35 posts tagged “meta”
2025
Meta’s AI rules have let bots hold ‘sensual’ chats with kids, offer false medical info. This is grim. Reuters got hold of a leaked copy Meta's internal "GenAI: Content Risk Standards" document:
Running to more than 200 pages, the document defines what Meta staff and contractors should treat as acceptable chatbot behaviors when building and training the company’s generative AI products.
Read the full story - there was some really nasty stuff in there.
It's understandable why this document was confidential, but also frustrating because documents like this are genuinely some of the best documentation out there in terms of how these systems can be expected to behave.
I'd love to see more transparency from AI labs around these kinds of decisions.
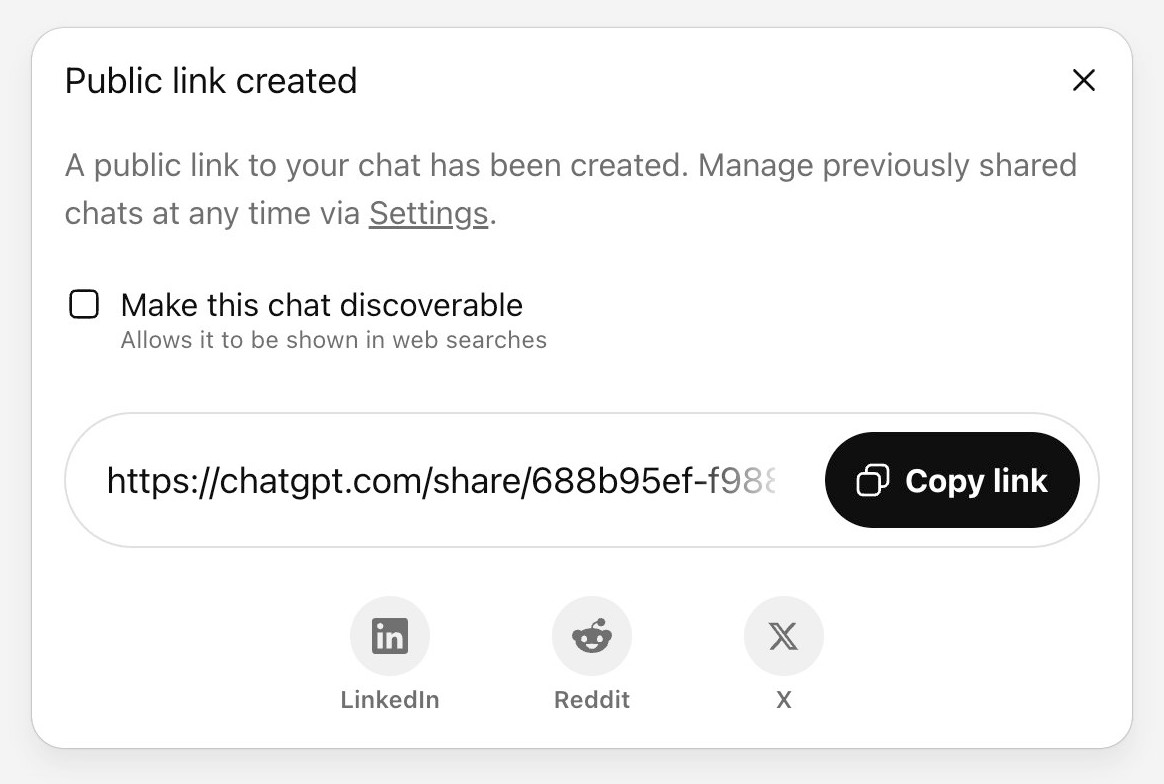
The ChatGPT sharing dialog demonstrates how difficult it is to design privacy preferences
ChatGPT just removed their “make this chat discoverable” sharing feature, after it turned out a material volume of users had inadvertantly made their private chats available via Google search.
[... 999 words]Today I learned - from a very short "we're sponsoring Python" sponsor blurb by Meta during the opening PyCon US welcome talks - that Python is now "the most-used language at Meta" - if you consider all of the different functional areas spread across the company.
They also have "over 3,000 Python developers working in the language every day".

The live captions for the event are once again provided by the excellent White Coat Captioning - real human beings! This got a cheer when it was pointed out by the conference chair a few moments earlier.
You also mentioned the whole Chatbot Arena thing, which I think is interesting and points to the challenge around how you do benchmarking. How do you know what models are good for which things?
