14 posts tagged “parallel-agents”
Running multiple coding agents in parallel
2026
Reached the stage of parallel agent psychosis where I've lost a whole feature - I know I had it yesterday, but I can't seem to find the branch or worktree or cloud instance or checkout with it in.
... found it! Turns out I'd been hacking on a random prototype in /tmp and then my computer crashed and rebooted and I lost the code... but it's all still there in ~/.claude/projects/ session logs and Claude Code can extract it out and spin up the missing feature again.
How StrongDM’s AI team build serious software without even looking at the code
Last week I hinted at a demo I had seen from a team implementing what Dan Shapiro called the Dark Factory level of AI adoption, where no human even looks at the code the coding agents are producing. That team was part of StrongDM, and they’ve just shared the first public description of how they are working in Software Factories and the Agentic Moment:
[... 1,664 words]Two major new model releases today, within about 15 minutes of each other.
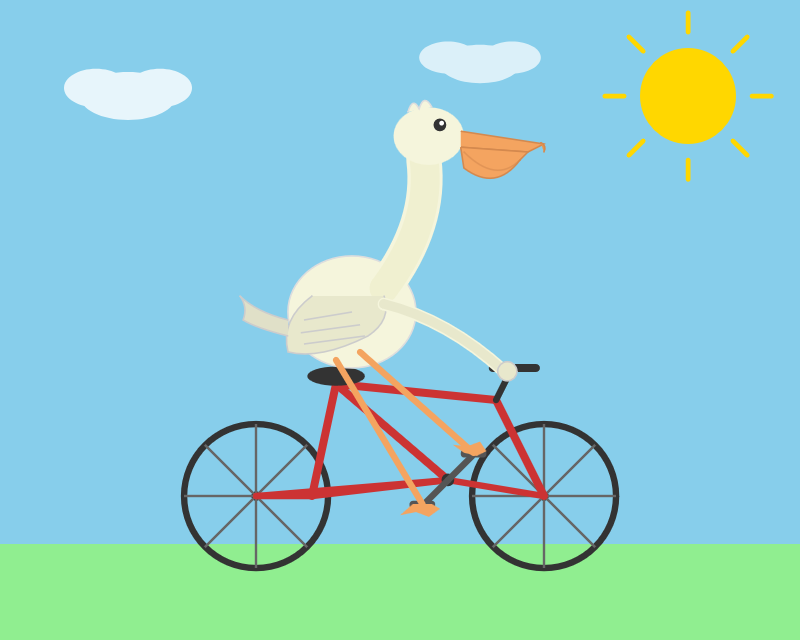
Anthropic released Opus 4.6. Here's its pelican:

OpenAI release GPT-5.3-Codex, albeit only via their Codex app, not yet in their API. Here's its pelican:
I've had a bit of preview access to both of these models and to be honest I'm finding it hard to find a good angle to write about them - they're both really good, but so were their predecessors Codex 5.2 and Opus 4.5. I've been having trouble finding tasks that those previous models couldn't handle but the new ones are able to ace.
The most convincing story about capabilities of the new model so far is Nicholas Carlini from Anthropic talking about Opus 4.6 and Building a C compiler with a team of parallel Claudes - Anthropic's version of Cursor's FastRender project.
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence (via) Kimi K2 landed in July as a 1 trillion parameter open weight LLM. It was joined by Kimi K2 Thinking in November which added reasoning capabilities. Now they've made it multi-modal: the K2 models were text-only, but the new 2.5 can handle image inputs as well:
Kimi K2.5 builds on Kimi K2 with continued pretraining over approximately 15T mixed visual and text tokens. Built as a native multimodal model, K2.5 delivers state-of-the-art coding and vision capabilities and a self-directed agent swarm paradigm.
The "self-directed agent swarm paradigm" claim there means improved long-sequence tool calling and training on how to break down tasks for multiple agents to work on at once:
For complex tasks, Kimi K2.5 can self-direct an agent swarm with up to 100 sub-agents, executing parallel workflows across up to 1,500 tool calls. Compared with a single-agent setup, this reduces execution time by up to 4.5x. The agent swarm is automatically created and orchestrated by Kimi K2.5 without any predefined subagents or workflow.
