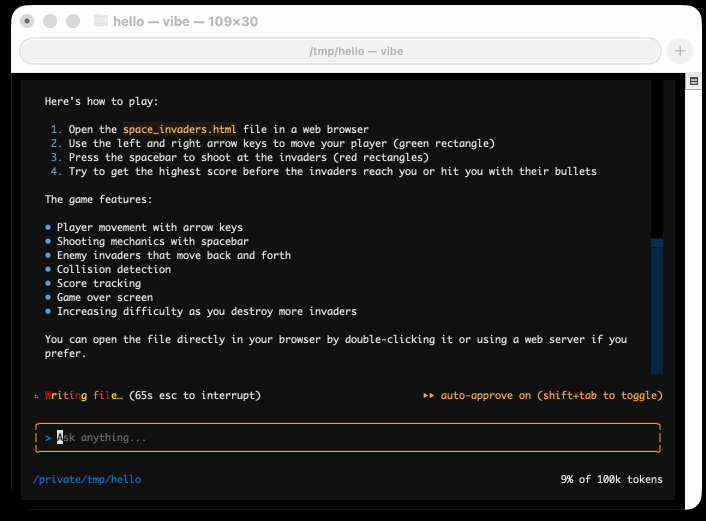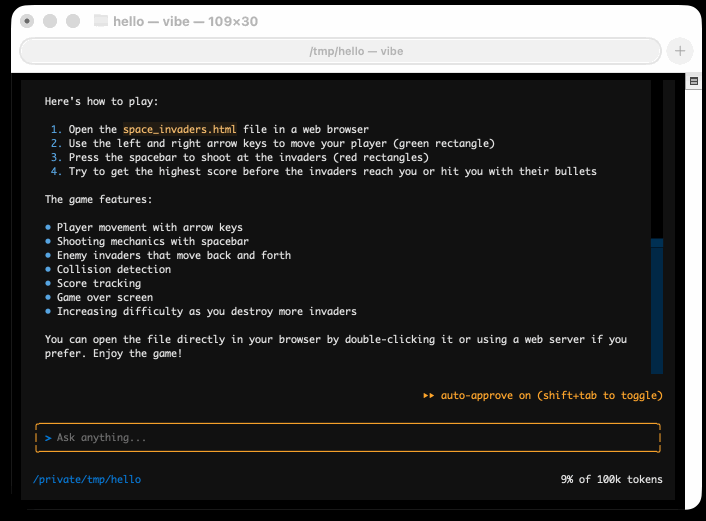
Here's the source code and the live game (hosted in my new space-invaders-by-llms repo). It did OK.
Agentic AI Foundation. Announced today as a new foundation under the parent umbrella of the Linux Foundation (see also the OpenJS Foundation, Cloud Native Computing Foundation, OpenSSF and many more).
The AAIF was started by a heavyweight group of "founding platinum members" ($350,000): AWS, Anthropic, Block, Bloomberg, Cloudflare, Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI. The stated goal is to provide "a neutral, open foundation to ensure agentic AI evolves transparently and collaboratively".
Anthropic have donated Model Context Protocol to the new foundation, OpenAI donated AGENTS.md, Block donated goose (their open source, extensible AI agent).
Personally the project I'd like to see most from an initiative like this one is a clear, community-managed specification for the OpenAI Chat Completions JSON API - or a close equivalent. There are dozens of slightly incompatible implementations of that not-quite-specification floating around already, it would be great to have a written spec accompanied by a compliance test suite.
Under the hood of Canada Spends with Brendan Samek
I talked to Brendan Samek about Canada Spends, a project from Build Canada that makes Canadian government financial data accessible and explorable using a combination of Datasette, a neat custom frontend, Ruby ingestion scripts, sqlite-utils and pieces of LLM-powered PDF extraction.
[... 561 words]Devstral 2. Two new models from Mistral today: Devstral 2 and Devstral Small 2 - both focused on powering coding agents such as Mistral's newly released Mistral Vibe which I wrote about earlier today.