One of the things we've generally tried to do over the last year is anchor more of our models in our Meta AI product north star use cases. The issue with open source benchmarks, and any given thing like the LM Arena stuff, is that they’re often skewed toward a very specific set of uses cases, which are often not actually what any normal person does in your product. [...]
So we're trying to anchor our north star on the product value that people report to us, what they say that they want, and what their revealed preferences are, and using the experiences that we have. Sometimes these benchmarks just don't quite line up. I think a lot of them are quite easily gameable.
On the Arena you'll see stuff like Sonnet 3.7, which is a great model, and it's not near the top. It was relatively easy for our team to tune a version of Llama 4 Maverick that could be way at the top. But the version we released, the pure model, actually has no tuning for that at all, so it's further down. So you just need to be careful with some of these benchmarks. We're going to index primarily on the products.
— Mark Zuckerberg, on Dwarkesh Patel's podcast
Now that Llama has very real competition in open weight models (Gemma 3, latest Mistrals, DeepSeek, Qwen) I think their janky license is becoming much more of a liability for them. It's just limiting enough that it could be the deciding factor for using something else.
Maybe Meta’s Llama claims to be open source because of the EU AI act
I encountered a theory a while ago that one of the reasons Meta insist on using the term “open source” for their Llama models despite the Llama license not actually conforming to the terms of the Open Source Definition is that the EU’s AI act includes special rules for open source models without requiring OSI compliance.
[... 852 words]We've seen questions from the community about the latest release of Llama-4 on Arena. To ensure full transparency, we're releasing 2,000+ head-to-head battle results for public review. [...]
In addition, we're also adding the HF version of Llama-4-Maverick to Arena, with leaderboard results published shortly. Meta’s interpretation of our policy did not match what we expect from model providers. Meta should have made it clearer that “Llama-4-Maverick-03-26-Experimental” was a customized model to optimize for human preference. As a result of that we are updating our leaderboard policies to reinforce our commitment to fair, reproducible evaluations so this confusion doesn’t occur in the future.
Initial impressions of Llama 4
Dropping a model release as significant as Llama 4 on a weekend is plain unfair! So far the best place to learn about the new model family is this post on the Meta AI blog. They’ve released two new models today: Llama 4 Maverick is a 400B model (128 experts, 17B active parameters), text and image input with a 1 million token context length. Llama 4 Scout is 109B total parameters (16 experts, 17B active), also multi-modal and with a claimed 10 million token context length—an industry first.
[... 1,468 words]The Llama series have been re-designed to use state of the art mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture and natively trained with multimodality. We’re dropping Llama 4 Scout & Llama 4 Maverick, and previewing Llama 4 Behemoth.
📌 Llama 4 Scout is highest performing small model with 17B activated parameters with 16 experts. It’s crazy fast, natively multimodal, and very smart. It achieves an industry leading 10M+ token context window and can also run on a single GPU!
📌 Llama 4 Maverick is the best multimodal model in its class, beating GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash across a broad range of widely reported benchmarks, while achieving comparable results to the new DeepSeek v3 on reasoning and coding – at less than half the active parameters. It offers a best-in-class performance to cost ratio with an experimental chat version scoring ELO of 1417 on LMArena. It can also run on a single host!
📌 Previewing Llama 4 Behemoth, our most powerful model yet and among the world’s smartest LLMs. Llama 4 Behemoth outperforms GPT4.5, Claude Sonnet 3.7, and Gemini 2.0 Pro on several STEM benchmarks. Llama 4 Behemoth is still training, and we’re excited to share more details about it even while it’s still in flight.
— Ahmed Al-Dahle, VP and Head of GenAI at Meta
Llama 4 is making great progress in training. Llama 4 mini is done with pre-training and our reasoning models and larger model are looking good too. Our goal with Llama 3 was to make open source competitive with closed models, and our goal for Llama 4 is to lead. Llama 4 will be natively multimodal -- it's an omni-model -- and it will have agentic capabilities, so it's going to be novel and it's going to unlock a lot of new use cases.
— Mark Zuckerberg, on Meta's quarterly earnings report
the Meta controlled, AI-generated Instagram and Facebook profiles going viral right now have been on the platform for well over a year and all of them stopped posting 10 months ago after users almost universally ignored them. [...]
What is obvious from scrolling through these dead profiles is that Meta’s AI characters are not popular, people do not like them, and that they did not post anything interesting. They are capable only of posting utterly bland and at times offensive content, and people have wholly rejected them, which is evidenced by the fact that none of them are posting anymore.