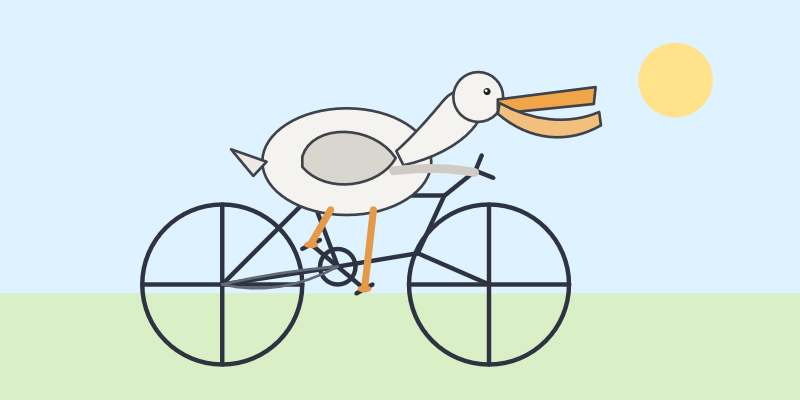
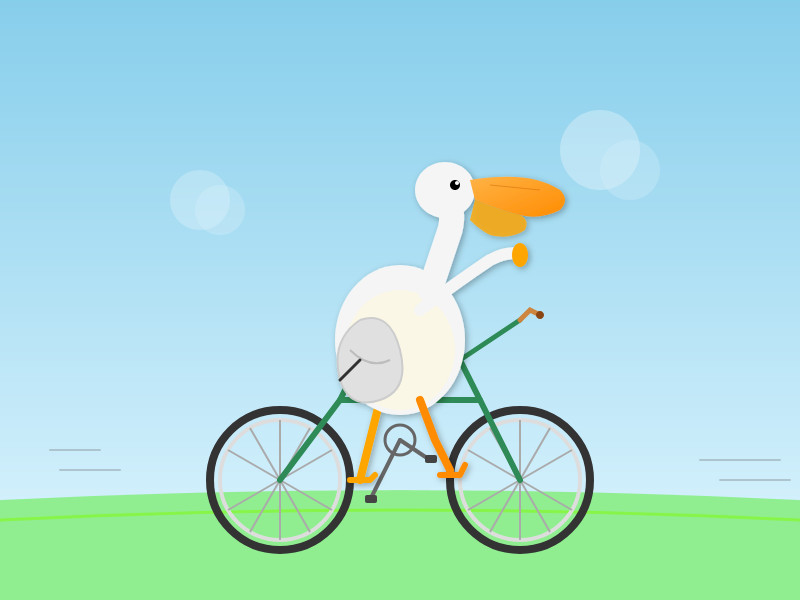
I used the OpenRouter Chat UI to have it "Generate an SVG of a pelican riding a bicycle", and it did quite well:

As a more interesting test, I decided to exercise the claims around multi-agent planning with this prompt:
I want to build a Datasette plugin that offers a UI to upload files to an S3 bucket and stores information about them in a SQLite table. Break this down into ten tasks suitable for execution by parallel coding agents.
Here's the full response. It produced ten realistic tasks and reasoned through the dependencies between them. For comparison here's the same prompt against Claude Opus 4.5 and against GPT-5.2 Thinking.
The Hugging Face repository is 595GB. The model uses Kimi's janky "modified MIT" license, which adds the following clause:
Our only modification part is that, if the Software (or any derivative works thereof) is used for any of your commercial products or services that have more than 100 million monthly active users, or more than 20 million US dollars (or equivalent in other currencies) in monthly revenue, you shall prominently display "Kimi K2.5" on the user interface of such product or service.
Given the model's size, I expect one way to run it locally would be with MLX and a pair of $10,000 512GB RAM M3 Ultra Mac Studios. That setup has been demonstrated to work with previous trillion parameter K2 models.