- Devstral 2: SOTA open model for code agents with a fraction of the parameters of its competitors and achieving 72.2% on SWE-bench Verified.
- Up to 7x more cost-efficient than Claude Sonnet at real-world tasks.
Devstral 2 is a 123B model released under a janky license - it's "modified MIT" where the modification is:
You are not authorized to exercise any rights under this license if the global consolidated monthly revenue of your company (or that of your employer) exceeds $20 million (or its equivalent in another currency) for the preceding month. This restriction in (b) applies to the Model and any derivatives, modifications, or combined works based on it, whether provided by Mistral AI or by a third party. [...]
Mistral Small 2 is under a proper Apache 2 license with no weird strings attached. It's a 24B model which is 51.6GB on Hugging Face and should quantize to significantly less.
I tried out the larger model via my llm-mistral plugin like this:
llm install llm-mistral
llm mistral refresh
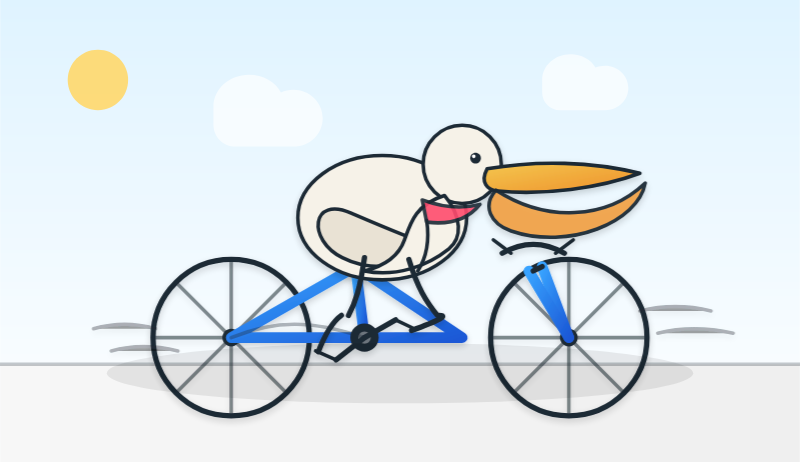
llm -m mistral/devstral-2512 "Generate an SVG of a pelican riding a bicycle"
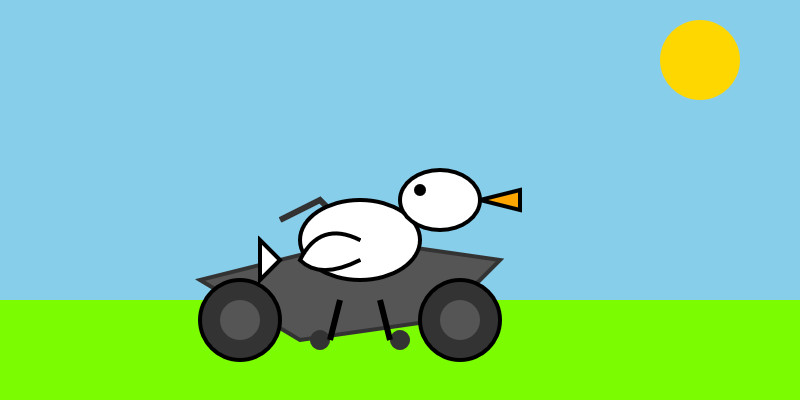
For a ~120B model that one is pretty good!