2024
Things we learned about LLMs in 2024
A lot has happened in the world of Large Language Models over the course of 2024. Here’s a review of things we figured out about the field in the past twelve months, plus my attempt at identifying key themes and pivotal moments.
[... 7,490 words]How we think about Threads’ iOS performance (via) This article by Dave LaMacchia and Jason Patterson provides an incredibly deep insight into what effective performance engineering looks like for an app with 100s of millions of users.
I always like hearing about custom performance metrics with their own acronyms. Here we are introduced to %FIRE - the portion of people who experience a frustrating image-render experience (based on how long an image takes to load after the user scrolls it into the viewport), TTNC (time-to-network content) measuring time from app launch to fresh content visible in the feed and cPSR (creation-publish success rate) for how often a user manages to post content that they started to create.
This article introduced me to the concept of a boundary test, described like this:
A boundary test is one where we measure extreme ends of a boundary to learn what the effect is. In our case, we introduced a slight bit of latency when a small percentage of our users would navigate to a user profile, to the conversion view for a post, or to their activity feed.
This latency would allow us to extrapolate what the effect would be if we similarly improved how we delivered content to those views.
[...]
We learned that iOS users don’t tolerate a lot of latency. The more we added, the less often they would launch the app and the less time they would stay in it. With the smallest latency injection, the impact was small or negligible for some views, but the largest injections had negative effects across the board. People would read fewer posts, post less often themselves, and in general interact less with the app. Remember, we weren’t injecting latency into the core feed, either; just into the profile, permalink, and activity.
There's a whole lot more in there, including details of their custom internal performance logger (SLATE, the “Systemic LATEncy” logger) and several case studies of surprising performance improvements made with the assistance of their metrics and tools, plus some closing notes on how Swift concurrency is being adopted throughout Meta.
DeepSeek_V3.pdf (via) The DeepSeek v3 paper (and model card) are out, after yesterday's mysterious release of the undocumented model weights.
Plenty of interesting details in here. The model pre-trained on 14.8 trillion "high-quality and diverse tokens" (not otherwise documented).
Following this, we conduct post-training, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) on the base model of DeepSeek-V3, to align it with human preferences and further unlock its potential. During the post-training stage, we distill the reasoning capability from the DeepSeek-R1 series of models, and meanwhile carefully maintain the balance between model accuracy and generation length.
By far the most interesting detail though is how much the training cost. DeepSeek v3 trained on 2,788,000 H800 GPU hours at an estimated cost of $5,576,000. For comparison, Meta AI's Llama 3.1 405B (smaller than DeepSeek v3's 685B parameters) trained on 11x that - 30,840,000 GPU hours, also on 15 trillion tokens.
DeepSeek v3 benchmarks comparably to Claude 3.5 Sonnet, indicating that it's now possible to train a frontier-class model (at least for the 2024 version of the frontier) for less than $6 million!
For reference, this level of capability is supposed to require clusters of closer to 16K GPUs, the ones being brought up today are more around 100K GPUs. E.g. Llama 3 405B used 30.8M GPU-hours, while DeepSeek-V3 looks to be a stronger model at only 2.8M GPU-hours (~11X less compute). If the model also passes vibe checks (e.g. LLM arena rankings are ongoing, my few quick tests went well so far) it will be a highly impressive display of research and engineering under resource constraints.
DeepSeek also announced their API pricing. From February 8th onwards:
Input: $0.27/million tokens ($0.07/million tokens with cache hits)
Output: $1.10/million tokens
Claude 3.5 Sonnet is currently $3/million for input and $15/million for output, so if the models are indeed of equivalent quality this is a dramatic new twist in the ongoing LLM pricing wars.
I can now run a GPT-4 class model on my laptop
Meta’s new Llama 3.3 70B is a genuinely GPT-4 class Large Language Model that runs on my laptop.
[... 2,905 words]Meta AI release Llama 3.3. This new Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct model from Meta AI makes some bold claims:
This model delivers similar performance to Llama 3.1 405B with cost effective inference that’s feasible to run locally on common developer workstations.
I have 64GB of RAM in my M2 MacBook Pro, so I'm looking forward to trying a slightly quantized GGUF of this model to see if I can run it while still leaving some memory free for other applications.
Update: Ollama have a 43GB GGUF available now. And here's an MLX 8bit version and other MLX quantizations.
Llama 3.3 has 70B parameters, a 128,000 token context length and was trained to support English, German, French, Italian, Portuguese, Hindi, Spanish, and Thai.
