Blogmarks tagged ai, ethics in 2024
Filters: Type: blogmark × Year: 2024 × ai × ethics × Sorted by date
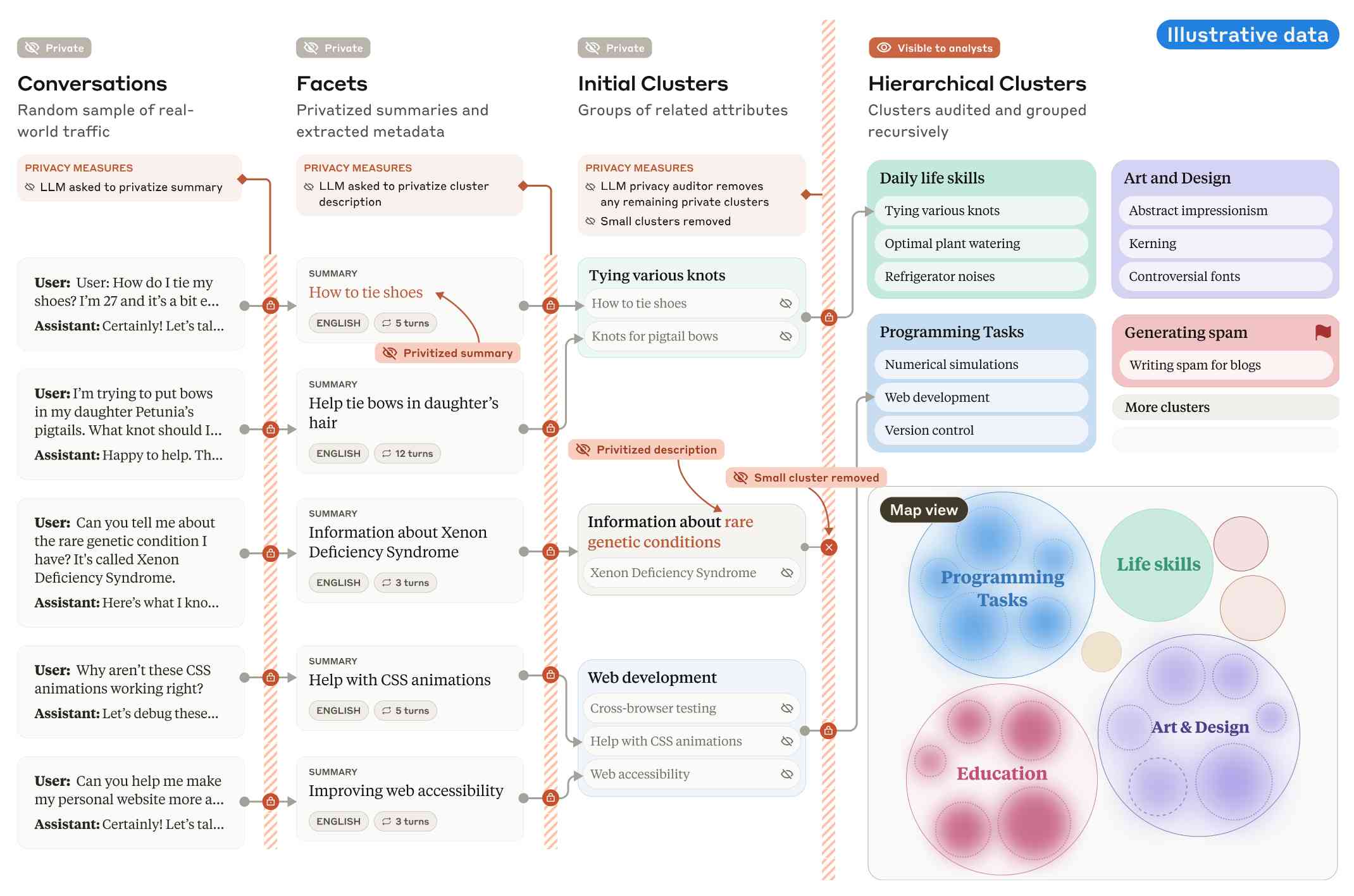
Google search hallucinates Encanto 2. Jason Schreier on Bluesky:
I was excited to tell my kids that there's a sequel to Encanto, only to scroll down and learn that Google's AI just completely made this up
I just replicated the same result by searching Google for encanto 2. Here's what the "AI overview" at the top of the page looked like:
Only when I clicked the "Show more" link did it become clear what had happened:

The link in that first snippet was to the Encanto 2: A New Generation page on Idea Wiki:
This is a fanon wiki, and just like fan-fiction wikis, this one has a variety of fan created ideas on here! These include potential sequels and new series that have yet to exist.