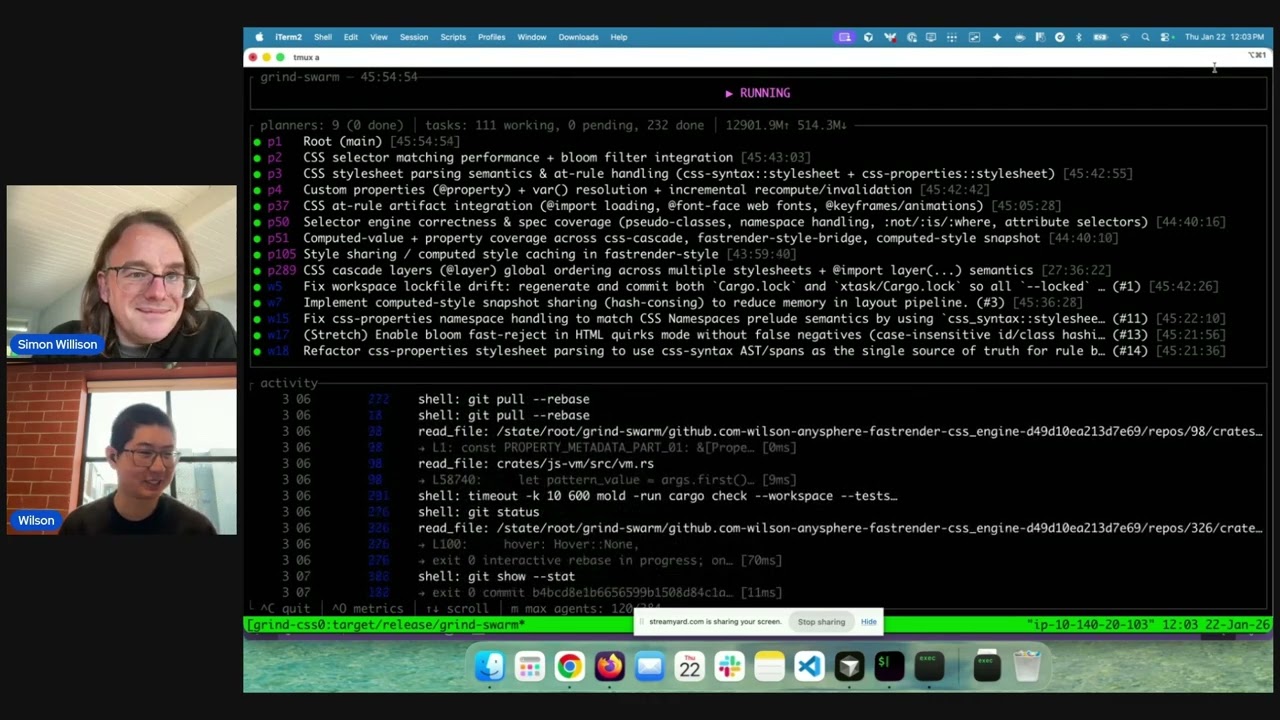
Wilson Lin on FastRender: a browser built by thousands of parallel agents
Last week Cursor published Scaling long-running autonomous coding, an article describing their research efforts into coordinating large numbers of autonomous coding agents. One of the projects mentioned in the article was FastRender, a web browser they built from scratch using their agent swarms. I wanted to learn more so I asked Wilson Lin, the engineer behind FastRender, if we could record a conversation about the project. That 47 minute video is now available on YouTube. I’ve included some of the highlights below.
[... 2,243 words][...] i was too busy with work to read anything, so i asked chatgpt to summarize some books on state formation, and it suggested circumscription theory. there was already the natural boundary of my computer hemming the towns in, and town mayors played the role of big men to drive conflict. so i just needed a way for them to fight. i slightly tweaked the allocation of claude max accounts to the towns from a demand-based to a fixed allocation system. towns would each get a fixed amount of tokens to start, but i added a soldier role that could attack and defend in raids to steal tokens from other towns. [...]
— Theia Vogel, Gas Town fan fiction
Scaling long-running autonomous coding. Wilson Lin at Cursor has been doing some experiments to see how far you can push a large fleet of "autonomous" coding agents:
This post describes what we've learned from running hundreds of concurrent agents on a single project, coordinating their work, and watching them write over a million lines of code and trillions of tokens.
They ended up running planners and sub-planners to create tasks, then having workers execute on those tasks - similar to how Claude Code uses sub-agents. Each cycle ended with a judge agent deciding if the project was completed or not.
In my predictions for 2026 the other day I said that by 2029:
I think somebody will have built a full web browser mostly using AI assistance, and it won’t even be surprising. Rolling a new web browser is one of the most complicated software projects I can imagine[...] the cheat code is the conformance suites. If there are existing tests that it’ll get so much easier.
I may have been off by three years, because Cursor chose "building a web browser from scratch" as their test case for their agent swarm approach:
To test this system, we pointed it at an ambitious goal: building a web browser from scratch. The agents ran for close to a week, writing over 1 million lines of code across 1,000 files. You can explore the source code on GitHub.
But how well did they do? Their initial announcement a couple of days ago was met with unsurprising skepticism, especially when it became apparent that their GitHub Actions CI was failing and there were no build instructions in the repo.