The model card says that the training data was "A new mix of publicly available online data" - 15 trillion tokens with a December 2023 cut-off.
They used "39.3M GPU hours of computation on H100-80GB (TDP of 700W) type hardware" which they calculate as 11,390 tons CO2eq. I believe that's equivalent to around 20 fully loaded passenger flights from New York to London (at ~550 tons per flight).
Update 19th January 2025: On further consideration I no longer trust my estimate here: it's surprisingly hard to track down reliable numbers but I think the total CO2 used by those flights may be more in the order of 200-400 tons, so my estimate for Llama 3.3 70B should have been more in the order of between 28 and 56 flights. Don't trust those numbers either though!
Ollama: Llama 3.2 Vision. Ollama released version 0.4 last week with support for Meta's first Llama vision model, Llama 3.2.
If you have Ollama installed you can fetch the 11B model (7.9 GB) like this:
ollama pull llama3.2-vision
Or the larger 90B model (55GB download, likely needs ~88GB of RAM) like this:
ollama pull llama3.2-vision:90b
I was delighted to learn that Sukhbinder Singh had already contributed support for LLM attachments to Sergey Alexandrov's llm-ollama plugin, which means the following works once you've pulled the models:
llm install --upgrade llm-ollama
llm -m llama3.2-vision:latest 'describe' \
-a https://static.simonwillison.net/static/2024/pelican.jpg
This image features a brown pelican standing on rocks, facing the camera and positioned to the left of center. The bird's long beak is a light brown color with a darker tip, while its white neck is adorned with gray feathers that continue down to its body. Its legs are also gray.
In the background, out-of-focus boats and water are visible, providing context for the pelican's environment.

That's not a bad description of this image, especially for a 7.9GB model that runs happily on my MacBook Pro.
Nous Hermes 3. The Nous Hermes family of fine-tuned models have a solid reputation. Their most recent release came out in August, based on Meta's Llama 3.1:
Our training data aggressively encourages the model to follow the system and instruction prompts exactly and in an adaptive manner. Hermes 3 was created by fine-tuning Llama 3.1 8B, 70B and 405B, and training on a dataset of primarily synthetically generated responses. The model boasts comparable and superior performance to Llama 3.1 while unlocking deeper capabilities in reasoning and creativity.
The model weights are on Hugging Face, including GGUF versions of the 70B and 8B models. Here's how to try the 8B model (a 4.58GB download) using the llm-gguf plugin:
llm install llm-gguf
llm gguf download-model 'https://huggingface.co/NousResearch/Hermes-3-Llama-3.1-8B-GGUF/resolve/main/Hermes-3-Llama-3.1-8B.Q4_K_M.gguf' -a Hermes-3-Llama-3.1-8B
llm -m Hermes-3-Llama-3.1-8B 'hello in spanish'
Nous Research partnered with Lambda Labs to provide inference APIs. It turns out Lambda host quite a few models now, currently providing free inference to users with an API key.
I just released the first alpha of a llm-lambda-labs plugin. You can use that to try the larger 405b model (very hard to run on a consumer device) like this:
llm install llm-lambda-labs
llm keys set lambdalabs
# Paste key here
llm -m lambdalabs/hermes3-405b 'short poem about a pelican with a twist'
Here's the source code for the new plugin, which I based on llm-mistral. The plugin uses httpx-sse to consume the stream of tokens from the API.
Running Llama 3.2 Vision and Phi-3.5 Vision on a Mac with mistral.rs
mistral.rs is an LLM inference library written in Rust by Eric Buehler. Today I figured out how to use it to run the Llama 3.2 Vision and Phi-3.5 Vision models on my Mac.
[... 1,231 words]I think individual creators or publishers tend to overestimate the value of their specific content in the grand scheme of [AI training]. […]
We pay for content when it’s valuable to people. We’re just not going to pay for content when it’s not valuable to people. I think that you’ll probably see a similar dynamic with AI, which my guess is that there are going to be certain partnerships that get made when content is really important and valuable. I’d guess that there are probably a lot of people who have a concern about the feel of it, like you’re saying. But then, when push comes to shove, if they demanded that we don’t use their content, then we just wouldn’t use their content. It’s not like that’s going to change the outcome of this stuff that much.
Llama 3.2. In further evidence that AI labs are terrible at naming things, Llama 3.2 is a huge upgrade to the Llama 3 series - they've released their first multi-modal vision models!