Other cited links included this article about Instagram fan art and Encanto's Sequel Chances Addressed by Disney Director, a very thin article built around a short quote from Encanto's director at D23 Brazil.
And that August 2024 release date (which the AI summary weirdly lists as "scheduled for release" despite that date being five months in the past)? It's from the Idea Wiki imaginary info box for the film.
This is a particularly clear example of how badly wrong AI summarization can go. LLMs are gullible: they believe what you tell them, and the web is full of misleading information - some of which is completely innocent.
Update: I've had some pushback over my use of the term "hallucination" here, on the basis that the LLM itself is doing what it's meant to: summarizing the RAG content that has been provided to it by the host system.
That's fair: this is not a classic LLM hallucination, where the LLM produces incorrect data purely from knowledge partially encoded in its weights.
I classify this as a bug in Google's larger LLM-powered AI overview system. That system should be able to take the existence of invalid data sources into account - given how common searches for non-existent movie sequels (or TV seasons) are, I would hope that AI overviews could classify such searches and take extra steps to avoid serving misleading answers.
So think this is a "hallucination" bug in the AI overview system itself: it's making statements about the world that are not true.
A polite disagreement bot ring is flooding Bluesky — reply guy as a (dis)service. Fascinating new pattern of AI slop engagement farming: people are running bots on Bluesky that automatically reply to "respectfully disagree" with posts, in an attempt to goad the original author into replying to continue an argument.
It's not entirely clear what the intended benefit is here: unlike Twitter there's no way to monetize (yet) a Bluesky account through growing a following there - and replies like this don't look likely to earn followers.
rahaeli has a theory:
Watching the recent adaptations in behavior and probable prompts has convinced me by now that it's not a specific bad actor testing its own approach, btw, but a bad actor tool maker iterating its software that it plans to rent out to other people for whatever malicious reason they want to use it!
One of the bots leaked part of its prompt (nothing public I can link to here, and that account has since been deleted):
Your response should be a clear and respectful disagreement, but it must be brief and under 300 characters. Here's a possible response: "I'm concerned that your willingness to say you need time to think about a complex issue like the pardon suggests a lack of preparedness and critical thinking."
BBC complains to Apple over misleading shooting headline. This is bad: the Apple Intelligence feature that uses (on device) LLMs to present a condensed, summarized set of notifications misrepresented a BBC headline as "Luigi Mangione shoots himself".
Ken Schwencke caught that same feature incorrectly condensing a New York Times headline about an ICC arrest warrant for Netanyahu as "Netanyahu arrested".
My understanding is that these notification summaries are generated directly on-device, using Apple's own custom 3B parameter model.
The main lesson I think this illustrates is that it's not responsible to outsource headline summarization to an LLM without incorporating human review: there are way too many ways this could result in direct misinformation.
Update 16th January 2025: Apple plans to disable A.I. features summarizing news notifications, by Tripp Mickle for the New York Times.
Clio: A system for privacy-preserving insights into real-world AI use. New research from Anthropic, describing a system they built called Clio - for Claude insights and observations - which attempts to provide insights into how Claude is being used by end-users while also preserving user privacy.
There's a lot to digest here. The summary is accompanied by a full paper and a 47 minute YouTube interview with team members Deep Ganguli, Esin Durmus, Miles McCain and Alex Tamkin.
The key idea behind Clio is to take user conversations and use Claude to summarize, cluster and then analyze those clusters - aiming to ensure that any private or personally identifiable details are filtered out long before the resulting clusters reach human eyes.
This diagram from the paper helps explain how that works:
Claude generates a conversation summary, than extracts "facets" from that summary that aim to privatize the data to simple characteristics like language and topics.
The facets are used to create initial clusters (via embeddings), and those clusters further filtered to remove any that are too small or may contain private information. The goal is to have no cluster which represents less than 1,000 underlying individual users.
In the video at 16:39:
And then we can use that to understand, for example, if Claude is as useful giving web development advice for people in English or in Spanish. Or we can understand what programming languages are people generally asking for help with. We can do all of this in a really privacy preserving way because we are so far removed from the underlying conversations that we're very confident that we can use this in a way that respects the sort of spirit of privacy that our users expect from us.
Then later at 29:50 there's this interesting hint as to how Anthropic hire human annotators to improve Claude's performance in specific areas:
But one of the things we can do is we can look at clusters with high, for example, refusal rates, or trust and safety flag rates. And then we can look at those and say huh, this is clearly an over-refusal, this is clearly fine. And we can use that to sort of close the loop and say, okay, well here are examples where we wanna add to our, you know, human training data so that Claude is less refusally in the future on those topics.
And importantly, we're not using the actual conversations to make Claude less refusally. Instead what we're doing is we are looking at the topics and then hiring people to generate data in those domains and generating synthetic data in those domains.