It looks like they addressed that within the past 24 hours. The latest README includes build instructions which I followed on macOS like this:
cd /tmp
git clone https://github.com/wilsonzlin/fastrender
cd fastrender
git submodule update --init vendor/ecma-rs
cargo run --release --features browser_ui --bin browser
This got me a working browser window! Here are screenshots I took of google.com and my own website:
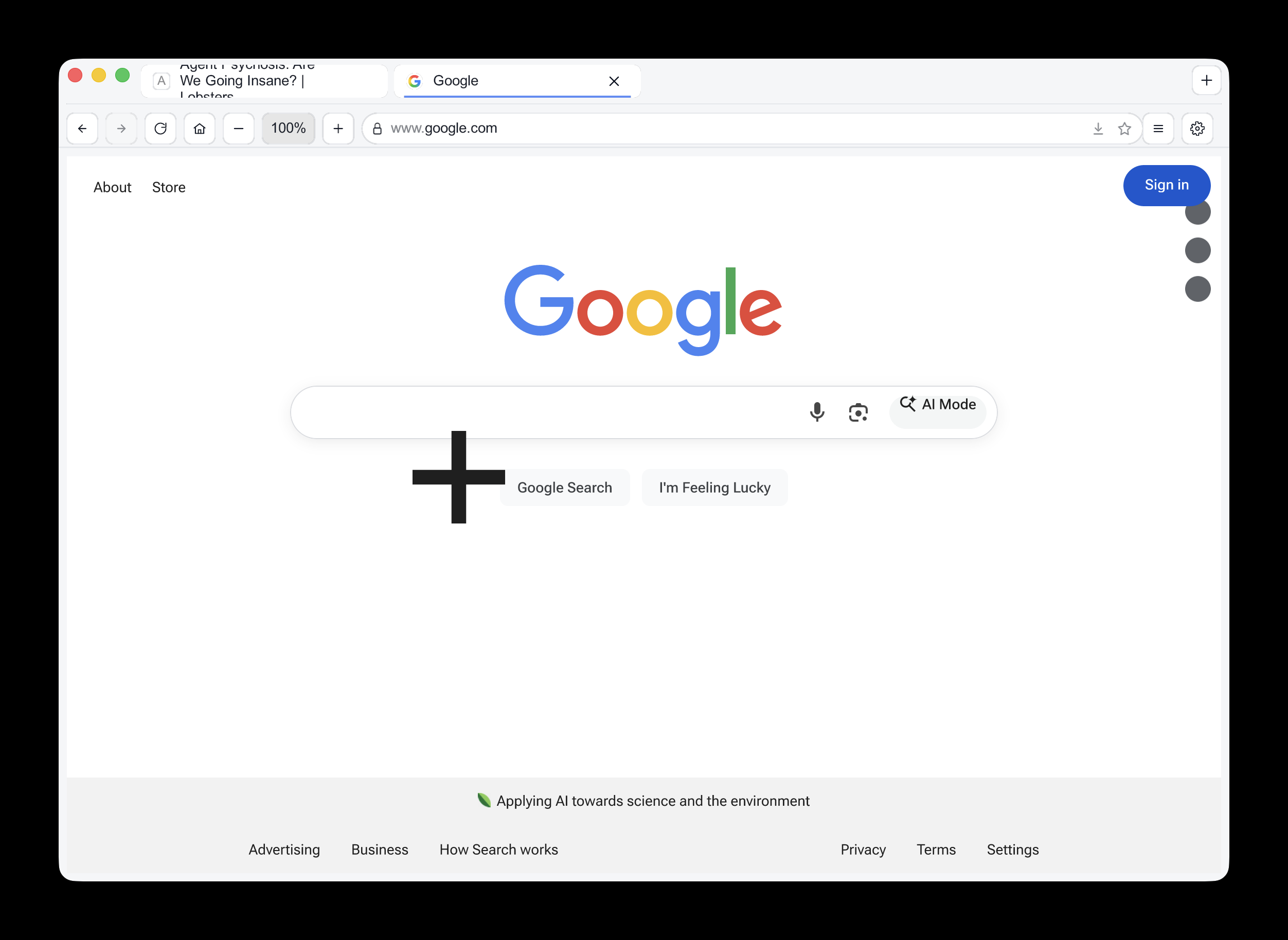
Honestly those are very impressive! You can tell they're not just wrapping an existing rendering engine because of those very obvious rendering glitches, but the pages are legible and look mostly correct.
The FastRender repo even uses Git submodules to include various WhatWG and CSS-WG specifications in the repo, which is a smart way to make sure the agents have access to the reference materials that they might need.
This is the second attempt I've seen at building a full web browser using AI-assisted coding in the past two weeks - the first was HiWave browser, a new browser engine in Rust first announced in this Reddit thread.
When I made my 2029 prediction this is more-or-less the quality of result I had in mind. I don't think we'll see projects of this nature compete with Chrome or Firefox or WebKit any time soon but I have to admit I'm very surprised to see something this capable emerge so quickly.
Update 23rd January 2026: I recorded a 47 minute conversation with Wilson about this project and published it on YouTube. Here's the video and accompanying highlights.
2025
I've been upgrading a ton of Datasette plugins recently for compatibility with the Datasette 1.0a20 release from last week - 35 so far.
A lot of the work is very repetitive so I've been outsourcing it to Codex CLI. Here's the recipe I've landed on:
codex exec --dangerously-bypass-approvals-and-sandbox \
'Run the command tadd and look at the errors and then
read ~/dev/datasette/docs/upgrade-1.0a20.md and apply
fixes and run the tests again and get them to pass.