Today, we’re releasing Llama 3.2, which includes small and medium-sized vision LLMs (11B and 90B), and lightweight, text-only models (1B and 3B) that fit onto edge and mobile devices, including pre-trained and instruction-tuned versions.
The 1B and 3B text-only models are exciting too, with a 128,000 token context length and optimized for edge devices (Qualcomm and MediaTek hardware get called out specifically).
Meta partnered directly with Ollama to help with distribution, here's the Ollama blog post. They only support the two smaller text-only models at the moment - this command will get the 3B model (2GB):
ollama run llama3.2
And for the 1B model (a 1.3GB download):
ollama run llama3.2:1b
I had to first upgrade my Ollama by clicking on the icon in my macOS task tray and selecting "Restart to update".
The two vision models are coming to Ollama "very soon".
Once you have fetched the Ollama model you can access it from my LLM command-line tool like this:
pipx install llm
llm install llm-ollama
llm chat -m llama3.2:1b
I tried running my djp codebase through that tiny 1B model just now and got a surprisingly good result - by no means comprehensive, but way better than I would ever expect from a model of that size:
files-to-prompt **/*.py -c | llm -m llama3.2:1b --system 'describe this code'
Here's a portion of the output:
The first section defines several test functions using the
@djp.hookimpldecorator from the djp library. These hook implementations allow you to intercept and manipulate Django's behavior.
test_middleware_order: This function checks that the middleware order is correct by comparing theMIDDLEWAREsetting with a predefined list.test_middleware: This function tests various aspects of middleware:- It retrieves the response from the URL
/from-plugin/using theClientobject, which simulates a request to this view.- It checks that certain values are present in the response:
X-DJP-Middleware-AfterX-DJP-MiddlewareX-DJP-Middleware-Before[...]
I found the GGUF file that had been downloaded by Ollama in my ~/.ollama/models/blobs directory. The following command let me run that model directly in LLM using the llm-gguf plugin:
llm install llm-gguf
llm gguf register-model ~/.ollama/models/blobs/sha256-74701a8c35f6c8d9a4b91f3f3497643001d63e0c7a84e085bed452548fa88d45 -a llama321b
llm chat -m llama321b
Meta themselves claim impressive performance against other existing models:
Our evaluation suggests that the Llama 3.2 vision models are competitive with leading foundation models, Claude 3 Haiku and GPT4o-mini on image recognition and a range of visual understanding tasks. The 3B model outperforms the Gemma 2 2.6B and Phi 3.5-mini models on tasks such as following instructions, summarization, prompt rewriting, and tool-use, while the 1B is competitive with Gemma.
Here's the Llama 3.2 collection on Hugging Face. You need to accept the new Llama 3.2 Community License Agreement there in order to download those models.
You can try the four new models out via the Chatbot Arena - navigate to "Direct Chat" there and select them from the dropdown menu. You can upload images directly to the chat there to try out the vision features.
Where Facebook’s AI Slop Comes From. Jason Koebler continues to provide the most insightful coverage of Facebook's weird ongoing problem with AI slop (previously).
Who's creating this stuff? It looks to primarily come from individuals in countries like India and the Philippines, inspired by get-rich-quick YouTube influencers, who are gaming Facebook's Creator Bonus Program and flooding the platform with AI-generated images.
Jason highlights this YouTube video by YT Gyan Abhishek (136,000 subscribers) and describes it like this:
He pauses on another image of a man being eaten by bugs. “They are getting so many likes,” he says. “They got 700 likes within 2-4 hours. They must have earned $100 from just this one photo. Facebook now pays you $100 for 1,000 likes … you must be wondering where you can get these images from. Don’t worry. I’ll show you how to create images with the help of AI.”
That video is in Hindi but you can request auto-translated English subtitles in the YouTube video settings. The image generator demonstrated in the video is Ideogram, which offers a free plan. (Here's pelicans having a tea party on a yacht.)