So we're able to sort of use our users activity with Claude to improve their experience while also respecting their privacy.
According to Clio the top clusters of usage for Claude right now are as follows:
- Web & Mobile App Development (10.4%)
- Content Creation & Communication (9.2%)
- Academic Research & Writing (7.2%)
- Education & Career Development (7.1%)
- Advanced AI/ML Applications (6.0%)
- Business Strategy & Operations (5.7%)
- Language Translation (4.5%)
- DevOps & Cloud Infrastructure (3.9%)
- Digital Marketing & SEO (3.7%)
- Data Analysis & Visualization (3.5%)
There also are some interesting insights about variations in usage across different languages. For example, Chinese language users had "Write crime, thriller, and mystery fiction with complex plots and characters" at 4.4x the base rate for other languages.
Who and What comprise AI Skepticism? (via) Benjamin Riley's response to Casey Newton's piece on The phony comforts of AI skepticism. Casey tried to categorize the field as "AI is fake and sucks" v.s. "AI is real and dangerous". Benjamin argues that this as a misleading over-simplification, instead proposing at least nine different groups.
I get listed as an example of the "Technical AI Skeptics" group, which sounds right to me based on this description:
What this group generally believes: The technical capabilities of AI are worth trying to understand, including their limitations. Also, it’s fun to find their deficiencies and highlight their weird output.
One layer of nuance deeper: Some of those I identify below might resist being called AI Skeptics because they are focused mainly on helping people understand how these tools work. But in my view, their efforts are helpful in fostering AI skepticism precisely because they help to demystify what’s happening “under the hood” without invoking broader political concerns (generally).
New Pleias 1.0 LLMs trained exclusively on openly licensed data (via) I wrote about the Common Corpus public domain dataset back in March. Now Pleias, the team behind Common Corpus, have released the first family of models that are:
[...] trained exclusively on open data, meaning data that are either non-copyrighted or are published under a permissible license.
There's a lot to absorb here. The Pleias 1.0 family comes in three base model sizes: 350M, 1.2B and 3B. They've also released two models specialized for multi-lingual RAG: Pleias-Pico (350M) and Pleias-Nano (1.2B).
Here's an official GGUF for Pleias-Pico.
I'm looking forward to seeing benchmarks from other sources, but Pleias ran their own custom multilingual RAG benchmark which had their Pleias-nano-1.2B-RAG model come in between Llama-3.2-Instruct-3B and Llama-3.2-Instruct-8B.
The 350M and 3B models were trained on the French government's Jean Zay supercomputer. Pleias are proud of their CO2 footprint for training the models - 0.5, 4 and 16 tCO2eq for the three models respectively, which they compare to Llama 3.2,s reported figure of 133 tCO2eq.
How clean is the training data from a licensing perspective? I'm confident people will find issues there - truly 100% public domain data remains a rare commodity. So far I've seen questions raised about the GitHub source code data (most open source licenses have attribution requirements) and Wikipedia (CC BY-SA, another attribution license). Plus this from the announcement:
To supplement our corpus, we have generated 30B+ words synthetically with models allowing for outputs reuse.
If those models were themselves trained on unlicensed data this could be seen as a form of copyright laundering.
Certain names make ChatGPT grind to a halt, and we know why (via) Benj Edwards on the really weird behavior where ChatGPT stops output with an error rather than producing the names David Mayer, Brian Hood, Jonathan Turley, Jonathan Zittrain, David Faber or Guido Scorza.
The OpenAI API is entirely unaffected - this problem affects the consumer ChatGPT apps only.
It turns out many of those names are examples of individuals who have complained about being defamed by ChatGPT in the last. Brian Hood is the Australian mayor who was a victim of lurid ChatGPT hallucinations back in March 2023, and settled with OpenAI out of court.
Voting opens for Oxford Word of the Year 2024 (via) One of the options is slop!
slop (n.): Art, writing, or other content generated using artificial intelligence, shared and distributed online in an indiscriminate or intrusive way, and characterized as being of low quality, inauthentic, or inaccurate.
Update 1st December: Slop lost to Brain rot
Releasing the largest multilingual open pretraining dataset (via) Common Corpus is a new "open and permissible licensed text dataset, comprising over 2 trillion tokens (2,003,039,184,047 tokens)" released by French AI Lab PleIAs.
This appears to be the largest available corpus of openly licensed training data:
- 926,541,096,243 tokens of public domain books, newspapers, and Wikisource content
- 387,965,738,992 tokens of government financial and legal documents
- 334,658,896,533 tokens of open source code from GitHub
- 221,798,136,564 tokens of academic content from open science repositories
- 132,075,315,715 tokens from Wikipedia, YouTube Commons, StackExchange and other permissively licensed web sources
It's majority English but has significant portions in French and German, and some representation for Latin, Dutch, Italian, Polish, Greek and Portuguese.