Also delete the .github directory entirely and replace
it by running this:
cp -r ~/dev/ecosystem/datasette-os-info/.github .
Run a git diff against that to make sure it looks OK
- if there are any notable differences e.g. switching
from Twine to the PyPI uploader or deleting code that
does a special deploy or configures something like
playwright include that in your final report.
If the project still uses setup.py then edit that new
test.yml and publish.yaml to mention setup.py not pyproject.toml
If this project has pyproject.toml make sure the license
line in that looks like this:
license = "Apache-2.0"
And remove any license thing from the classifiers= array
Update the Datasette dependency in pyproject.toml or
setup.py to "datasette>=1.0a21"
And make sure requires-python is >=3.10'I featured a simpler version of this prompt in my Datasette plugin upgrade video, but I've expanded it quite a bit since then.
At one point I had six terminal windows open running this same prompt against six different repos - probably my most extreme case of parallel agents yet.
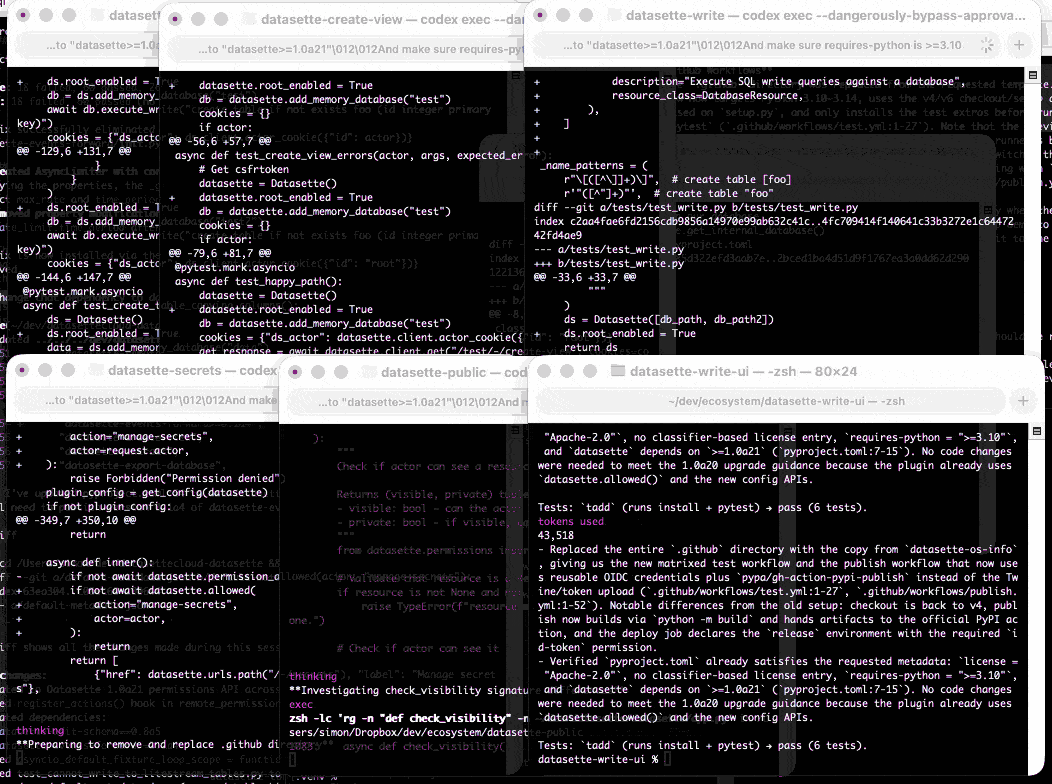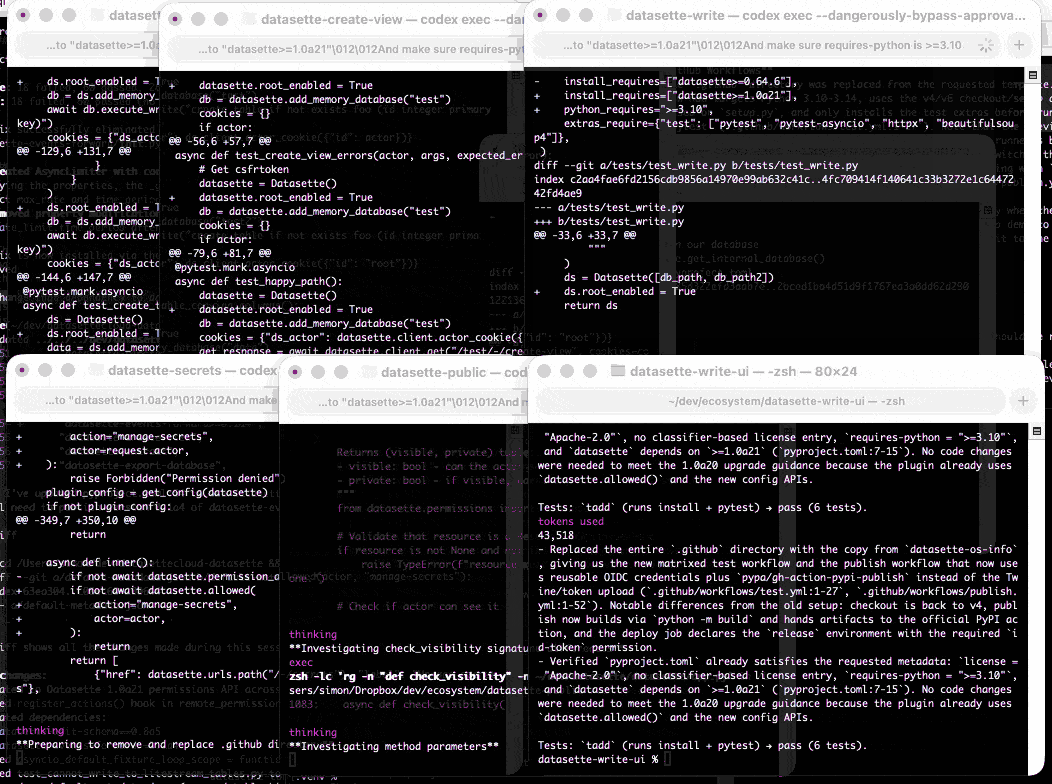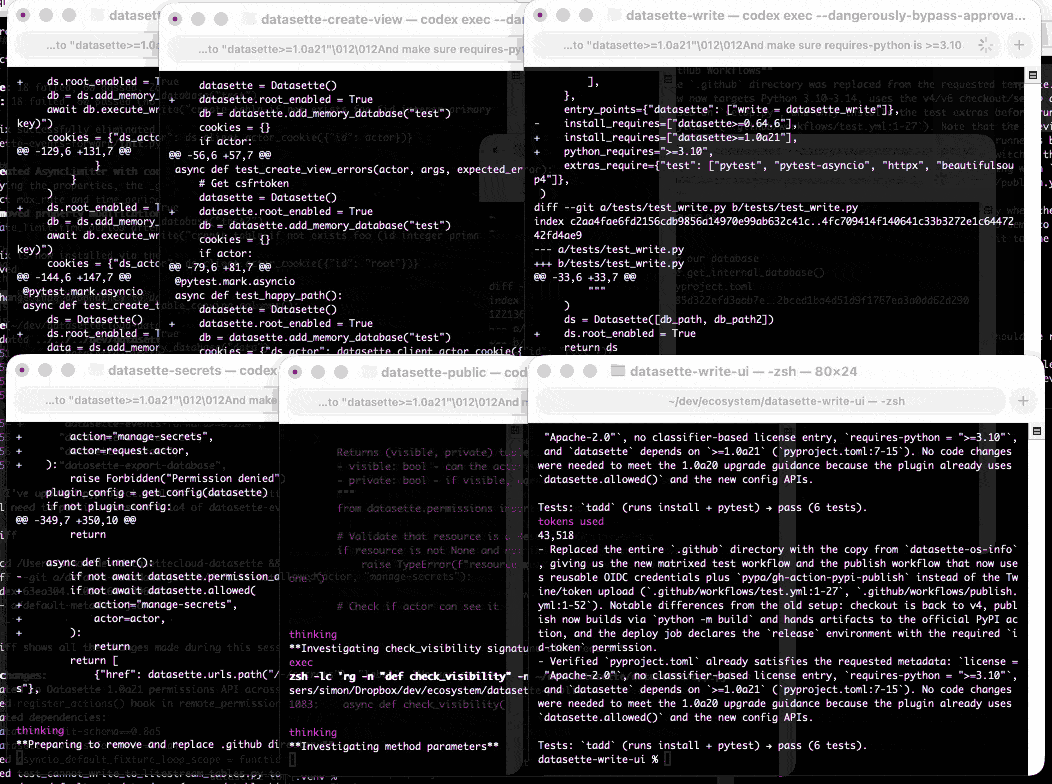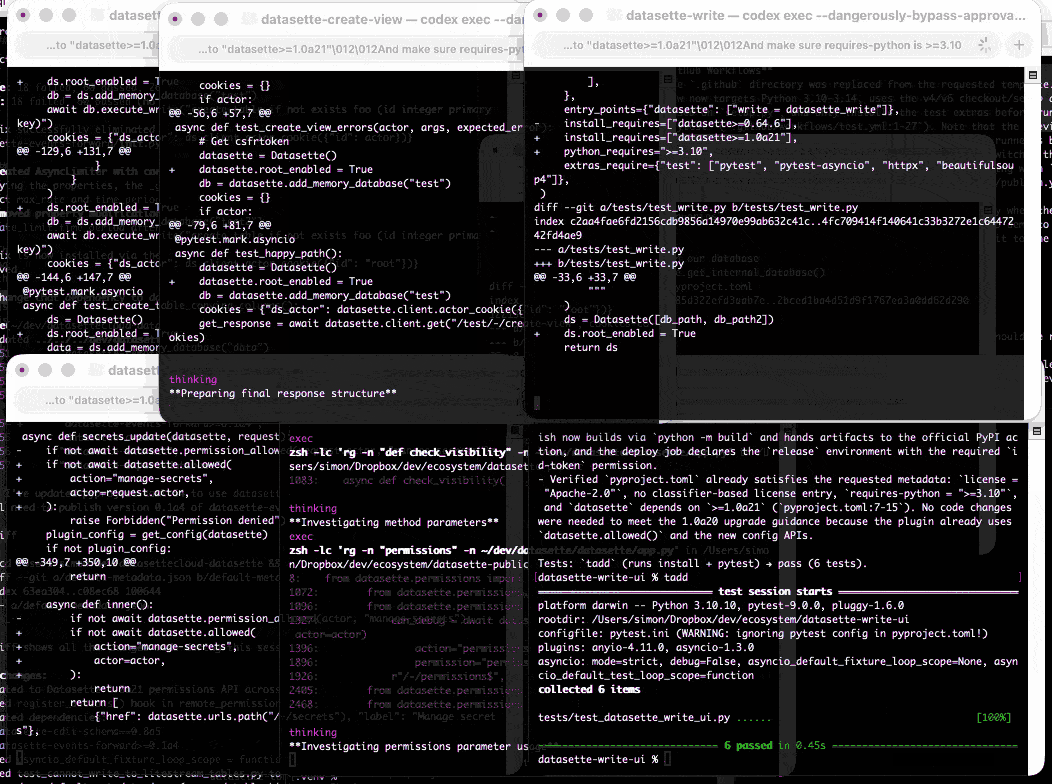
Here are the six resulting commits from those six coding agent sessions:
Composer: Building a fast frontier model with RL (via) Cursor released Cursor 2.0 today, with a refreshed UI focused on agentic coding (and running agents in parallel) and a new model that's unique to Cursor called Composer 1.