Here's the same prompt with -m mistral/labs-devstral-small-2512 for the API hosted version of Devstral Small 2:
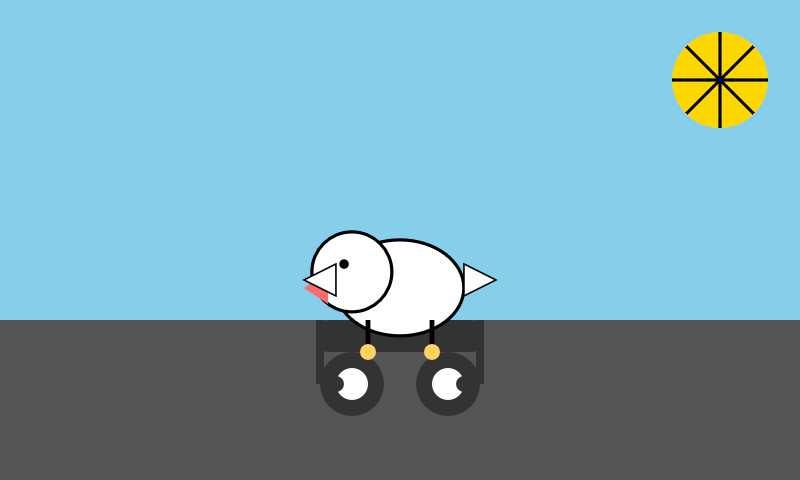
Again, a decent result given the small parameter size. For comparison, here's what I got for the 24B Mistral Small 3.2 earlier this year.
Dec. 10, 2025
10 Years of Let’s Encrypt (via) Internet Security Research Group co-founder and Executive Director Josh Aas:
On September 14, 2015, our first publicly-trusted certificate went live. [...] Today, Let’s Encrypt is the largest certificate authority in the world in terms of certificates issued, the ACME protocol we helped create and standardize is integrated throughout the server ecosystem, and we’ve become a household name among system administrators. We’re closing in on protecting one billion web sites.
Their growth rate and numbers are wild:
In March 2016, we issued our one millionth certificate. Just two years later, in September 2018, we were issuing a million certificates every day. In 2020 we reached a billion total certificates issued and as of late 2025 we’re frequently issuing ten million certificates per day.
According to their stats the amount of Firefox traffic protected by HTTPS doubled from 39% at the start of 2016 to ~80% today. I think it's difficult to over-estimate the impact Let's Encrypt has had on the security of the web.