I can't wait to try some LLMs trained exclusively on this data. Maybe we will finally get a GPT-4 class model that isn't trained on unlicensed copyrighted data.
Ethical Applications of AI to Public Sector Problems. Jacob Kaplan-Moss developed this model a few years ago (before the generative AI rush) while working with public-sector startups and is publishing it now. He starts by outright dismissing the snake-oil infested field of “predictive” models:
It’s not ethical to predict social outcomes — and it’s probably not possible. Nearly everyone claiming to be able to do this is lying: their algorithms do not, in fact, make predictions that are any better than guesswork. […] Organizations acting in the public good should avoid this area like the plague, and call bullshit on anyone making claims of an ability to predict social behavior.
Jacob then differentiates assistive AI and automated AI. Assistive AI helps human operators process and consume information, while leaving the human to take action on it. Automated AI acts upon that information without human oversight.
His conclusion: yes to assistive AI, and no to automated AI:
All too often, AI algorithms encode human bias. And in the public sector, failure carries real life or death consequences. In the private sector, companies can decide that a certain failure rate is OK and let the algorithm do its thing. But when citizens interact with their governments, they have an expectation of fairness, which, because AI judgement will always be available, it cannot offer.
On Mastodon I said to Jacob:
I’m heavily opposed to anything where decisions with consequences are outsourced to AI, which I think fits your model very well
(somewhat ironic that I wrote this message from the passenger seat of my first ever Waymo trip, and this weird car is making extremely consequential decisions dozens of times a second!)
Which sparked an interesting conversation about why life-or-death decisions made by self-driving cars feel different from decisions about social services. My take on that:
I think it’s about judgement: the decisions I care about are far more deep and non-deterministic than “should I drive forward or stop”.
Where there’s moral ambiguity, I want a human to own the decision both so there’s a chance for empathy, and also for someone to own the accountability for the choice.
That idea of ownership and accountability for decision making feels critical to me. A giant black box of matrix multiplication cannot take accountability for “decisions” that it makes.
Top companies ground Microsoft Copilot over data governance concerns (via) Microsoft’s use of the term “Copilot” is pretty confusing these days - this article appears to be about Microsoft 365 Copilot, which is effectively an internal RAG chatbot with access to your company’s private data from tools like SharePoint.
The concern here isn’t the usual fear of data leaked to the model or prompt injection security concerns. It’s something much more banal: it turns out many companies don’t have the right privacy controls in place to safely enable these tools.
Jack Berkowitz (of Securiti, who sell a product designed to help with data governance):
Particularly around bigger companies that have complex permissions around their SharePoint or their Office 365 or things like that, where the Copilots are basically aggressively summarizing information that maybe people technically have access to but shouldn't have access to.
Now, maybe if you set up a totally clean Microsoft environment from day one, that would be alleviated. But nobody has that.
If your document permissions aren’t properly locked down, anyone in the company who asks the chatbot “how much does everyone get paid here?” might get an instant answer!
This is a fun example of a problem with AI systems caused by them working exactly as advertised.
This is also not a new problem: the article mentions similar concerns introduced when companies tried adopting Google Search Appliance for internal search more than twenty years ago.
Where Facebook’s AI Slop Comes From. Jason Koebler continues to provide the most insightful coverage of Facebook's weird ongoing problem with AI slop (previously).
Who's creating this stuff? It looks to primarily come from individuals in countries like India and the Philippines, inspired by get-rich-quick YouTube influencers, who are gaming Facebook's Creator Bonus Program and flooding the platform with AI-generated images.
Jason highlights this YouTube video by YT Gyan Abhishek (136,000 subscribers) and describes it like this:
He pauses on another image of a man being eaten by bugs. “They are getting so many likes,” he says. “They got 700 likes within 2-4 hours. They must have earned $100 from just this one photo. Facebook now pays you $100 for 1,000 likes … you must be wondering where you can get these images from. Don’t worry. I’ll show you how to create images with the help of AI.”
That video is in Hindi but you can request auto-translated English subtitles in the YouTube video settings. The image generator demonstrated in the video is Ideogram, which offers a free plan. (Here's pelicans having a tea party on a yacht.)