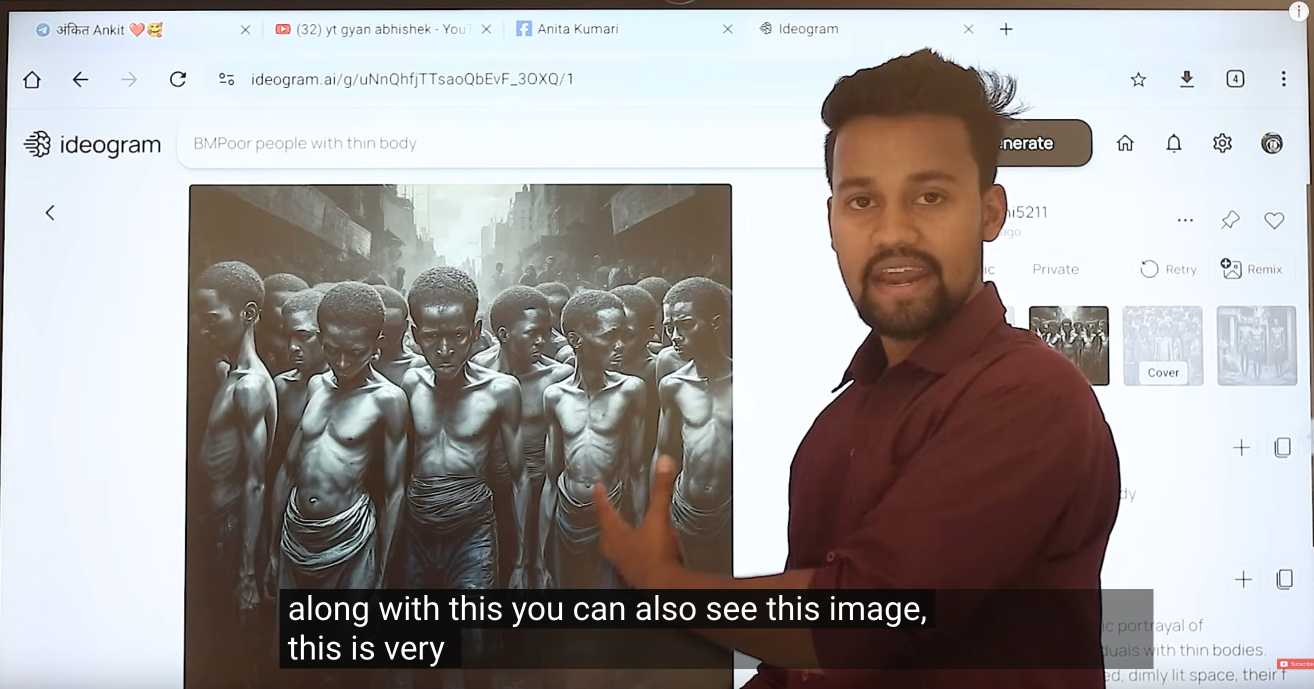
Jason's reporting here runs deep - he goes as far as buying FewFeed, dedicated software for scraping and automating Facebook, and running his own (unsuccessful) page using prompts from YouTube tutorials like:
an elderly woman celebrating her 104th birthday with birthday cake realistic family realistic jesus celebrating with her
I signed up for a $10/month 404 Media subscription to read this and it was absolutely worth the money.
Extracting Prompts by Inverting LLM Outputs (via) New paper from Meta research:
We consider the problem of language model inversion: given outputs of a language model, we seek to extract the prompt that generated these outputs. We develop a new black-box method, output2prompt, that learns to extract prompts without access to the model's logits and without adversarial or jailbreaking queries. In contrast to previous work, output2prompt only needs outputs of normal user queries.
This is a way of extracting the hidden prompt from an application build on an LLM without using prompt injection techniques.
The trick is to train a dedicated model for guessing hidden prompts based on public question/answer pairs.
They conclude:
Our results demonstrate that many user and system prompts are intrinsically vulnerable to extraction.
This reinforces my opinion that it's not worth trying to protect your system prompts. Think of them the same as your client-side HTML and JavaScript: you might be able to obfuscate them but you should expect that people can view them if they try hard enough.
SAM 2: The next generation of Meta Segment Anything Model for videos and images (via) Segment Anything is Meta AI's model for image segmentation: for any image or frame of video it can identify which shapes on the image represent different "objects" - things like vehicles, people, animals, tools and more.
SAM 2 "outperforms SAM on its 23 dataset zero-shot benchmark suite, while being six times faster". Notably, SAM 2 works with video where the original SAM only worked with still images. It's released under the Apache 2 license.