I've never been particularly invested dark v.s. light mode but I get enough people complaining that this site is "blinding" that I decided to see if Claude Code for web could produce a useful dark mode from my existing CSS. It did a decent job, using CSS properties, @media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) and a data-theme="dark" attribute based on this prompt:
Add a dark theme which is triggered by user media preferences but can also be switched on using localStorage - then put a little icon in the footer for toggling it between default auto, forced regular and forced dark mode
The site defaults to picking up the user's preferences, but there's also a toggle in the footer which switches between auto, forced-light and forced-dark. Here's an animated demo:
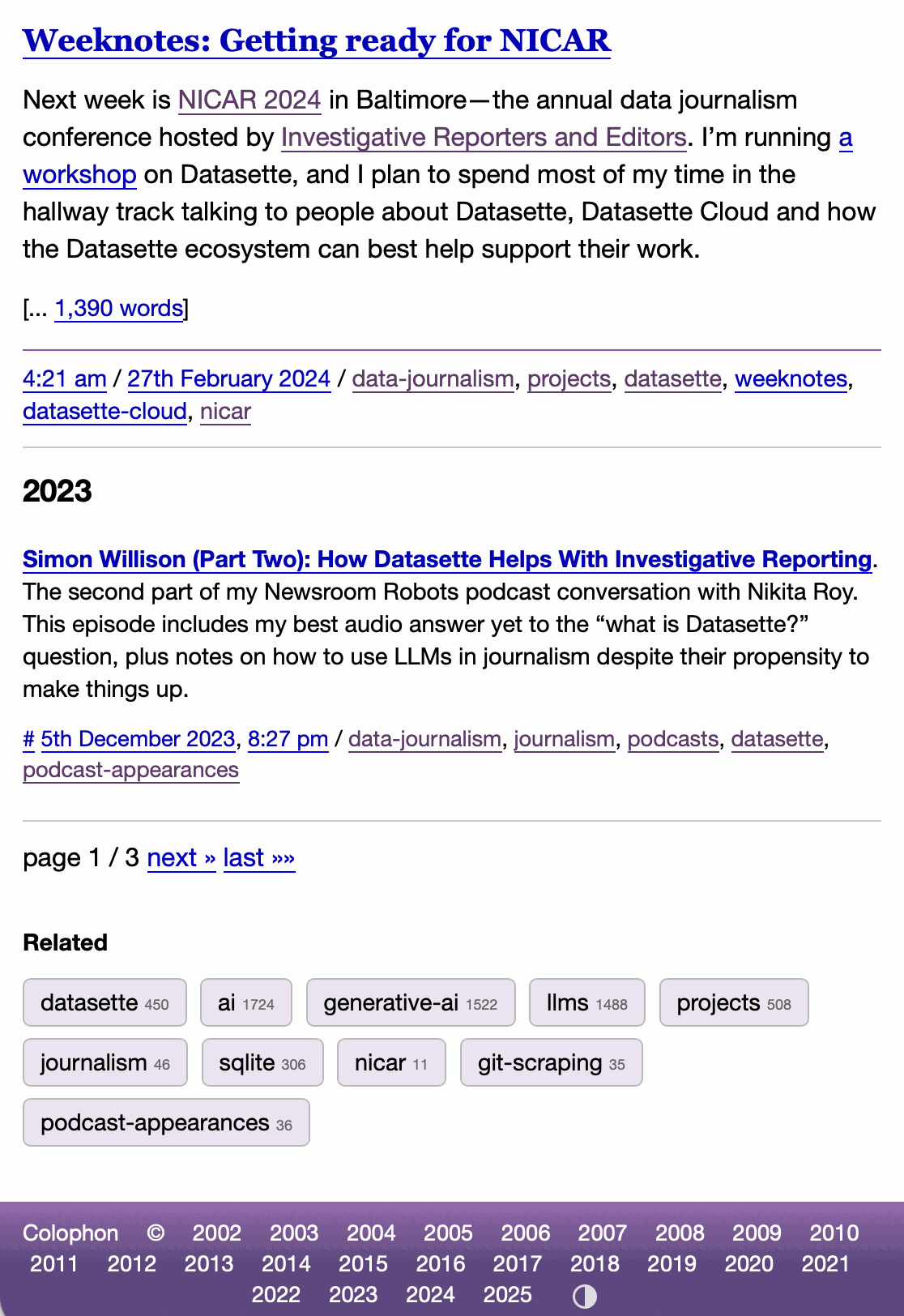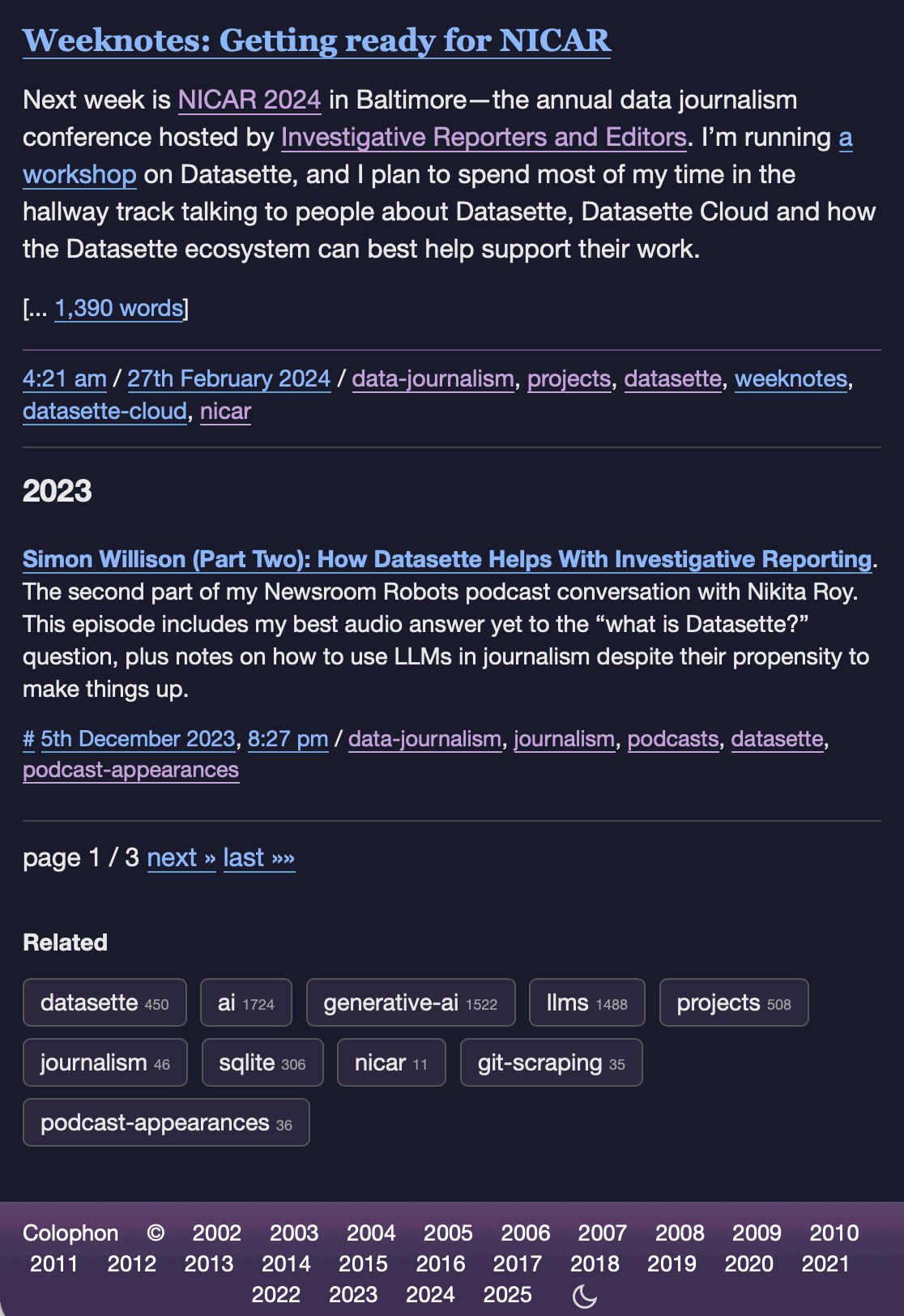
I had Claude Code make me that GIF from two static screenshots - it used this ImageMagick recipe:
magick -delay 300 -loop 0 one.png two.png \
-colors 128 -layers Optimize dark-mode.gif
The CSS ended up with some duplication due to the need to handle both the media preference and the explicit user selection. We fixed that with Cog.
The Normalization of Deviance in AI. This thought-provoking essay from Johann Rehberger directly addresses something that I’ve been worrying about for quite a while: in the absence of any headline-grabbing examples of prompt injection vulnerabilities causing real economic harm, is anyone going to care?
Johann describes the concept of the “Normalization of Deviance” as directly applying to this question.
Coined by Diane Vaughan, the key idea here is that organizations that get away with “deviance” - ignoring safety protocols or otherwise relaxing their standards - will start baking that unsafe attitude into their culture. This can work fine… until it doesn’t. The Space Shuttle Challenger disaster has been partially blamed on this class of organizational failure.
As Johann puts it:
In the world of AI, we observe companies treating probabilistic, non-deterministic, and sometimes adversarial model outputs as if they were reliable, predictable, and safe.
Vendors are normalizing trusting LLM output, but current understanding violates the assumption of reliability.
The model will not consistently follow instructions, stay aligned, or maintain context integrity. This is especially true if there is an attacker in the loop (e.g indirect prompt injection).