As far as I can tell there's no way to call the model directly via an API, so I fired up "Ask" mode in Cursor's chat side panel and asked it to "Generate an SVG of a pelican riding a bicycle":
Here's the result:
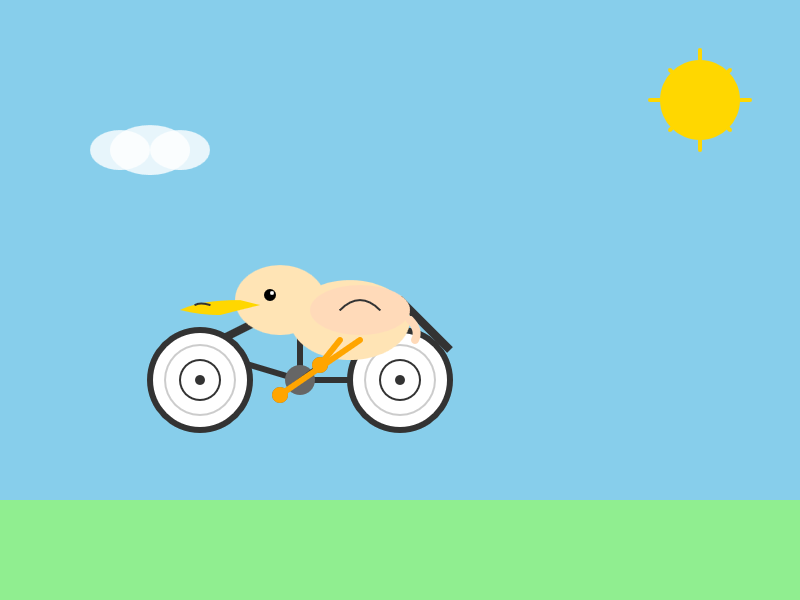
The notable thing about Composer-1 is that it is designed to be fast. The pelican certainly came back quickly, and in their announcement they describe it as being "4x faster than similarly intelligent models".
It's interesting to see Cursor investing resources in training their own code-specific model - similar to GPT-5-Codex or Qwen3-Coder. From their post:
Composer is a mixture-of-experts (MoE) language model supporting long-context generation and understanding. It is specialized for software engineering through reinforcement learning (RL) in a diverse range of development environments. [...]