The best way to understand SAM 2 is to try it out. Meta have a web demo which worked for me in Chrome but not in Firefox. I uploaded a recent video of my brand new cactus tweezers (for removing detritus from my cacti without getting spiked) and selected the succulent and the tweezers as two different objects:
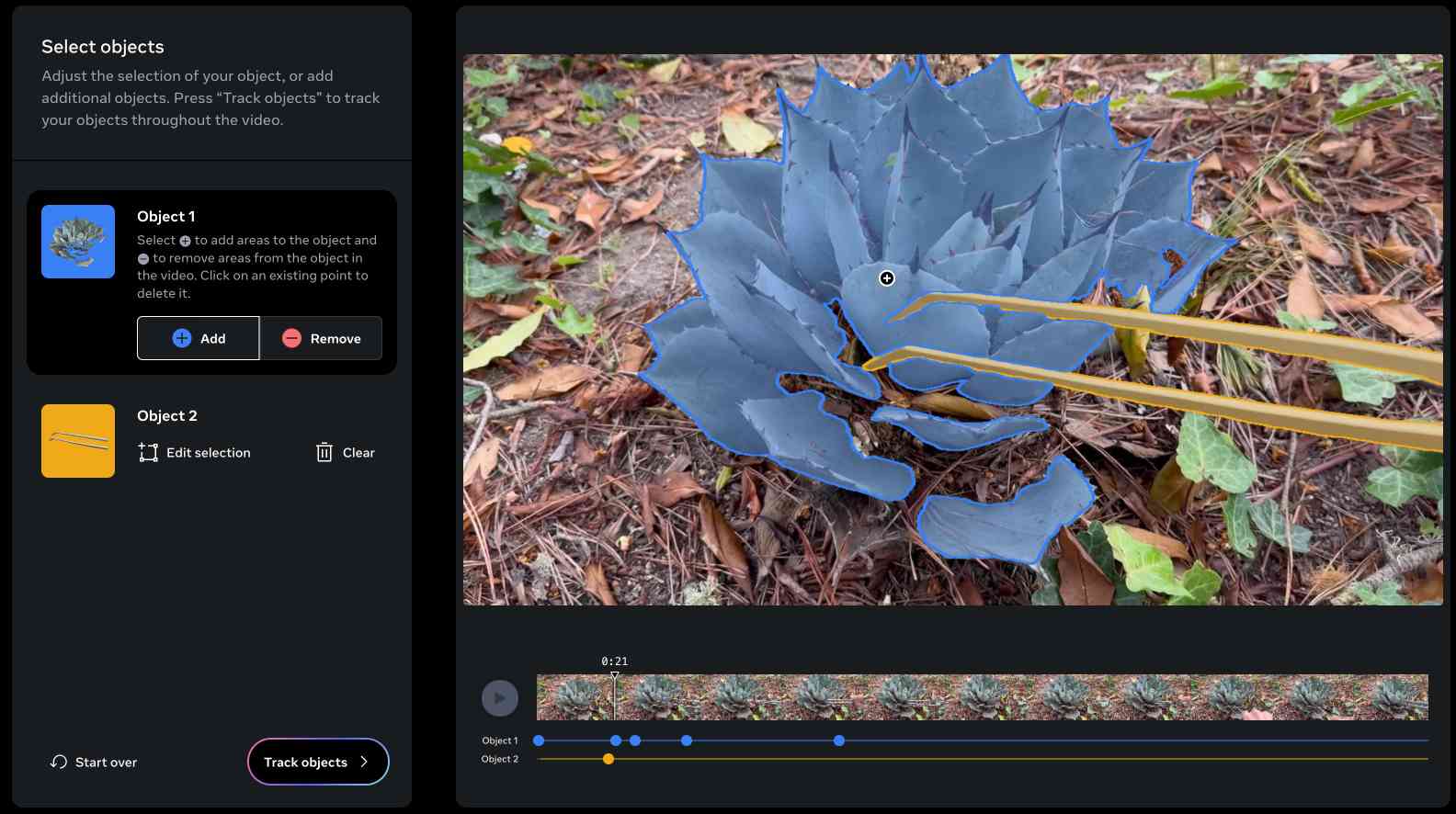
Then I applied a "desaturate" filter to the background and exported this resulting video, with the background converted to black and white while the succulent and tweezers remained in full colour:
Also released today: the full SAM 2 paper, the SA-V dataset of "51K diverse videos and 643K spatio-temporal segmentation masks" and a Dataset explorer tool (again, not supported by Firefox) for poking around in that collection.
One interesting observation is the impact of environmental factors on training performance at scale. For Llama 3 405B , we noted a diurnal 1-2% throughput variation based on time-of-day. This fluctuation is the result of higher mid-day temperatures impacting GPU dynamic voltage and frequency scaling.