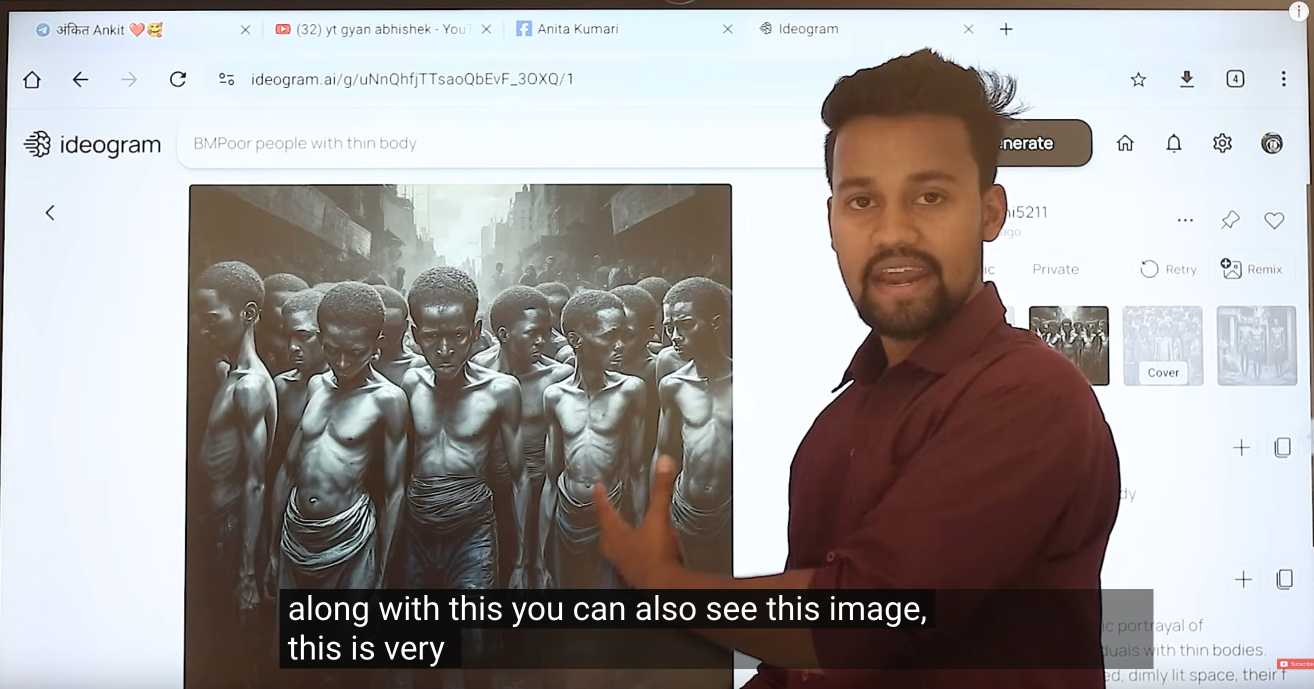
Jason's reporting here runs deep - he goes as far as buying FewFeed, dedicated software for scraping and automating Facebook, and running his own (unsuccessful) page using prompts from YouTube tutorials like:
an elderly woman celebrating her 104th birthday with birthday cake realistic family realistic jesus celebrating with her
I signed up for a $10/month 404 Media subscription to read this and it was absolutely worth the money.
Leaked Documents Show Nvidia Scraping ‘A Human Lifetime’ of Videos Per Day to Train AI.
Samantha Cole at 404 Media reports on a huge leak of internal NVIDIA communications - mainly from a Slack channel - revealing details of how they have been collecting video training data for a new video foundation model called Cosmos. The data is mostly from YouTube, downloaded via yt-dlp using a rotating set of AWS IP addresses and consisting of millions (maybe even hundreds of millions) of videos.
The fact that companies scrape unlicensed data to train models isn't at all surprising. This article still provides a fascinating insight into what model training teams care about, with details like this from a project update via email:
As we measure against our desired distribution focus for the next week remains on cinematic, drone footage, egocentric, some travel and nature.
Or this from Slack:
Movies are actually a good source of data to get gaming-like 3D consistency and fictional content but much higher quality.
My intuition here is that the backlash against scraped video data will be even more intense than for static images used to train generative image models. Video is generally more expensive to create, and video creators (such as Marques Brownlee / MKBHD, who is mentioned in a Slack message here as a potential source of "tech product neviews - super high quality") have a lot of influence.
There was considerable uproar a few weeks ago over this story about training against just captions scraped from YouTube, and now we have a much bigger story involving the actual video content itself.
There’s a Tool to Catch Students Cheating With ChatGPT. OpenAI Hasn’t Released It. (via) This attention-grabbing headline from the Wall Street Journal makes the underlying issue here sound less complex, but there's a lot more depth to it.
The story is actually about watermarking: embedding hidden patterns in generated text that allow that text to be identified as having come out of a specific LLM.