However, we see more and more systems allowing untrusted output to take consequential actions. Most of the time it goes well, and over time vendors and organizations lower their guard or skip human oversight entirely, because “it worked last time.”
This dangerous bias is the fuel for normalization: organizations confuse the absence of a successful attack with the presence of robust security.
Useful patterns for building HTML tools
I’ve started using the term HTML tools to refer to HTML applications that I’ve been building which combine HTML, JavaScript, and CSS in a single file and use them to provide useful functionality. I have built over 150 of these in the past two years, almost all of them written by LLMs. This article presents a collection of useful patterns I’ve discovered along the way.
[... 4,231 words]Dec. 11, 2025
GPT-5.2
OpenAI reportedly declared a “code red” on the 1st of December in response to increasingly credible competition from the likes of Google’s Gemini 3. It’s less than two weeks later and they just announced GPT-5.2, calling it “the most capable model series yet for professional knowledge work”.
[... 964 words]Dec. 12, 2025
LLM 0.28. I released a new version of my LLM Python library and CLI tool for interacting with Large Language Models. Highlights from the release notes:
- New OpenAI models:
gpt-5.1,gpt-5.1-chat-latest,gpt-5.2andgpt-5.2-chat-latest. #1300, #1317- When fetching URLs as fragments using
llm -f URL, the request now includes a custom user-agent header:llm/VERSION (https://llm.datasette.io/). #1309- Fixed a bug where fragments were not correctly registered with their source when using
llm chat. Thanks, Giuseppe Rota. #1316- Fixed some file descriptor leak warnings. Thanks, Eric Bloch. #1313
- Type annotations for the OpenAI Chat, AsyncChat and Completion
execute()methods. Thanks, Arjan Mossel. #1315- The project now uses
uvand dependency groups for development. See the updated contributing documentation. #1318
That last bullet point about uv relates to the dependency groups pattern I wrote about in a recent TIL. I'm currently working through applying it to my other projects - the net result is that running the test suite is as simple as doing:
git clone https://github.com/simonw/llm
cd llm
uv run pytest
The new dev dependency group defined in pyproject.toml is automatically installed by uv run in a new virtual environment which means everything needed to run pytest is available without needing to add any extra commands.
OpenAI are quietly adopting skills, now available in ChatGPT and Codex CLI
One of the things that most excited me about Anthropic’s new Skills mechanism back in October is how easy it looked for other platforms to implement. A skill is just a folder with a Markdown file and some optional extra resources and scripts, so any LLM tool with the ability to navigate and read from a filesystem should be capable of using them. It turns out OpenAI are doing exactly that, with skills support quietly showing up in both their Codex CLI tool and now also in ChatGPT itself.
[... 1,360 words]Dec. 13, 2025
How to use a skill (progressive disclosure):
- After deciding to use a skill, open its
SKILL.md. Read only enough to follow the workflow.- If
SKILL.mdpoints to extra folders such asreferences/, load only the specific files needed for the request; don't bulk-load everything.- If
scripts/exist, prefer running or patching them instead of retyping large code blocks.- If
assets/or templates exist, reuse them instead of recreating from scratch.Description as trigger: The YAML
descriptioninSKILL.mdis the primary trigger signal; rely on it to decide applicability. If unsure, ask a brief clarification before proceeding.
— OpenAI Codex CLI, core/src/skills/render.rs, full prompt
If the part of programming you enjoy most is the physical act of writing code, then agents will feel beside the point. You’re already where you want to be, even just with some Copilot or Cursor-style intelligent code auto completion, which makes you faster while still leaving you fully in the driver’s seat about the code that gets written.
But if the part you care about is the decision-making around the code, agents feel like they clear space. They take care of the mechanical expression and leave you with judgment, tradeoffs, and intent. Because truly, for someone at my experience level, that is my core value offering anyway. When I spend time actually typing code these days with my own fingers, it feels like a waste of my time.
— Obie Fernandez, What happens when the coding becomes the least interesting part of the work