During training, tens of thousands of GPUs may increase or decrease power consumption at the same time, for example, due to all GPUs waiting for checkpointing or collective communications to finish, or the startup or shutdown of the entire training job. When this happens, it can result in instant fluctuations of power consumption across the data center on the order of tens of megawatts, stretching the limits of the power grid. This is an ongoing challenge for us as we scale training for future, even larger Llama models.
llm-gguf. I just released a new alpha plugin for LLM which adds support for running models from Meta's new Llama 3.1 family that have been packaged as GGUF files - it should work for other GGUF chat models too.
If you've already installed LLM the following set of commands should get you setup with Llama 3.1 8B:
llm install llm-gguf
llm gguf download-model \
https://huggingface.co/lmstudio-community/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF/resolve/main/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf \
--alias llama-3.1-8b-instruct --alias l31i
This will download a 4.92GB GGUF from lmstudio-community/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF on Hugging Face and save it (at least on macOS) to your ~/Library/Application Support/io.datasette.llm/gguf/models folder.
Once installed like that, you can run prompts through the model like so:
llm -m l31i "five great names for a pet lemur"
Or use the llm chat command to keep the model resident in memory and run an interactive chat session with it:
llm chat -m l31i
I decided to ship a new alpha plugin rather than update my existing llm-llama-cpp plugin because that older plugin has some design decisions baked in from the Llama 2 release which no longer make sense, and having a fresh plugin gave me a fresh slate to adopt the latest features from the excellent underlying llama-cpp-python library by Andrei Betlen.
I believe the Llama 3.1 release will be an inflection point in the industry where most developers begin to primarily use open source, and I expect that approach to only grow from here.
Introducing Llama 3.1: Our most capable models to date. We've been waiting for the largest release of the Llama 3 model for a few months, and now we're getting a whole new model family instead.
Meta are calling Llama 3.1 405B "the first frontier-level open source AI model" and it really is benchmarking in that GPT-4+ class, competitive with both GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
I'm equally excited by the new 8B and 70B 3.1 models - both of which now support a 128,000 token context and benchmark significantly higher than their Llama 3 equivalents. Same-sized models getting more powerful and capable a very reassuring trend. I expect the 8B model (or variants of it) to run comfortably on an array of consumer hardware, and I've run a 70B model on a 64GB M2 in the past.
The 405B model can at least be run on a single server-class node:
To support large-scale production inference for a model at the scale of the 405B, we quantized our models from 16-bit (BF16) to 8-bit (FP8) numerics, effectively lowering the compute requirements needed and allowing the model to run within a single server node.
Meta also made a significant change to the license:
We’ve also updated our license to allow developers to use the outputs from Llama models — including 405B — to improve other models for the first time.
We’re excited about how this will enable new advancements in the field through synthetic data generation and model distillation workflows, capabilities that have never been achieved at this scale in open source.
I'm really pleased to see this. Using models to help improve other models has been a crucial technique in LLM research for over a year now, especially for fine-tuned community models release on Hugging Face. Researchers have mostly been ignoring this restriction, so it's reassuring to see the uncertainty around that finally cleared up.
Lots more details about the new models in the paper The Llama 3 Herd of Models including this somewhat opaque note about the 15 trillion token training data:
Our final data mix contains roughly 50% of tokens corresponding to general knowledge, 25% of mathematical and reasoning tokens, 17% code tokens, and 8% multilingual tokens.
Update: I got the Llama 3.1 8B Instruct model working with my LLM tool via a new plugin, llm-gguf.
I have a child who is also 2e and has been part of the NYC G&T program. We've had a positive experience with the citywide program, specifically with the program at The Anderson School.
— Meta AI bot, answering a question on a forum
2023
Meta/Threads Interoperating in the Fediverse Data Dialogue Meeting yesterday. Johannes Ernst reports from a recent meeting hosted by Meta aimed at bringing together staff from Meta’s Threads social media platform with representatives from the Fediverse.
Meta have previously announced an intention for Threads to join the Fediverse. It sounds like they’re being extremely thoughtful about how to go about this.
Two points that stood out for me:
“Rolling out a large node – like Threads will be – in a complex, distributed system that’s as decentralized and heterogeneous as the Fediverse is not something anybody really has done before.”
And:
“When we think of privacy risks when Meta connects to the Fediverse, we usually think of what happens to data that moves from today’s Fediverse into Meta. I didn’t realize the opposite is also quite a challenge (personal data posted to Threads, making its way into the Fediverse) for an organization as heavily monitored by regulators around the world as is Meta.”