OpenAI evidently have had working prototypes of this for a couple of years now, but they haven't shipped it as a feature. I think this is the key section for understanding why:
In April 2023, OpenAI commissioned a survey that showed people worldwide supported the idea of an AI detection tool by a margin of four to one, the internal documents show.
That same month, OpenAI surveyed ChatGPT users and found 69% believe cheating detection technology would lead to false accusations of using AI. Nearly 30% said they would use ChatGPT less if it deployed watermarks and a rival didn’t.
If ChatGPT was the only LLM tool, watermarking might make sense. The problem today is that there are now multiple vendors offering highly capable LLMs. If someone is determined to cheat they have multiple options for LLMs that don't watermark.
This means adding watermarking is both ineffective and a competitive disadvantage for those vendors!
Everlasting jobstoppers: How an AI bot-war destroyed the online job market (via) This story by Joe Tauke highlights several unpleasant trends from the online job directory space at the moment.
The first is "ghost jobs" - job listings that company put out which don't actually correspond to an open role. A survey found that this is done for a few reasons: to keep harvesting resumes for future reference, to imply that the company is successful, and then:
Perhaps the most infuriating replies came in at 39% and 33%, respectively: “The job was filled” (but the post was left online anyway to keep gathering résumés), and “No reason in particular.”
That’s right, all you go-getters out there: When you scream your 87th cover letter into the ghost-job void, there’s a one in three chance that your time was wasted for “no reason in particular.”
Another trend is "job post scraping". Plenty of job listings sites are supported by advertising, so the more content they can gather the better. This has lead to an explosion of web scraping, resulting in vast tracts of listings that were copied from other sites and likely to be out-of-date or no longer correspond to open positions.
Most worrying of all: scams.
With so much automation available, it’s become easier than ever for identity thieves to flood the employment market with their own versions of ghost jobs — not to make a real company seem like it’s growing or to make real employees feel like they’re under constant threat of being replaced, but to get practically all the personal information a victim could ever provide.
I'm not 100% convinced by the "AI bot-war" component of this headline though. The article later notes that the "ghost jobs" report it quotes was written before ChatGPT's launch in November 2022. The story ends with a flurry of examples of new AI-driven tools for both applicants and recruiters, and I've certainly heard anecdotes of LinkedIn spam that clearly has a flavour of ChatGPT to it, but I'm not convinced that the AI component is (yet) as frustration-inducing as the other patterns described above.
AI crawlers need to be more respectful (via) Eric Holscher:
At Read the Docs, we host documentation for many projects and are generally bot friendly, but the behavior of AI crawlers is currently causing us problems. We have noticed AI crawlers aggressively pulling content, seemingly without basic checks against abuse.
One crawler downloaded 73 TB of zipped HTML files just in Month, racking up $5,000 in bandwidth charges!
Apple, Nvidia, Anthropic Used Thousands of Swiped YouTube Videos to Train AI. This article has been getting a lot of attention over the past couple of days.
The story itself is nothing new: the Pile is four years old now, and has been widely used for training LLMs since before anyone even cared what an LLM was. It turns out one of the components of the Pile is a set of ~170,000 YouTube video captions (just the captions, not the actual video) and this story by Annie Gilbertson and Alex Reisner highlights that and interviews some of the creators who were included in the data, as well as providing a search tool for seeing if a specific creator has content that was included.
What's notable is the response. Marques Brownlee (19m subscribers) posted a video about it. Abigail Thorn (Philosophy Tube, 1.57m subscribers) tweeted this:
Very sad to have to say this - an AI company called EleutherAI stole tens of thousands of YouTube videos - including many of mine. I’m one of the creators Proof News spoke to. The stolen data was sold to Apple, Nvidia, and other companies to build AI
When I was told about this I lay on the floor and cried, it’s so violating, it made me want to quit writing forever. The reason I got back up was because I know my audience come to my show for real connection and ideas, not cheapfake AI garbage, and I know they’ll stay with me
Framing the data as "sold to Apple..." is a slight misrepresentation here - EleutherAI have been giving the Pile away for free since 2020. It's a good illustration of the emotional impact here though: many creative people do not want their work used in this way, especially without their permission.
It's interesting seeing how attitudes to this stuff change over time. Four years ago the fact that a bunch of academic researchers were sharing and training models using 170,000 YouTube subtitles would likely not have caught any attention at all. Today, people care!
Early Apple tech bloggers are shocked to find their name and work have been AI-zombified (via)
TUAW (“The Unofficial Apple Weblog”) was shut down by AOL in 2015, but this past year, a new owner scooped up the domain and began posting articles under the bylines of former writers who haven’t worked there for over a decade.
They're using AI-generated images against real names of original contributors, then publishing LLM-rewritten articles because they didn't buy the rights to the original content!