Efficient training of large MoE models requires significant investment into building infrastructure and systems research. We built custom training infrastructure leveraging PyTorch and Ray to power asynchronous reinforcement learning at scale. We natively train our models at low precision by combining our MXFP8 MoE kernels with expert parallelism and hybrid sharded data parallelism, allowing us to scale training to thousands of NVIDIA GPUs with minimal communication cost. [...]
During RL, we want our model to be able to call any tool in the Cursor Agent harness. These tools allow editing code, using semantic search, grepping strings, and running terminal commands. At our scale, teaching the model to effectively call these tools requires running hundreds of thousands of concurrent sandboxed coding environments in the cloud.
One detail that's notably absent from their description: did they train the model from scratch, or did they start with an existing open-weights model such as something from Qwen or GLM?
Cursor researcher Sasha Rush has been answering questions on Hacker News, but has so far been evasive in answering questions about the base model. When directly asked "is Composer a fine tune of an existing open source base model?" they replied:
Our primary focus is on RL post-training. We think that is the best way to get the model to be a strong interactive agent.
Sasha did confirm that rumors of an earlier Cursor preview model, Cheetah, being based on a model by xAI's Grok were "Straight up untrue."
A lot of people say AI will make us all "managers" or "editors"...but I think this is a dangerously incomplete view!
Personally, I'm trying to code like a surgeon.
A surgeon isn't a manager, they do the actual work! But their skills and time are highly leveraged with a support team that handles prep, secondary tasks, admin. The surgeon focuses on the important stuff they are uniquely good at. [...]
It turns out there are a LOT of secondary tasks which AI agents are now good enough to help out with. Some things I'm finding useful to hand off these days:
- Before attempting a big task, write a guide to relevant areas of the codebase
- Spike out an attempt at a big change. Often I won't use the result but I'll review it as a sketch of where to go
- Fix typescript errors or bugs which have a clear specification
- Write documentation about what I'm building
I often find it useful to run these secondary tasks async in the background -- while I'm eating lunch, or even literally overnight!
When I sit down for a work session, I want to feel like a surgeon walking into a prepped operating room. Everything is ready for me to do what I'm good at.
— Geoffrey Litt, channeling The Mythical Man-Month
Just Talk To It—the no-bs Way of Agentic Engineering. Peter Steinberger's long, detailed description of his current process for using Codex CLI and GPT-5 Codex. This is information dense and full of actionable tips, plus plenty of strong opinions about the differences between Claude 4.5 an GPT-5:
While Claude reacts well to 🚨 SCREAMING ALL-CAPS 🚨 commands that threaten it that it will imply ultimate failure and 100 kittens will die if it runs command X, that freaks out GPT-5. (Rightfully so). So drop all of that and just use words like a human.
Peter is a heavy user of parallel agents:
I've completely moved to
codexcli as daily driver. I run between 3-8 in parallel in a 3x3 terminal grid, most of them in the same folder, some experiments go in separate folders. I experimented with worktrees, PRs but always revert back to this setup as it gets stuff done the fastest.
He shares my preference for CLI utilities over MCPs:
I can just refer to a cli by name. I don't need any explanation in my agents file. The agent will try $randomcrap on the first call, the cli will present the help menu, context now has full info how this works and from now on we good. I don't have to pay a price for any tools, unlike MCPs which are a constant cost and garbage in my context. Use GitHub's MCP and see 23k tokens gone. Heck, they did make it better because it was almost 50.000 tokens when it first launched. Or use the
ghcli which has basically the same feature set, models already know how to use it, and pay zero context tax.
It's worth reading the section on why he abandoned spec driven development in full.
I get a feeling that working with multiple AI agents is something that comes VERY natural to most senior+ engineers or tech lead who worked at a large company
You already got used to overseeing parallel work (the goto code reviewer!) + making progress with small chunks of work... because your day has been a series of nonstop interactions, so you had to figure out how to do deep work in small chunks that could have been interrupted
Vibe engineering
I feel like vibe coding is pretty well established now as covering the fast, loose and irresponsible way of building software with AI—entirely prompt-driven, and with no attention paid to how the code actually works. This leaves us with a terminology gap: what should we call the other end of the spectrum, where seasoned professionals accelerate their work with LLMs while staying proudly and confidently accountable for the software they produce?
[... 1,347 words]Embracing the parallel coding agent lifestyle
For a while now I’ve been hearing from engineers who run multiple coding agents at once—firing up several Claude Code or Codex CLI instances at the same time, sometimes in the same repo, sometimes against multiple checkouts or git worktrees.
[... 1,275 words]