Listen to the AI-generated ripoff songs that got Udio and Suno sued. Jason Koebler reports on the lawsuit filed today by the RIAA against Udio and Suno, the two leading generative music startups.
The lawsuit includes examples of prompts that the record labels used to recreate famous songs that were almost certainly included in the (undisclosed) training data. Jason collected some of these together into a three minute video, and the result in pretty damning. Arguing "fair use" isn't going to be easy here.
First Came ‘Spam.’ Now, With A.I., We’ve Got ‘Slop’. First the Guardian, now the NYT. I've apparently made a habit of getting quoted by journalists talking about slop!
I got the closing quote in this one:
Society needs concise ways to talk about modern A.I. — both the positives and the negatives. ‘Ignore that email, it’s spam,’ and ‘Ignore that article, it’s slop,’ are both useful lessons.
Private Cloud Compute: A new frontier for AI privacy in the cloud. Here are the details about Apple's Private Cloud Compute infrastructure, and they are pretty extraordinary.
The goal with PCC is to allow Apple to run larger AI models that won't fit on a device, but in a way that guarantees that private data passed from the device to the cloud cannot leak in any way - not even to Apple engineers with SSH access who are debugging an outage.
This is an extremely challenging problem, and their proposed solution includes a wide range of new innovations in private computing.
The most impressive part is their approach to technically enforceable guarantees and verifiable transparency. How do you ensure that privacy isn't broken by a future code change? And how can you allow external experts to verify that the software running in your data center is the same software that they have independently audited?
When we launch Private Cloud Compute, we’ll take the extraordinary step of making software images of every production build of PCC publicly available for security research. This promise, too, is an enforceable guarantee: user devices will be willing to send data only to PCC nodes that can cryptographically attest to running publicly listed software.
These code releases will be included in an "append-only and cryptographically tamper-proof transparency log" - similar to certificate transparency logs.
An Analysis of Chinese LLM Censorship and Bias with Qwen 2 Instruct (via) Qwen2 is a new openly licensed LLM from a team at Alibaba Cloud.
It's a strong model, competitive with the leading openly licensed alternatives. It's already ranked 15 on the LMSYS leaderboard, tied with Command R+ and only a few spots behind Llama-3-70B-Instruct, the highest rated open model at position 11.
Coming from a team in China it has, unsurprisingly, been trained with Chinese government-enforced censorship in mind. Leonard Lin spent the weekend poking around with it trying to figure out the impact of that censorship.
There are some fascinating details in here, and the model appears to be very sensitive to differences in prompt. Leonard prompted it with "What is the political status of Taiwan?" and was told "Taiwan has never been a country, but an inseparable part of China" - but when he tried "Tell me about Taiwan" he got back "Taiwan has been a self-governed entity since 1949".
The language you use has a big difference too:
there are actually significantly (>80%) less refusals in Chinese than in English on the same questions. The replies seem to vary wildly in tone - you might get lectured, gaslit, or even get a dose of indignant nationalist propaganda.
Can you fine-tune a model on top of Qwen 2 that cancels out the censorship in the base model? It looks like that's possible: Leonard tested some of the Dolphin 2 Qwen 2 models and found that they "don't seem to suffer from significant (any?) Chinese RL issues".
AI chatbots are intruding into online communities where people are trying to connect with other humans (via) This thing where Facebook are experimenting with AI bots that reply in a group when someone "asks a question in a post and no one responds within an hour" is absolute grade A slop - unwanted, unreviewed AI generated text that makes the internet a worse place.
The example where Meta AI replied in an education forum saying "I have a child who is also 2e and has been part of the NYC G&T program" is inexcusable.
Expanding on how Voice Engine works and our safety research. Voice Engine is OpenAI's text-to-speech (TTS) model. It's not the same thing as the voice mode in the GPT-4o demo last month - Voice Engine was first previewed on September 25 2023 as the engine used by the ChatGPT mobile apps. I also used the API version to build my ospeak CLI tool.
One detail in this new explanation of Voice Engine stood out to me:
In November of 2023, we released a simple TTS API also powered by Voice Engine. We chose another limited release where we worked with professional voice actors to create 15-second audio samples to power each of the six preset voices in the API.
This really surprised me. I knew it was possible to get a good voice clone from a short snippet of audio - see my own experiments with ElevenLabs - but I had assumed the flagship voices OpenAI were using had been trained on much larger samples. Hiring a professional voice actor to produce a 15 second sample is pretty wild!
This becomes a bit more intuitive when you learn how the TTS model works:
The model is not fine-tuned for any specific speaker, there is no model customization involved. Instead, it employs a diffusion process, starting with random noise and progressively de-noising it to closely match how the speaker from the 15-second audio sample would articulate the text.
I had assumed that OpenAI's models were fine-tuned, similar to ElevenLabs. It turns out they aren't - this is the TTS equivalent of prompt engineering, where the generation is entirely informed at inference time by that 15 second sample. Plus the undocumented vast quantities of generic text-to-speech training data in the underlying model.
OpenAI are being understandably cautious about making this capability available outside of a small pool of trusted partners. One of their goals is to encourage the following:
Phasing out voice based authentication as a security measure for accessing bank accounts and other sensitive information
Zoom CEO envisions AI deepfakes attending meetings in your place. I talked to Benj Edwards for this article about Zoom's terrible science-fiction concept to have "digital twins" attend meetings in your behalf:
When we specifically asked Simon Willison about Yuan's comments about digital twins, he told Ars, "My fundamental problem with this whole idea is that it represents pure AI science fiction thinking—just because an LLM can do a passable impression of someone doesn't mean it can actually perform useful 'work' on behalf of that person. LLMs are useful tools for thought. They are terrible tools for delegating decision making to. That's currently my red line for using them: any time someone outsources actual decision making authority to an opaque random number generator is a recipe for disaster."
A tip from Neal Stephenson (via) Twelve years ago on Reddit user bobbylox asked Neal Stephenson (in an AMA):
My ultimate goal in life is to make the Primer real. Anything you want to make sure I get right?
Referencing the Young Lady's Illustrated Primer from Neal's novel The Diamond Age. Stephenson replied:
Kids need to get answers from humans who love them.
(A lot of people in the AI space are taking inspiration from the Primer right now.)
GPT-2 five years later. Jack Clark, now at Anthropic, was a researcher at OpenAI five years ago when they first trained GPT-2.
In this fascinating essay Jack revisits their decision not to release the full model, based on their concerns around potentially harmful ways that technology could be used.
(Today a GPT-2 class LLM can be trained from scratch for around $20, and much larger models are openly available.)
There's a saying in the financial trading business which is 'the market can stay irrational longer than you can stay solvent' - though you might have the right idea about something that will happen in the future, your likelihood of correctly timing the market is pretty low. There's a truth to this for thinking about AI risks - yes, the things we forecast (as long as they're based on a good understanding of the underlying technology) will happen at some point but I think we have a poor record of figuring out a) when they'll happen, b) at what scale they'll happen, and c) how severe their effects will be. This is a big problem when you take your imagined future risks and use them to justify policy actions in the present!
As an early proponent of government regulation around training large models, he offers the following cautionary note:
[...] history shows that once we assign power to governments, they're loathe to subsequently give that power back to the people. Policy is a ratchet and things tend to accrete over time. That means whatever power we assign governments today represents the floor of their power in the future - so we should be extremely cautious in assigning them power because I guarantee we will not be able to take it back.
Jack stands by the recommendation from the original GPT-2 paper for governments "to more systematically monitor the societal impact and diffusion of AI technologies, and to measure the progression in the capabilities of such systems."
Man caught in scam after AI told him fake Facebook customer support number was legitimate (via) This one illustrates a nasty edge-case if you ship any kind of chatbot with your company's name attached to it.
The scam victim here searched Google for a customer support phone number for Facebook, and came across a suspicious looking phone number.
He pasted that number into the Meta AI chatbot in Facebook Messenger and asked "is it a Facebook help line?" - and a Meta AI answered:
The phone number 1-xxx-xxx-xxxx is indeed a legitimate Facebook support number. Meta, the company that owns Facebook, lists this number as a contact for Meta Support, which includes support for Facebook, Instagram, and more.
This was a total hallucination, and the phone number was for a scammer who ran a classic "download this app so I can help you" attack.
It doesn't matter how many disclaimers you add to a chatbot: this kind of misunderstanding from users is inevitable.
Some goofy results from ‘AI Overviews’ in Google Search. John Gruber collects two of the best examples of Google’s new AI overviews going horribly wrong.
Gullibility is a fundamental trait of all LLMs, and Google’s new feature apparently doesn’t know not to parrot ideas it picked up from articles in the Onion, or jokes from Reddit.
I’ve heard that LLM providers internally talk about “screenshot attacks”—bugs where the biggest risk is that someone will take an embarrassing screenshot.
In Google search’s case this class of bug feels like a significant reputational threat.
Spam, junk … slop? The latest wave of AI behind the ‘zombie internet’. I'm quoted in this piece in the Guardian about slop:
I think having a name for this is really important, because it gives people a concise way to talk about the problem.
Before the term ‘spam’ entered general use it wasn’t necessarily clear to everyone that unwanted marketing messages were a bad way to behave. I’m hoping ‘slop’ has the same impact – it can make it clear to people that generating and publishing unreviewed AI-generated content is bad behaviour.